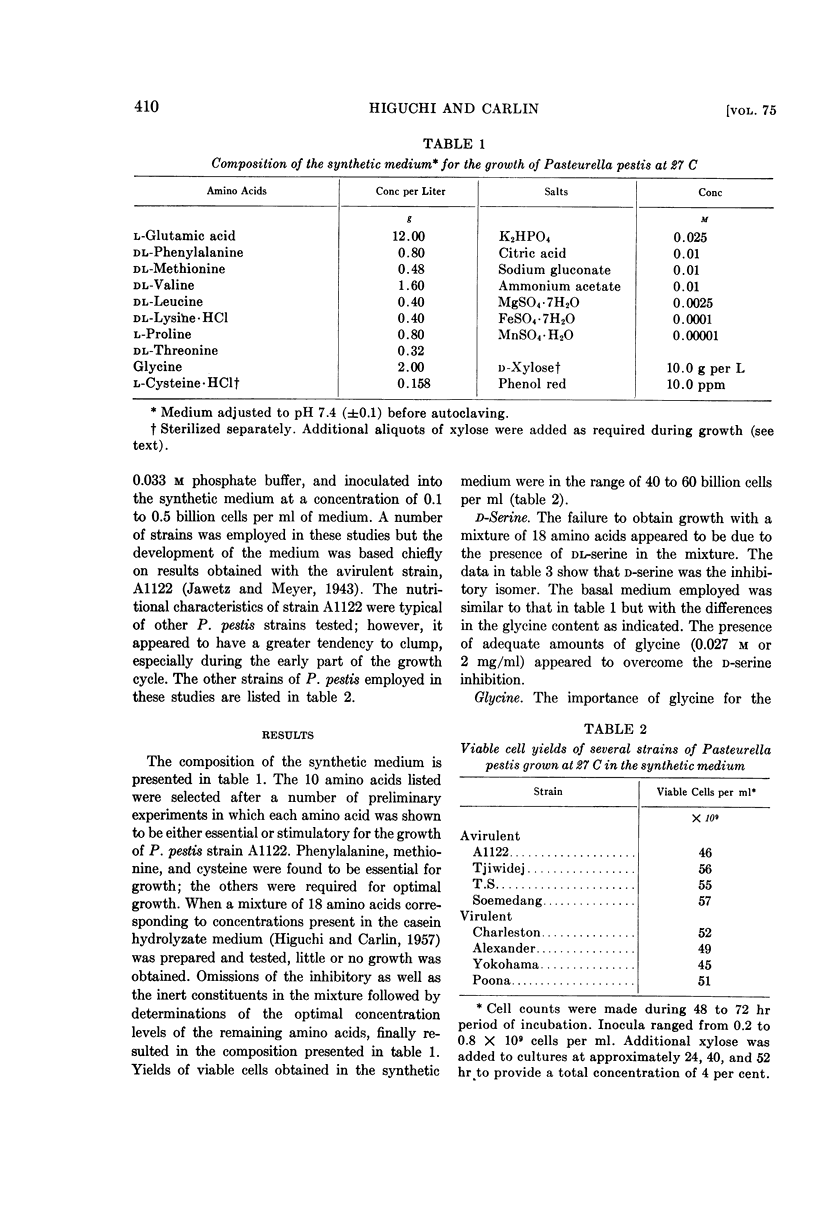
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ENGLESBERG E. The irreversibility of methionine synthesis from cysteine in pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1952 May;63(5):675–680. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.5.675-680.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKUI G. M., OGG J. E., WESSMAN G. E., SURGALLA M. J. Studies on the relation of cultural conditions and virulence of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1957 Dec;74(6):714–717. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.6.714-717.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGUCHI K., CARLIN C. E. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. I. A casein hydrolyzate medium for the growth of Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jan;73(1):122–129. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.1.122-129.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILLS G. M., SPURR E. D. The effect of temperature on the nutritional requirements of Pasteurella pestis. J Gen Microbiol. 1952 Feb;6(1-2):64–73. doi: 10.1099/00221287-6-1-2-64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAAS W. K., DAVIS B. D. Pantothenate studies. I. Interference by D-serine and L-aspartic acid with pantothenate synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1950 Dec;60(6):733–745. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.6.733-745.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCKENMACHER M., JAMES H. A., ELBERG S. S. Studies on the nutrition and physiology of Pasteurella pestis. I. A chemically defined culture medium for Pasteurella pestis. J Bacteriol. 1952 Jun;63(6):785–794. doi: 10.1128/jb.63.6.785-794.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN S. J., HIGUCHI K., MEYERS E. Production of protective antigens by Pasteurella pestis in a synthetic medium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 May;86(1):112–114. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



