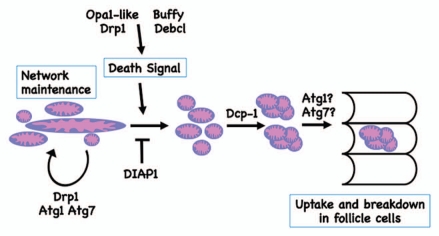
Figure 1.
A model for mitochondrial regulation and clustering during cell death in mid-oogenesis. In healthy egg chambers, mitochondrial networks extend throughout the egg chamber. Upon induction of cell death, mitochondria remodel, followed by the formation of clusters and then uptake by the surrounding follicle cells. Through genetic analysis, we showed that mitochondrial remodeling occurs upstream of effector caspases, and that cluster formation requires the caspase Dcp-1. In addition, the Bcl-2 family proteins, Buffy and Debcl, and mitochondrial fission and fusion regulators, Drp1 and Opa1-like, regulate mitochondrial remodeling as well as activation of cell death. The autophagic proteins, Atg1 and Atg7, are involved in normal mitochondrial network maintenance and remodeling during cell death. Autophagic proteins also may have a role in cluster uptake into the follicle cells, or in the degradation of the nurse cell material within the follicle cells.