Abstract
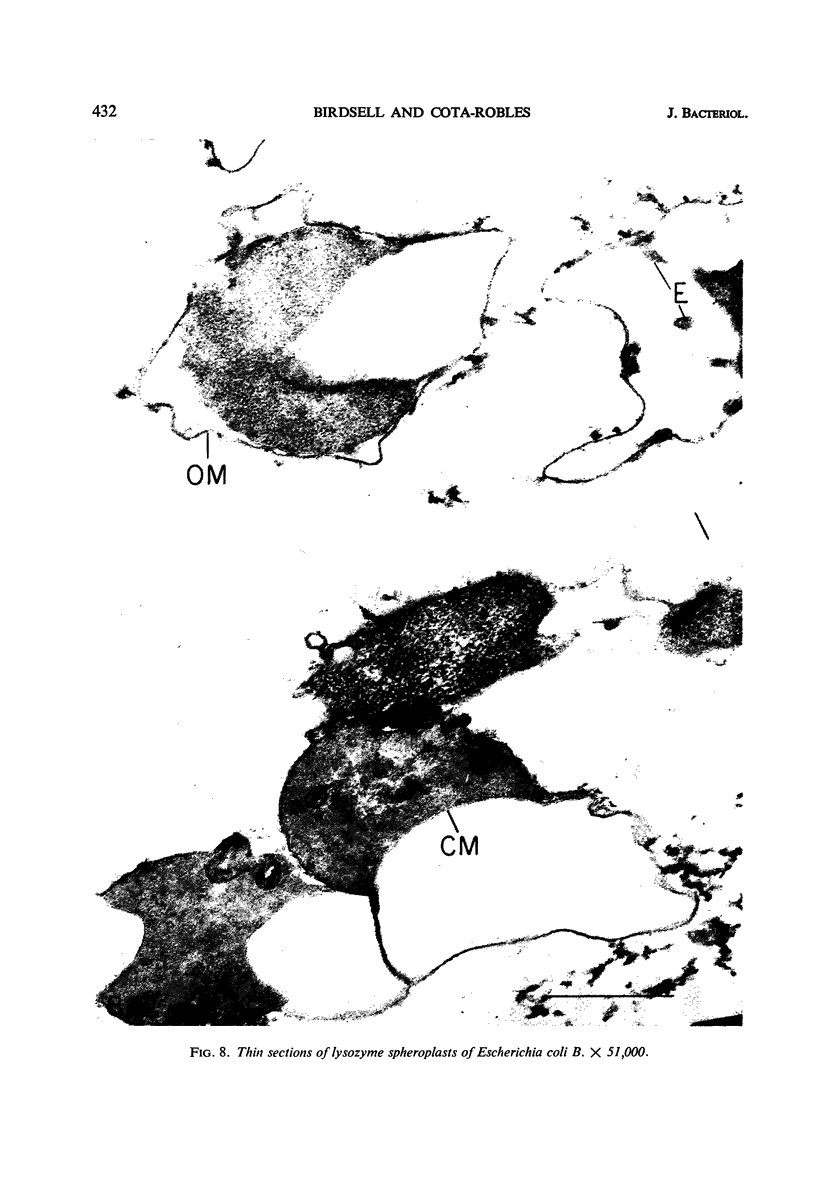
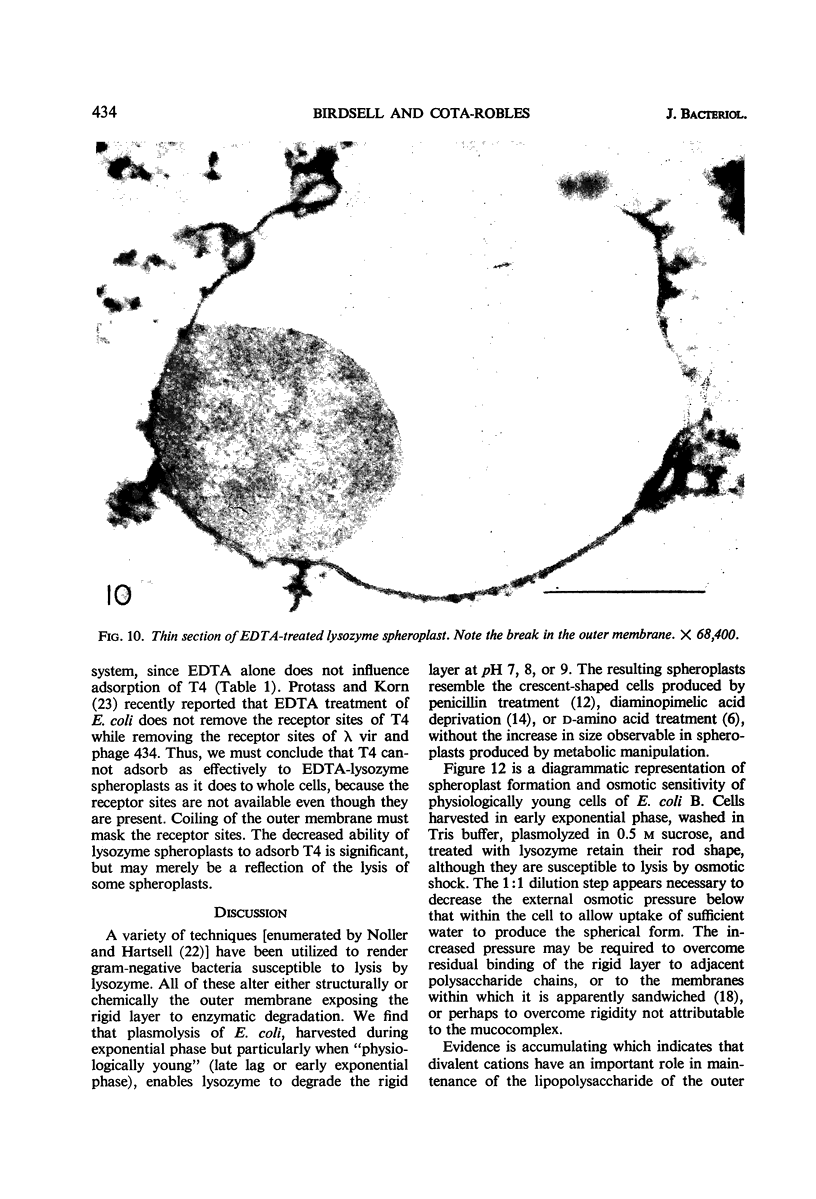
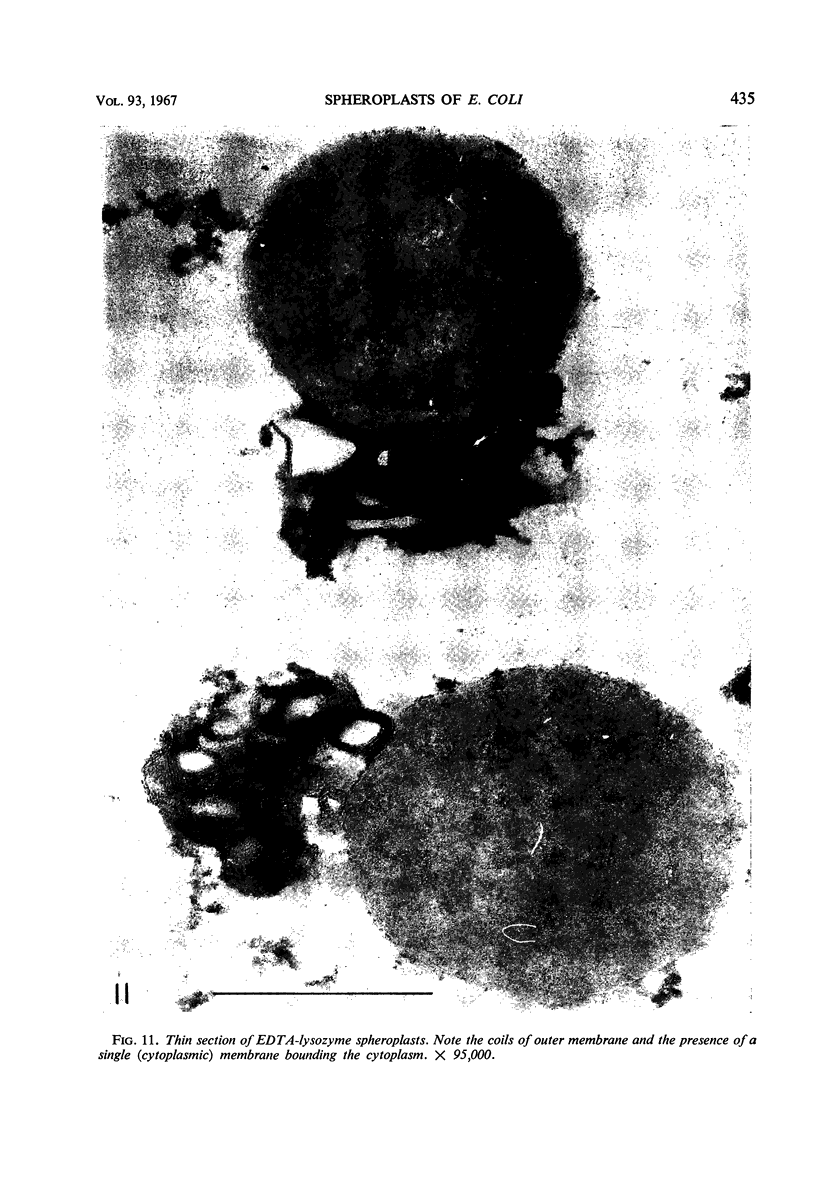
Spheroplast production by lysozyme and ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA) was examined as a means of obtaining osmotically sensitive cells for studies of enzyme localization. Physiologically young cells plasmolyzed with 0.5 m sucrose in 0.01 m tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (Tris) buffer (pH 7, 8, or 9) were quantitatively converted to plasmolyzed osmotically sensitive rods after lysozyme treatment. Although such cells were osmotically sensitive, a 1:1 dilution in Tris buffer was necessary for conversion of rods into spheroplasts. Addition of EDTA resulted in a rapid conversion of the plasmolyzed spheroplasts into spherical structures devoid of a plasmolysis vacuole. These structures, which we call EDTA-lysozyme spheroplasts, contained a number of attached membranes. We believe that this conversion results from a weakening of the outer trilaminar component of the cell wall by EDTA, resulting in the collapse of the plasmolysis vacuole. Dilution of sucrose below 0.15 m also resulted in the collapse of the plasmolysis vacuole. Both the lysozyme spheroplasts and the EDTA-lysozyme spheroplasts were osmotically sensitive. Thin sections of the EDTA-lysozyme spheroplasts demonstrated that the outer trilaminar component of the cell wall was broken, exposing large areas of the cytoplasmic membrane to the environment.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbell M. A., Eagon R. G. The role of multivalent cations in the organization and structure of bacterial cell walls. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Mar 22;22(6):664–671. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTA-ROBLES E. H., DUNCAN P. H. The effect of D-glutamic acid upon spheroplast formation in Escherichia coli B. Exp Cell Res. 1962 Nov;28:342–349. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(62)90288-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson K. J., Eagon R. G. Lysozyme sensitivity of the cell wall of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Further evidence for the role of the non-peptidoglycan components in cell wall rigidity. