Abstract
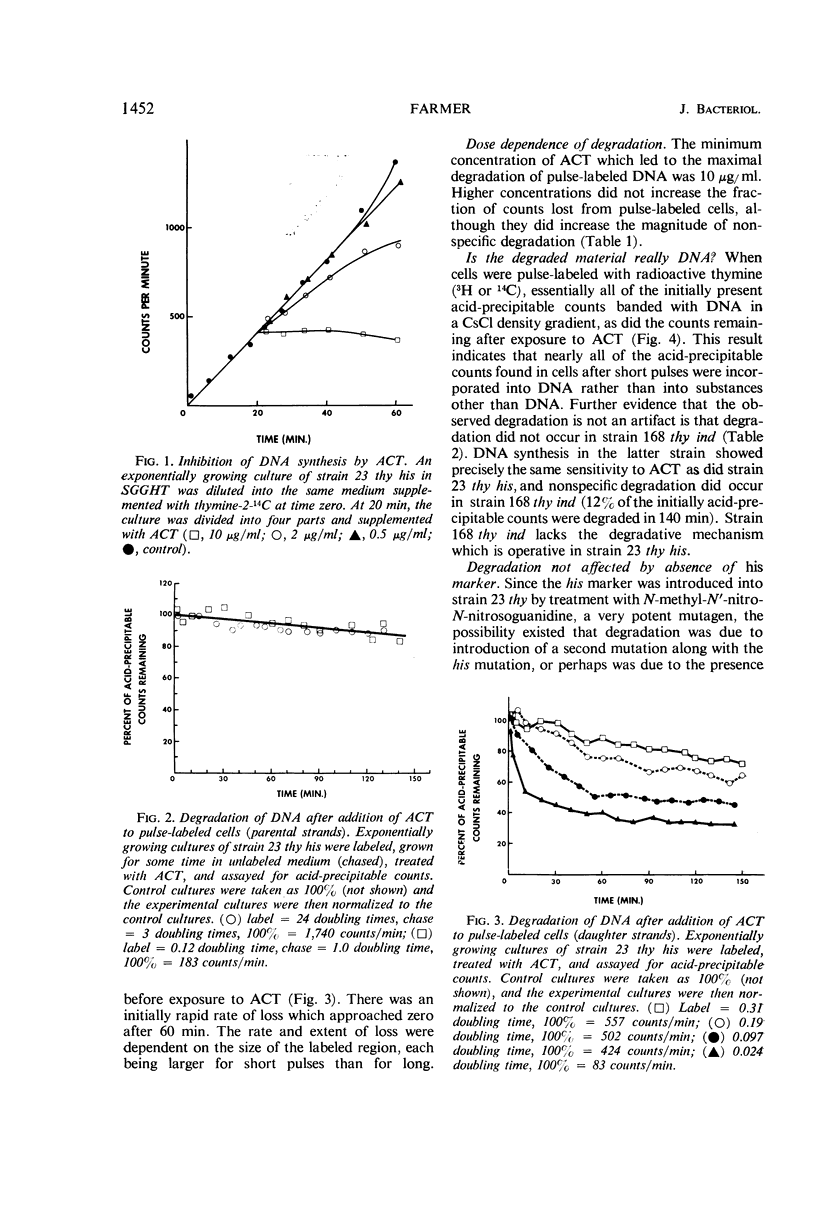
