Abstract
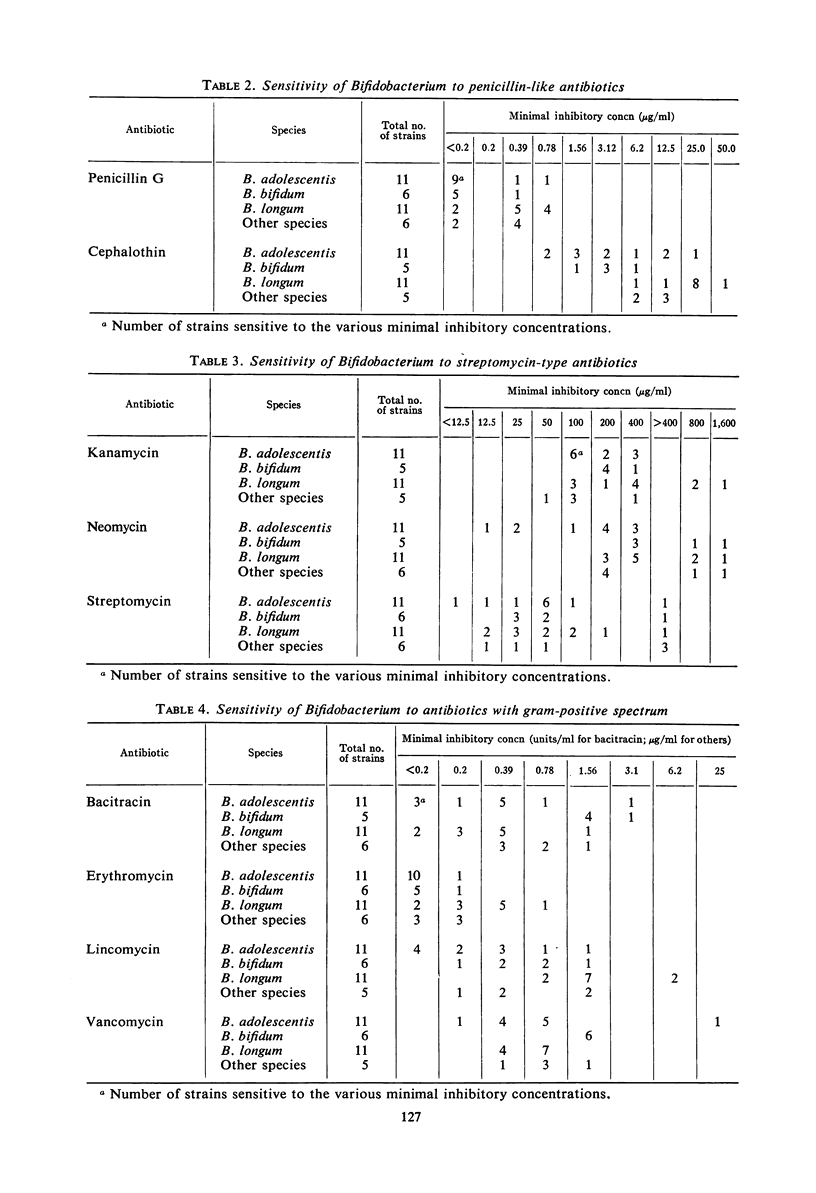
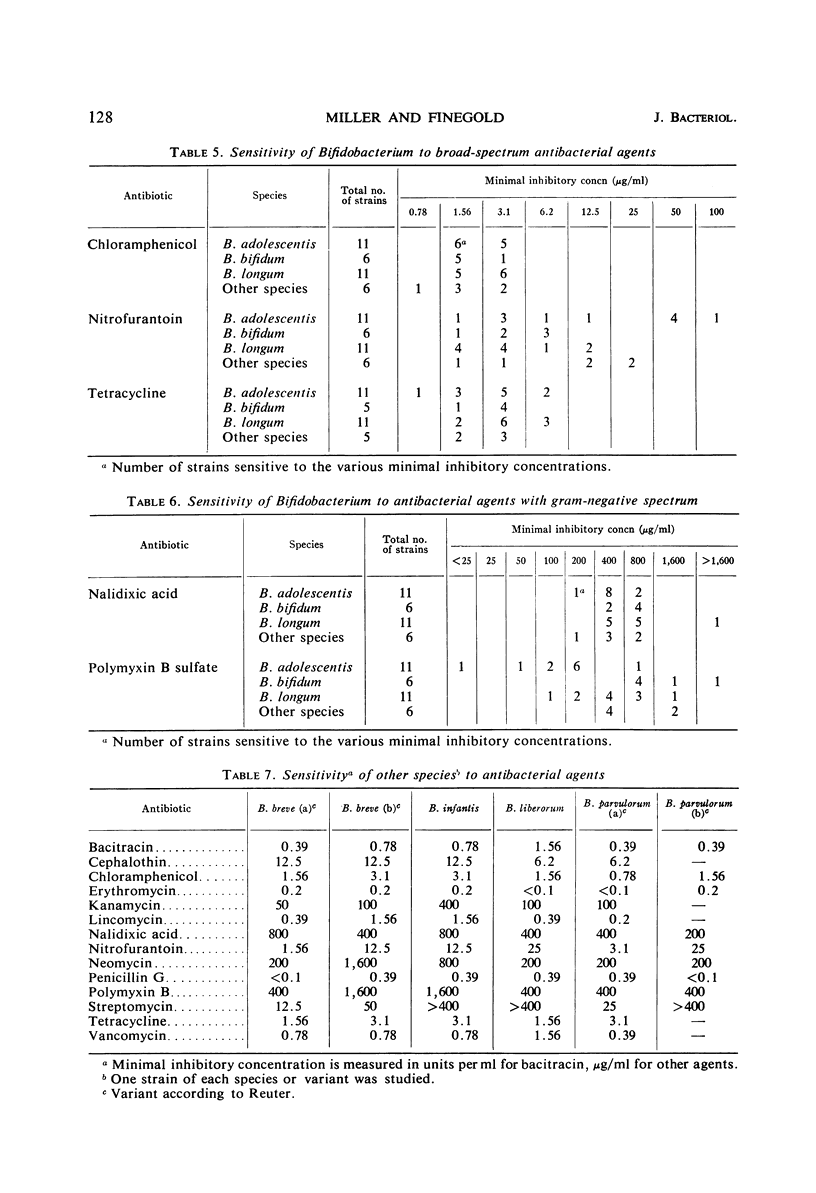
The antibacterial sensitivity patterns of gram-positive, nonsporeforming, anaerobic bacilli variously classed as Lactobacillus bifidus, Actinomyces bifidus, or Bifidobacterium were studied by the plate dilution method. A total of 34 strains, mostly from human feces, was studied. Three species, B. longum, B. adolescentis, and B. bifidum, were represented with 11, 11, and 6 strains, respectively. The other six strains fell into four other species. Most strains of all types resisted 100 μg/ml or more of neomycin, polymyxin B, and nalidixic acid. They were somewhat less resistant to kanamycin and still less so to streptomycin. All strains were inhibited by less than 1 μg/ml of penicillin G and erythromycin, by 3.1 units or less per ml of bacitracin, by 3.1 μg/ml or less of chloramphenicol, and by 6.2 μg/ml or less of tetracycline and lincomycin. Most strains were inhibited by 3.1 μg/ml of vancomycin. Results were very variable with cephalothin and nitrofurantoin, with some strains quite resistant. With half of the drugs tested, there were moderate differences in sensitivity between different species. These data are discussed in relation to the effect of antimicrobial agents on bifid bacilli in the normal human fecal flora, in relation to the implications thereof, and in relation to the usefulness of several agents (particularly neomycin, nalidixic acid, and polymyxin B) in selective media for Bifidobacterium.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOHNHOFF M., MILLER C. P., MARTIN W. R. RESISTANCE OF THE MOUSE'S INTESTINAL TRACT TO EXPERIMENTAL SALMONELLA INFECTION. I. FACTORS WHICH INTERFERE WITH THE INITIATION OF INFECTION BY ORAL INOCULATION. J Exp Med. 1964 Nov 1;120:805–816. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.5.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUN O. H., DEHNERT J., HOFFMANN K., KIENITZ M., MAYER J. B., REPLOH H., REUTER G., SEELIGER H. P., WERNER H. DIE BIFIDUSKEIME DES MENSCHEN. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1964 Aug 28;89:1647–1652. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1113179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE LAVERGNE E., BURDIN J. C., SCHMITT J., MANCIAUX M. [Sensitivity of Bifidibacterium bifidum to 11 antibiotics]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1959 Jul;97:104–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegold S. M., Harada N. E., Miller L. G. Lincomycin: activity against anaerobes and effect on normal human fecal flora. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1965;5:659–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS H. Beeinflussung der Darmflora durch Breitband-Antibiotica. Neue Osterr Z Kinderheilkd. 1956;1(4):556–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAENEL H., KOEHLER F., MERTSCH H., PARDEMANN C. [On the effect of tetracycline on the fecal flora of TPE carriers]. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1960 Jan;177:41–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haenel H., Mertsch H., Köhler F., Müller-Beuthow W. Veränderungen der faekalen Mikroflora bei Jugnedlichen durch Paromomycin. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1965 Feb;195(3):385–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knothe H., Wiedemann B. Die Wirkung von Ampicillin auf die Darmflora des gesunden Menschen. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1965 Aug;197(2):234–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuoka T., Sega T., Yamamoto S. Eine verbesserte Methodik der qualitativen und quantitativen Analyse der Darmflora von Menschen und Tieren. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1965 Mar;195(4):455–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REUTER G. VERGLEICHENDE UNTERSUCHUNGEN UEBER DIE BIFIDUS-FLORA IM SAEUGLINGS- UND ERWACHSENENSTUHL. ZUGLEICH EIN BEITRAG ZUR SYSTEMATISIERUNG UND NOMENKLATUR DER BIFIDUS-KEIME. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1963;191:486–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHABINSKI G., ALTHAMMER R. Untersuchungen über die Darmwirksamkeit von Streptomycin. Klin Wochenschr. 1958 Nov 1;36(21):1013–1017. doi: 10.1007/BF01487971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEELIGER H. P. Die Wirkung von Erythromycin auf die Darm-Flora des gesunden Menschen. Arzneimittelforschung. 1957 Oct;7(10):629–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