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Feb;12(1):105–108. doi: 10.1139/m66-015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordonnier C., Bernardi G. Localization of E. coli endonuclease I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Sep 8;20(5):555–559. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90434-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRESDEN M., HOAGLAND M. B. POLYRIBOSOMES FROM ESCHERICHIA COLI: ENZYMATIC METHOD FOR ISOLATION. Science. 1965 Aug 6;149(3684):647–649. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3684.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER D., JERREL E. A. The amino acid composition of T3 bacteriophage. J Biol Chem. 1953 Nov;205(1):291–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTHRIE G. D., SINSHEIMER R. L. Observations on the infection of bacterial protoplasts with the deoxyribonucleic acid of bacteriophage phi X174. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jun 25;72:290–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLENBERGER E., RYTER A. Cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 May 25;4(3):323–326. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.3.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J., ST CLAIR J. Protoplasts and L-type growth of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1958 Feb;75(2):143–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.2.143-160.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L. Release of lipopolysaccharide by EDTA treatment of E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):290–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALAMY M. H., HORECKER B. L. PURIFICATION AND CRYSTALLIZATION OF THE ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Biochemistry. 1964 Dec;3:1893–1897. doi: 10.1021/bi00900a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALAMY M. H., HORECKER B. L. RELEASE OF ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE FROM CELLS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI UPON LYSOZYME SPHEROPLAST FORMATION. Biochemistry. 