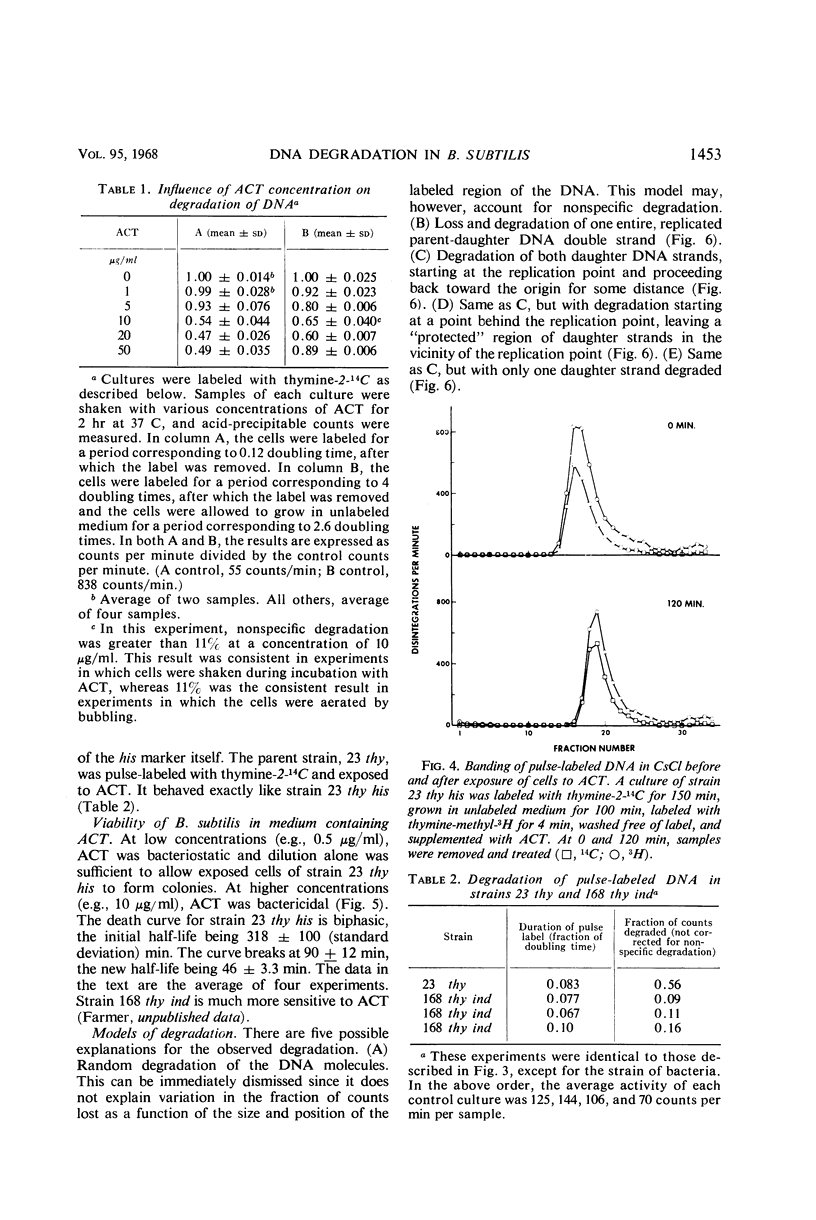
