Abstract
Stocks, Peter K. (Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge), and C. S. McCleskey. Identity of the pink-pigmented methanol-oxidizing bacteria as Vibrio extorquens. J. Bacteriol. 88:1065–1070. 1964.—Pink-pigmented bacteria isolated from enrichment cultures of methane oxidizers were found to possess similar morphological, cultural, and physiological characteristics. All the strains utilized methanol, formate, oxalate, succinate, glycerol, and benzene as sole carbon sources; methanol, formate, and glycerol afforded best growth. Most strains utilized fructose and ribose; other carbohydrates tested were not available as carbon and energy sources. There was strain variation in the use of hexane, heptane, n-propanol, n-butanol, acetate, and propionate. Methane, ethane, n-propane, and n-butane were not utilized. Our isolates, and Pseudomonas methanica of Harrington and Kallio (not the methane-dependent P. methanica of Dworkin and Foster), Pseudomonas AM1 of Peele and Quayle, Pseudomonas PRL-W4 of Kaneda and Roxburgh, and Protaminobacter ruber den Dooren de Jong are nearly identical with Vibrio extorquens (Bassalik) Bhat and Barker, and should be considered the same species.
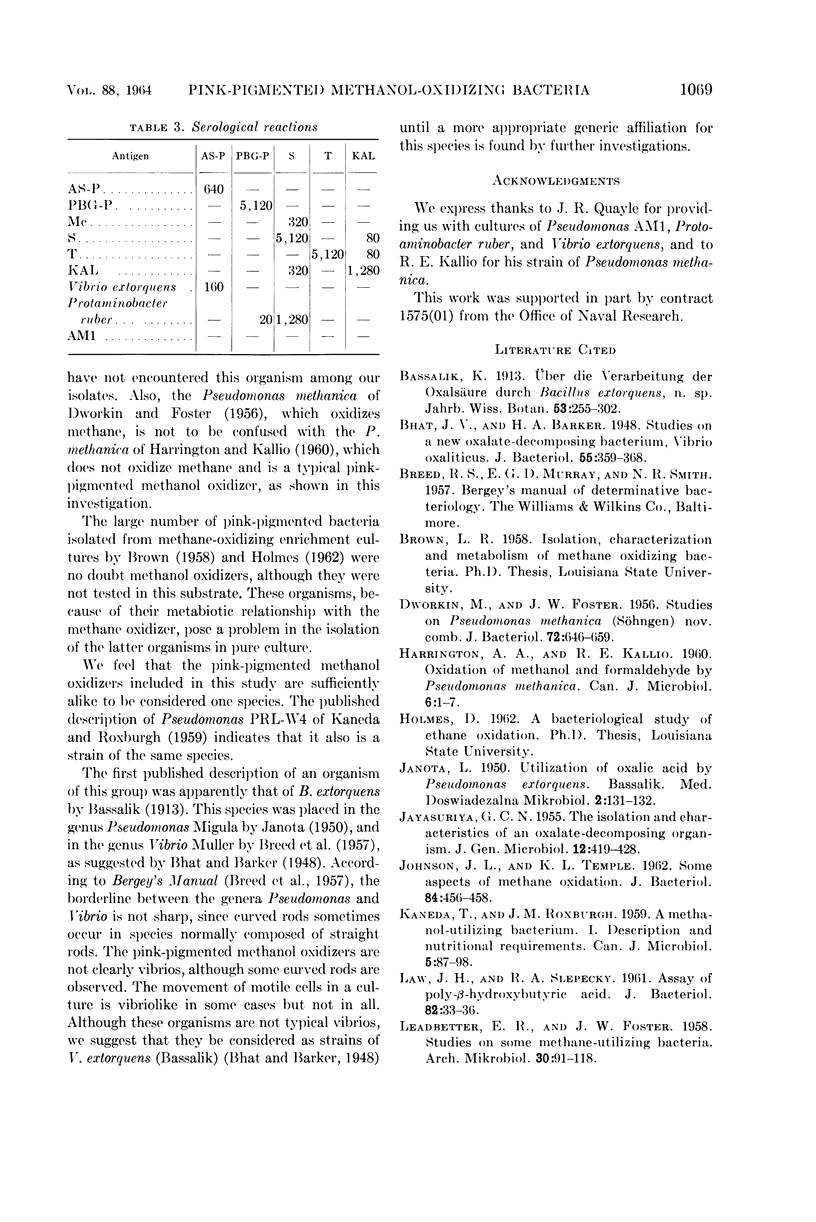
Full text
PDF
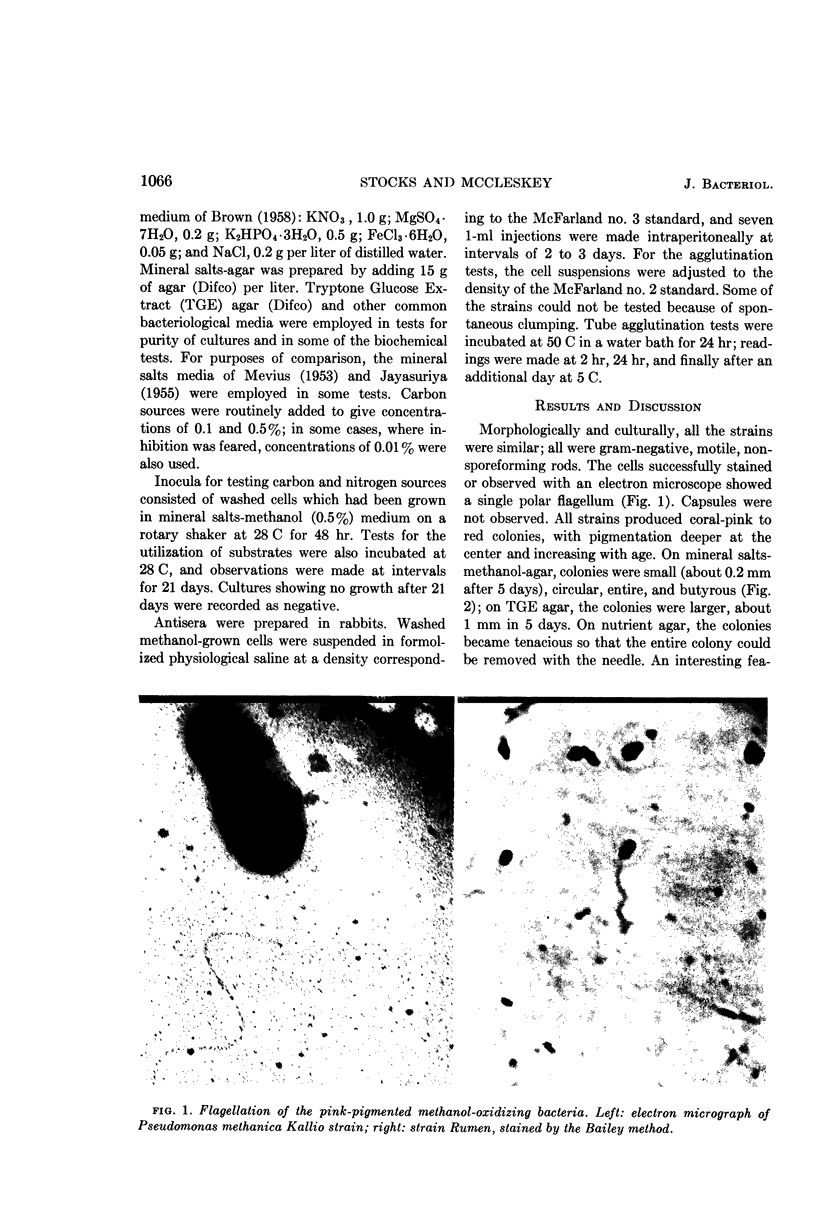


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhat J. V., Barker H. A. Studies on a New Oxalate-Decomposing Bacterium, Vibrio oxaliticus. J Bacteriol. 1948 Mar;55(3):359–368. doi: 10.1128/jb.55.3.359-368.1948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M., FOSTER J. W. Studies on Pseudomonas methanica (Söhngen) nov. comb. J Bacteriol. 1956 Nov;72(5):646–659. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.5.646-659.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRINGTON A. A., KALLIO R. E. Oxidation of methanol and formaldehyde by pseudomonas methanica. Can J Microbiol. 1960 Feb;6:1–7. doi: 10.1139/m60-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANOTA L. Przebieg zuzywania kwasu szczawiowego przez Pseudomonas extorquens Bassalik, w zalezności od poczatkowej liczby komórek. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 1950;2(2):131–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAYASURIYA G. C. The isolation and characteristics of an oxalate-decomposing organism. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Jun;12(3):419–428. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-3-419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Temple K. L. SOME ASPECTS OF METHANE OXIDATION. J Bacteriol. 1962 Sep;84(3):456–458. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.3.456-458.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAW J. H., SLEPECKY R. A. Assay of poly-beta-hydroxybutyric acid. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jul;82:33–36. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.1.33-36.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEADBETTER E. R., FOSTER J. W. Bacterial oxidation of gaseous alkanes. Arch Mikrobiol. 1960;35:92–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00425597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEADBETTER E. R., FOSTER J. W. Studies on some methane-utilizing bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1958;30(1):91–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00509229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEVIUS W., Jr Beiträge zur Kenntnis von Hyphomicrobium vulgare Stutzer et Hartleb. Arch Mikrobiol. 1953;19(1):1–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00412312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEEL D., QUAYLE J. R. Microbial growth on C1 compounds. I. Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas AM 1. Biochem J. 1961 Dec;81:465–469. doi: 10.1042/bj0810465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOCKS P. K., MCCLESKEY C. S. MORPHOLOGY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF METHANOMONAS METHANOOXIDANS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1071–1077. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1071-1077.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]