1964 Dec;3:1889–1893. doi: 10.1021/bi00900a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER F., MACKAL R. P., TAO M., EVANS E. A., Jr Infectious deoxyribonucleic acid from gamma bacteriophage. J Biol Chem. 1961 Apr;236:1141–1143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., STEED P., ELSON H. E. THE LOCATION OF THE MUCOPEPTIDE IN SECTIONS OF THE CELL WALL OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND OTHER GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Jun;11:547–560. doi: 10.1139/m65-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEU H. C., HEPPEL L. A. THE RELEASE OF RIBONUCLEASE INTO THE MEDIUM WHEN ESCHERICHIA COLI CELLS ARE CONVERTED TO SPEROPLASTS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Nov;239:3893–3900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOLLER E. C., HARTSELL S. E. Bacteriolysis of Enterobacteriaceae. I. Lysis by four lytic systems utilizing lysozyme. J Bacteriol. 1961 Mar;81:482–491. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.3.482-491.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. On the surface localization of enzymes in E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1964 Oct 14;17(3):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(64)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protass J. J., Korn D. Impairment of Temperate Bacteriophage Adsorption by Brief Treatment of Escherichia coli with Dilute Solutions of Ethylenediaminetetraacetate. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):143–147. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.143-147.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Jacob F. Etude morphologique de la liaison du noyau à la membrane chez E. coli et chez les protoplastes de B. subtilis. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Jun;110(6):801–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISTROM W. R. On the physical state of the intracellularly accumulates substrates of beta-galactoside-permease in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Sep;29(3):579–587. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENABLE J. H., COGGESHALL R. A SIMPLIFIED LEAD CITRATE STAIN FOR USE IN ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. J Cell Biol. 1965 May;25:407–408. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.2.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOSS J. G. LYSOZYME LYSIS OF GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA WITHOUT PRODUCTION OF SPHEROPLASTS. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 May;35:313–317. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-2-313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