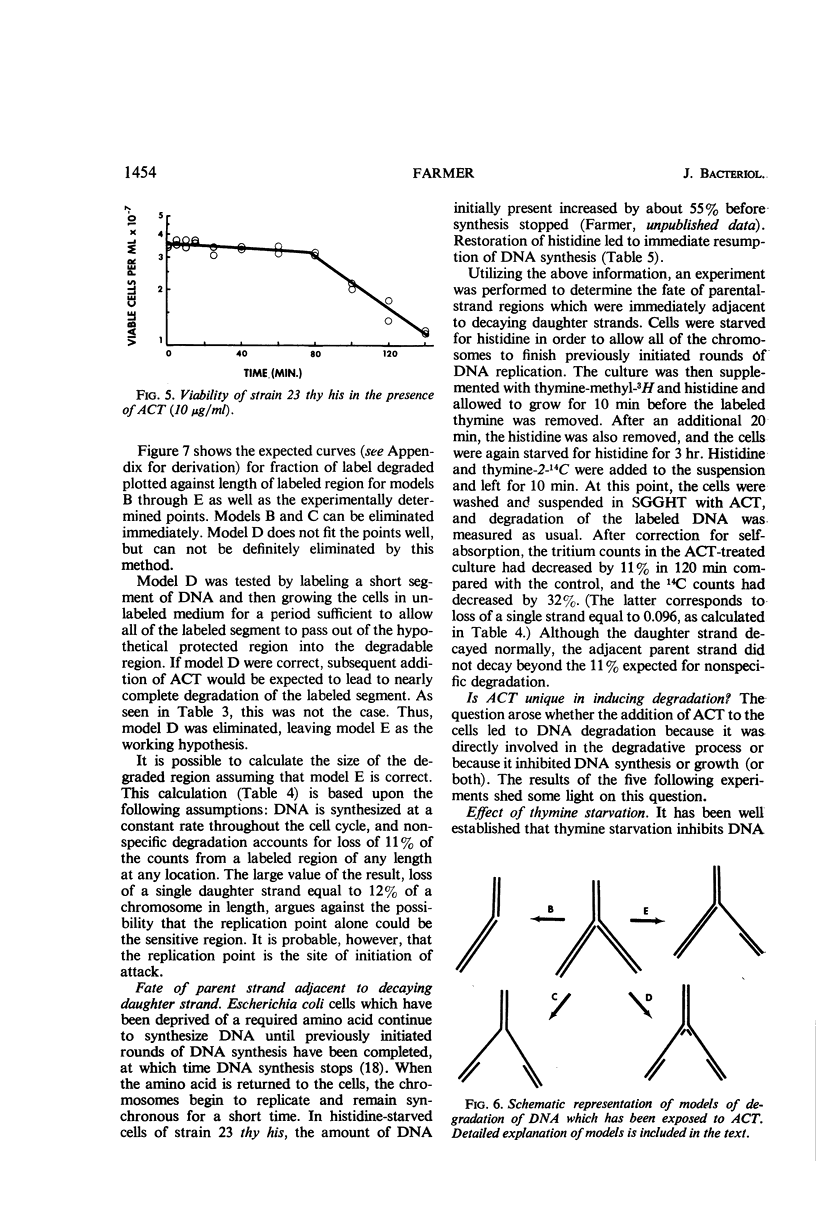
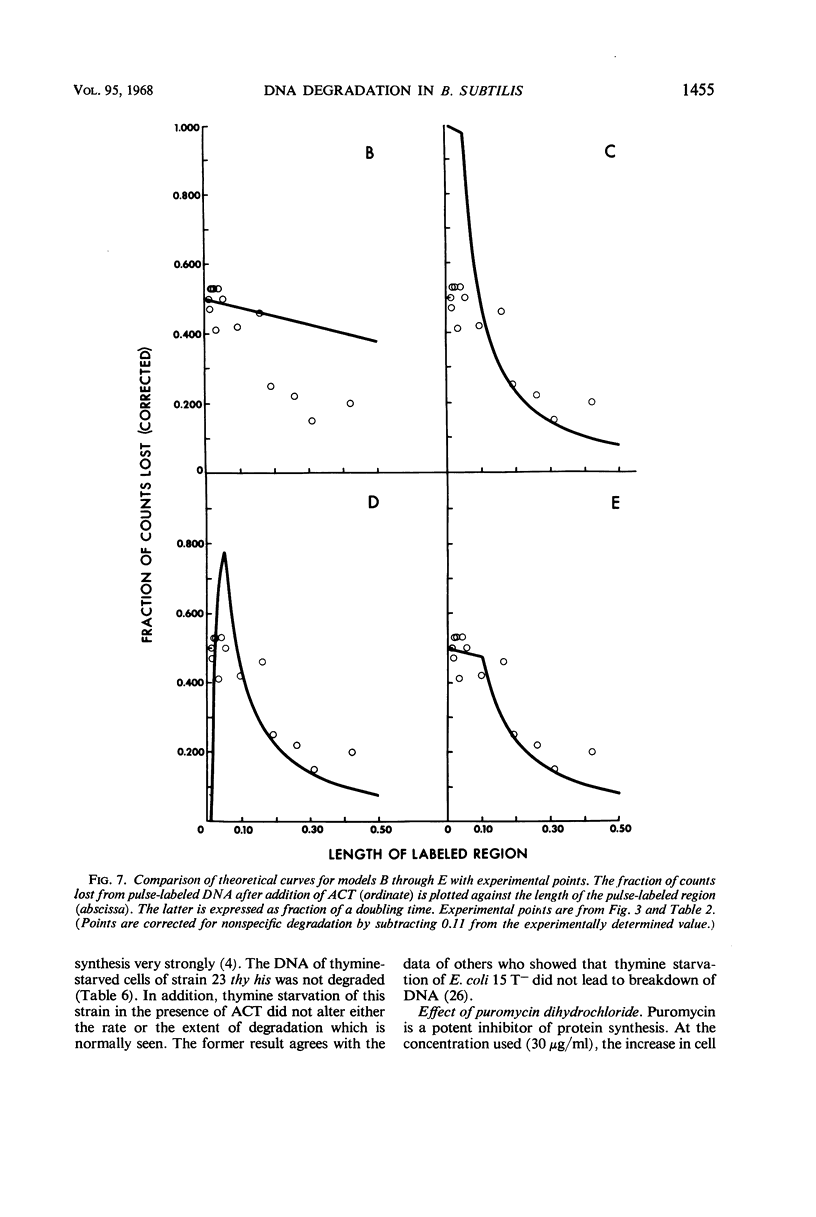
