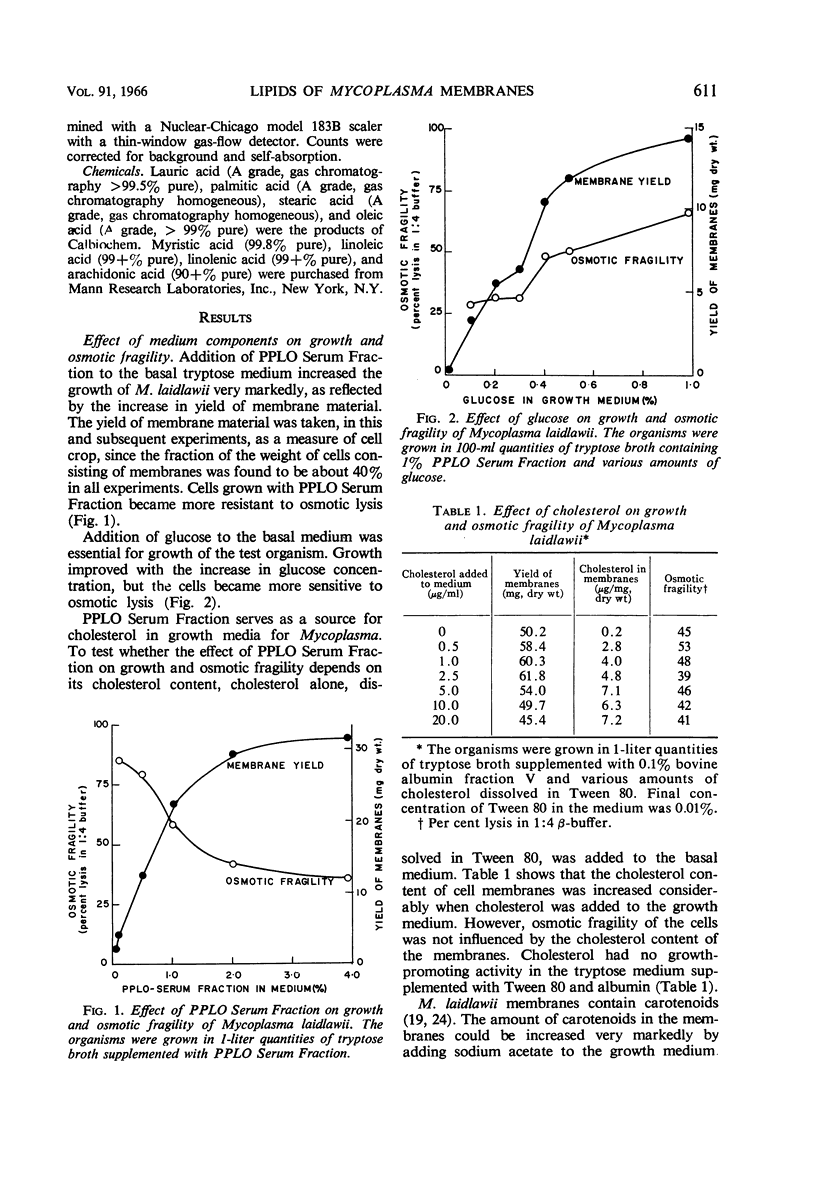
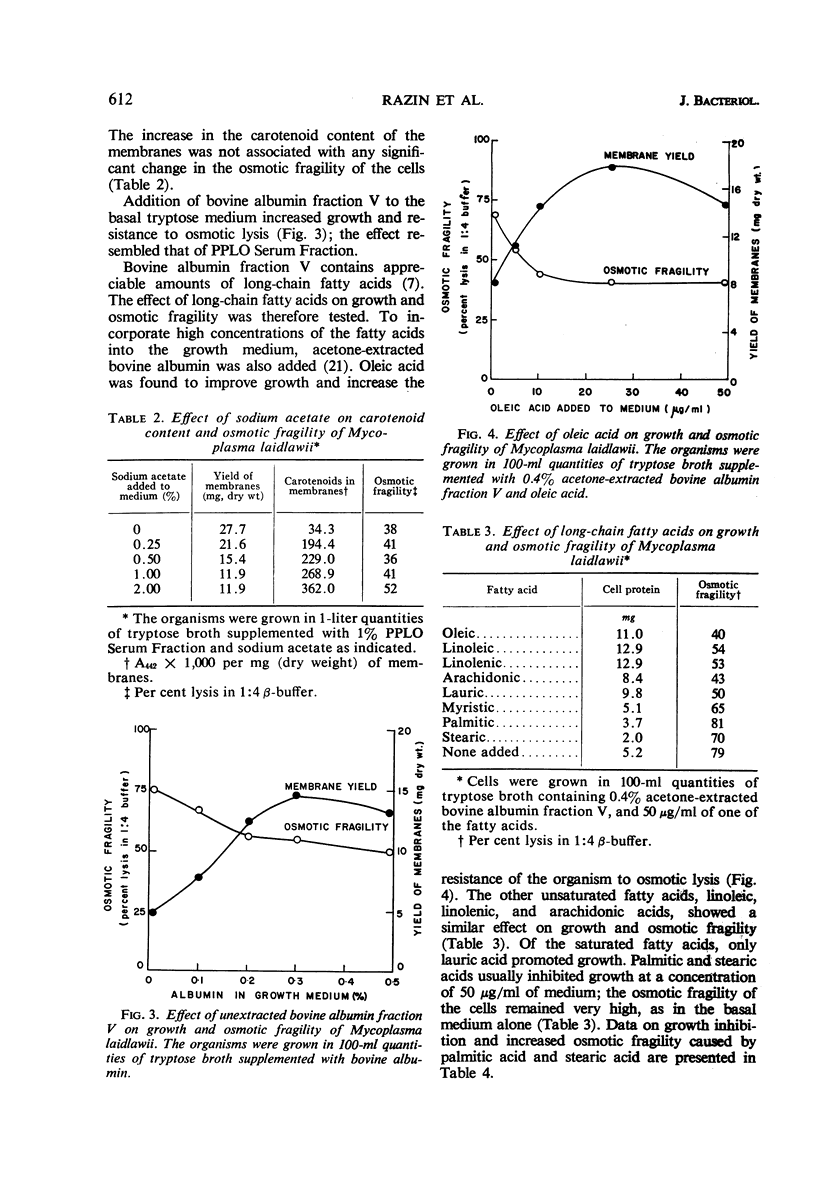
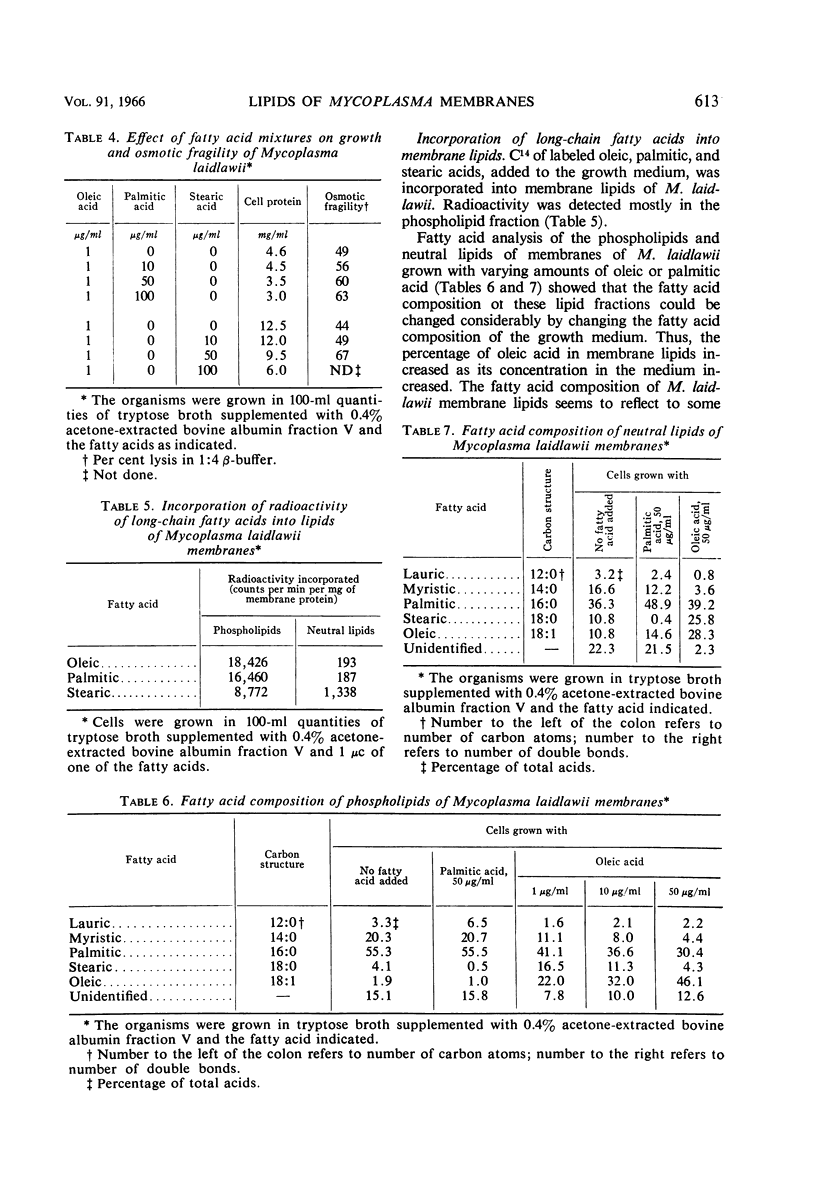
Abstract
Razin, S. (University of Connecticut, Storrs), M. E. Tourtellotte, R. N. McElhaney, and J. D. Pollack. Influence of lipid components of Mycoplasma laidlawii membranes on osmotic fragility of cells. J. Bacteriol. 91:609–616. 1966.—Lipid composition of Mycoplasma laidlawii membranes could be significantly changed by variations in the growth medium. The effect of these changes on the osmotic fragility of the cells was studied. Cholesterol, incorporated into the membrane from the growth medium, had no significant effect on osmotic fragility. Carotenoids, synthesized by the cells from acetate, were likewise without effect. Unsaturated long-chain fatty acids increased markedly the resistance of M. laidlawii to osmotic lysis and promoted growth. The fatty acids of the growth medium were incorporated mainly into membrane phospholipids. The ratio between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids in membrane lipids depended on that of the growth medium.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARGAMAN M., RAZIN S. CHOLESTEROL AND CHOLESTEROL ESTERS IN MYCOPLASMA. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jan;38:153–160. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-1-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOMERMUTH C. H., NIELSEN M. H., FREUNDT E. A., BIRCH-ANDERSEN A. ULTRASTRUCTURE OF MYCOPLASMA SPECIES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:727–744. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.727-744.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. G., FITZGERALD W. A. Cholesterol in the growth of organisms of the pleuropneumonia group. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Aug;5(3):576–586. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-3-576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. S. Preparation of human serum albumin free of long-chain fatty acids. Science. 1957 Jun 28;125(3261):1296–1297. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3261.1296. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long C., Staples D. A. Chromatographic separation of brain lipids: cerebroside and sulphatide. Biochem J. 1961 Jan;78(1):179–185. doi: 10.1042/bj0780179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniloff J., Morowitz H. J., Barrnett R. J. Ultrastructure and Ribosomes of Mycoplasma gallisepticum. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):193–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.193-204.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'BRIEN J. S. STABILITY OF THE MYELIN MEMBRANE. Science. 1965 Mar 5;147(3662):1099–1107. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3662.1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. D., Razin S., Pollack M. E., Cleverdon R. C. Fractionation of mycoplasma cells for enzyme localization. Life Sci. 1965 May;4(9):973–977. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90200-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., ARGAMAN M., AVIGAN J. CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF MYCOPLASMA CELLS AND MEMBRANES. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:477–487. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., ARGAMAN M. Lysis of Mycoplasma, bacterial protoplasts, spheroplasts and L-forms by various agents. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jan;30:155–172. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-1-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S. FACTORS INFLUENCING OSMOTIC FRAGILITY OF MYCOPLASMA. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Sep;36:451–459. doi: 10.1099/00221287-36-3-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S. OSMOTIC LYSIS OF MYCOPLASMA. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:471–475. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., ROTTEM S. FATTY ACID REQUIREMENTS OF MYCOPLASMA LAIDLAWII. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:459–470. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODWELL A. W., ABBOT A. The function of glycerol, cholesterol and long-chain fatty acids in the nutrition of Mycoplasma mycoides. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Jun;25:201–214. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-2-201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHBLAT G. H., ELLIS D. S., KRITCHEVSKY D. THE CAROTENOID PIGMENTS OF MICROCOCCUS LYSODEIKTICUS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jun 15;84:340–347. doi: 10.1016/0926-6542(64)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHBLAT G. H., SMITH P. F. Nonsaponifiable lipids of representative pleuropneumonia-like organisms. J Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:479–491. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.4.479-491.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Morowitz H. J., Terry T. M. Membrane subunits of Mycoplasma laidlawii and their assembly to membranelike structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Jul;54(1):219–225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.1.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F. THE CAROTENOID PIGMENTS OF MYCOPLASMA. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Sep;32:307–319. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-3-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F., Koostra W. L., Henrikson C. V. Diphosphatidyl Glycerol in Mycoplasma laidlawii. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):282–283. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.282-283.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TOURTELLOTTE M. E., JENSEN R. G., GANDER G. W., MOROWITZ H. J. LIPID COMPOSITION AND SYNTHESIS IN THE PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM MYCOPLASMA GALLISEPTICUM. J Bacteriol. 1963 Sep;86:370–379. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.3.370-379.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLMER E. N. Steroids and cell surfaces. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1961 Aug;36:368–398. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1961.tb01295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van ITERSON, RUYS A. C. The fine structure of the Mycoplasmataceae (microorganisms of the pleuropneumonia group PPLO). 1. Mycoplasma hominis, M. fermentans and M. salivarium. J Ultrastruct Res. 1960 Feb;3:282–301. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(60)80015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



