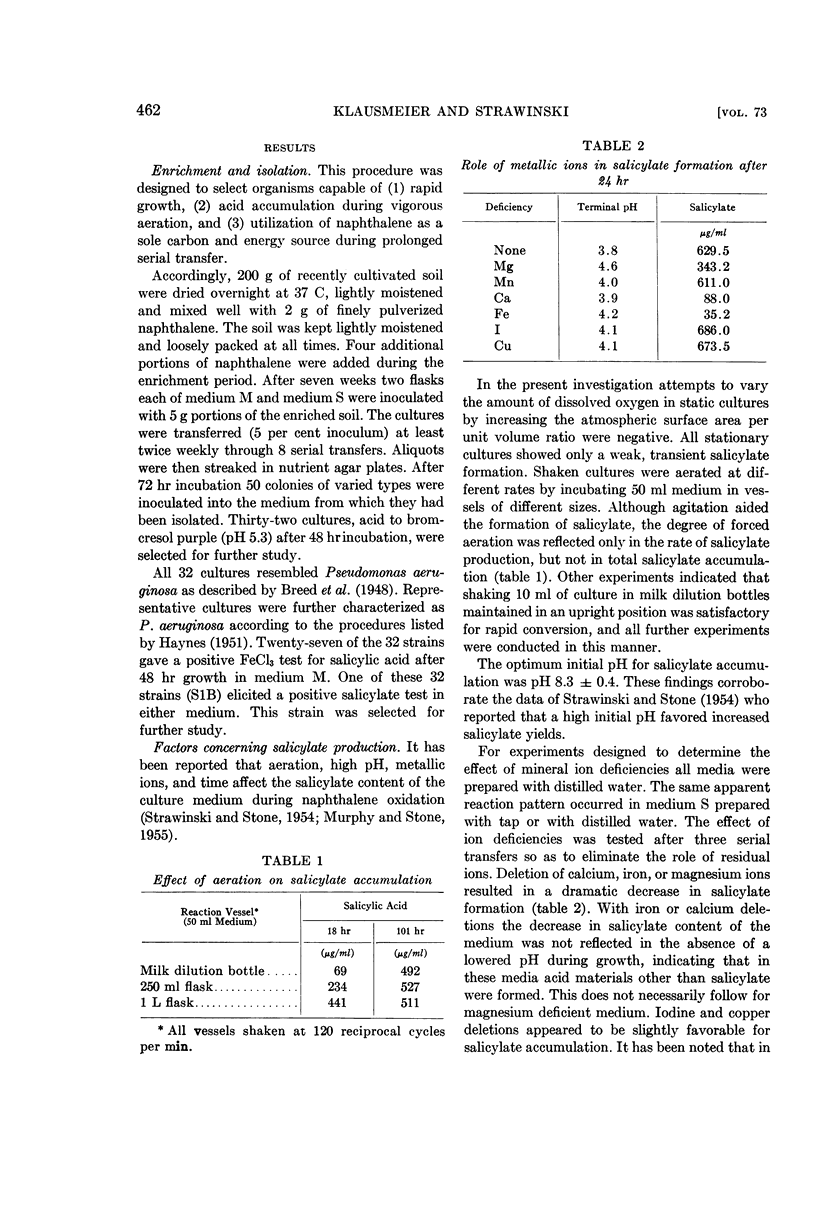
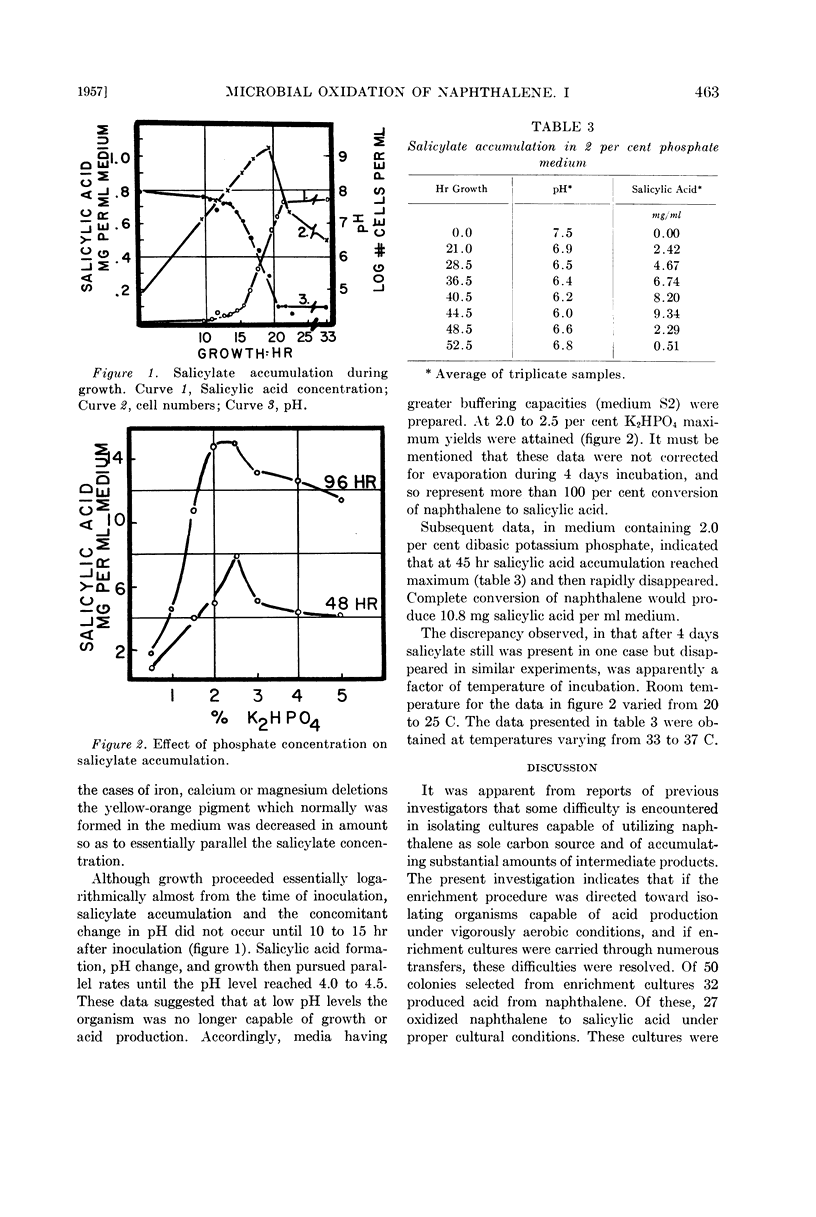
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HAYNES W. C. Pseudomonas aeruginosa--its characterization and identification. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Nov;5(5 Suppl):939–950. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-5-939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY J. F., STONE R. W. The bacterial dissimilation of naphthalene. Can J Microbiol. 1955 Aug;1(7):579–588. doi: 10.1139/m55-070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAWINSKI R. J., STONE R. W. Biological oxidation of naphthalene. Can J Microbiol. 1954 Dec;1(3):206–210. doi: 10.1139/m55-027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER N., WILTSHIRE G. H. The breakdown of naphthalene by a soil bacterium. J Gen Microbiol. 1953 Apr;8(2):273–276. doi: 10.1099/00221287-8-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


