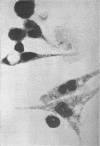
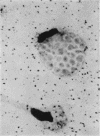
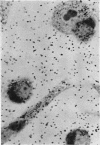
Abstract
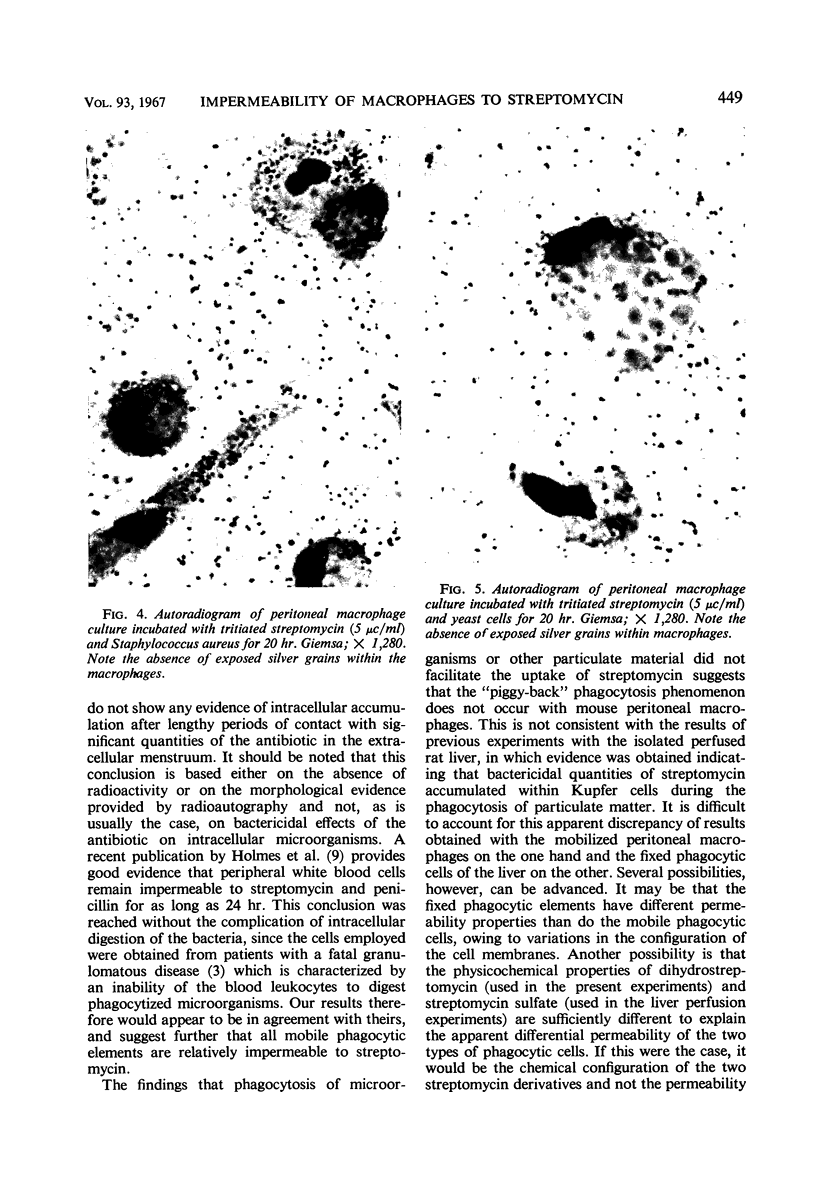
Cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages were found to be relatively impermeable to streptomycin. Based on radioactivity measurements and radioautographic evidence, macrophages were impermeable to tritiated dihydrostreptomycin for periods up to 20 hr of incubation. Little or no intracellular streptomycin could be detected even when incubation was carried out in the presence of therapeutic blood levels of carrier dihydrostreptomycin. When the cultured mouse macrophages were allowed to phagocytize staphylococci, yeast cells, or polystyrene latex particles in the presence of tritiated streptomycin, the impermeability of the cells to the antibiotic was not affected. These observations suggested that the process of phagocytosis does not facilitate the intracellular accumulation of streptomycin, as seems to be the case for the fixed phagocytic cells of the liver.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRIDGES R. A., BERENDES H., GOOD R. A. A fatal granulomatous disease of childhood; the clinical, pathological, and laboratory features of a new syndrome. AMA J Dis Child. 1959 Apr;97(4):387–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUMFITT W., GLYNN A. A., PERCIVAL A. FACTORS INFLUENCING THE PHAGOCYTOSIS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI. Br J Exp Pathol. 1965 Apr;46:215–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Oxman E. Phagocytosis and intracellular disposition of viable bacteria by the isolated perfused rat liver. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1965 Nov;2(4):313–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., BENSON B. THE IN VITRO DIFFERENTIATION OF MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES. II. THE INFLUENCE OF SERUM ON GRANULE FORMATION, HYDROLASE PRODUCTION, AND PINOCYTOSIS. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:835–848. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A., Benson B. The in vitro differentiation of mononuclear phagocytes. 3. The reversibility of granule and hydrolytic enzyme formation and the turnover of granule constituents. J Exp Med. 1965 Sep 1;122(3):455–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.3.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Quie P. G., Windhorst D. B., Pollara B., Good R. A. Protection of phagocytized bacteria from the killing action of antibiotics. Nature. 1966 Jun 11;210(5041):1131–1132. doi: 10.1038/2101131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKIN C., BENACERRAF B. In vitro studies on the interaction between mouse peritoneal macrophages and strains of Salmonella and Escherichia coli. J Exp Med. 1960 Aug 1;112:403–417. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARLSBAD G., KESSEL R. W., DE PETRIS S., MONACO L. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE OBSERVATIONS OF BRUCELLA ABORTUS GROWN WITHIN MONOCYTES IN VITRO. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Jun;35:383–390. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-3-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. The phagocytosis and inactivation of staphylococci by macrophages of normal rabbits. J Exp Med. 1960 Jul 1;112:35–53. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORELLO J. A., BAKER E. E. INTERACTION OF SALMONELLA WITH PHAGOCYTES IN VITRO. J Infect Dis. 1965 Apr;115:131–141. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OYAMA V. I., EAGLE H. Measurement of cell growth in tissue culture with a phenol reagent (folin-ciocalteau). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Feb;91(2):305–307. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., SHIRLEY W., BARDAWIL W. A. 'Piggy-back' phagocytosis. Nature. 1962 Apr 21;194:255–256. doi: 10.1038/194255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TYE R., ENGEL J. D. LIQUID SCINTILLATION COUNTING OF CARBON-14 IN AQUEOUS DIGESTS OF WHOLE TISSUES. Anal Chem. 1965 Sep;37:1225–1227. doi: 10.1021/ac60229a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]