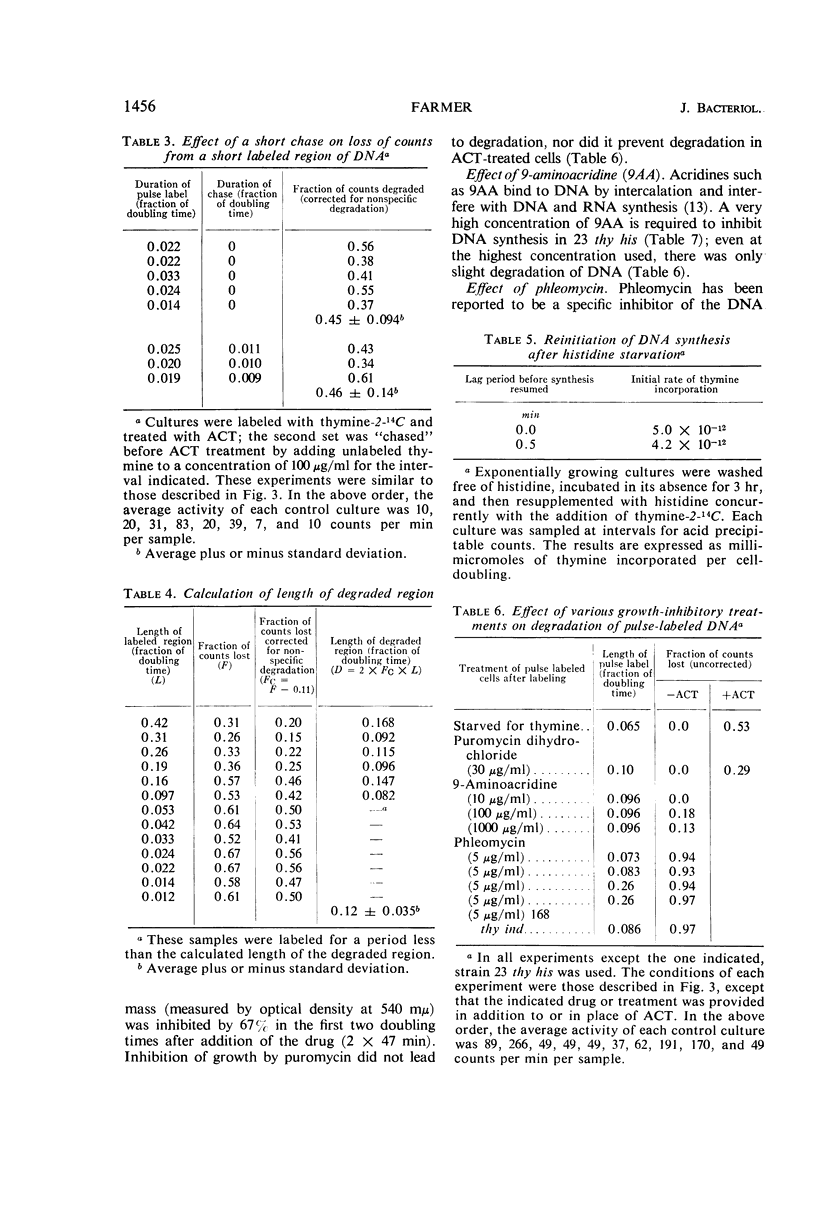
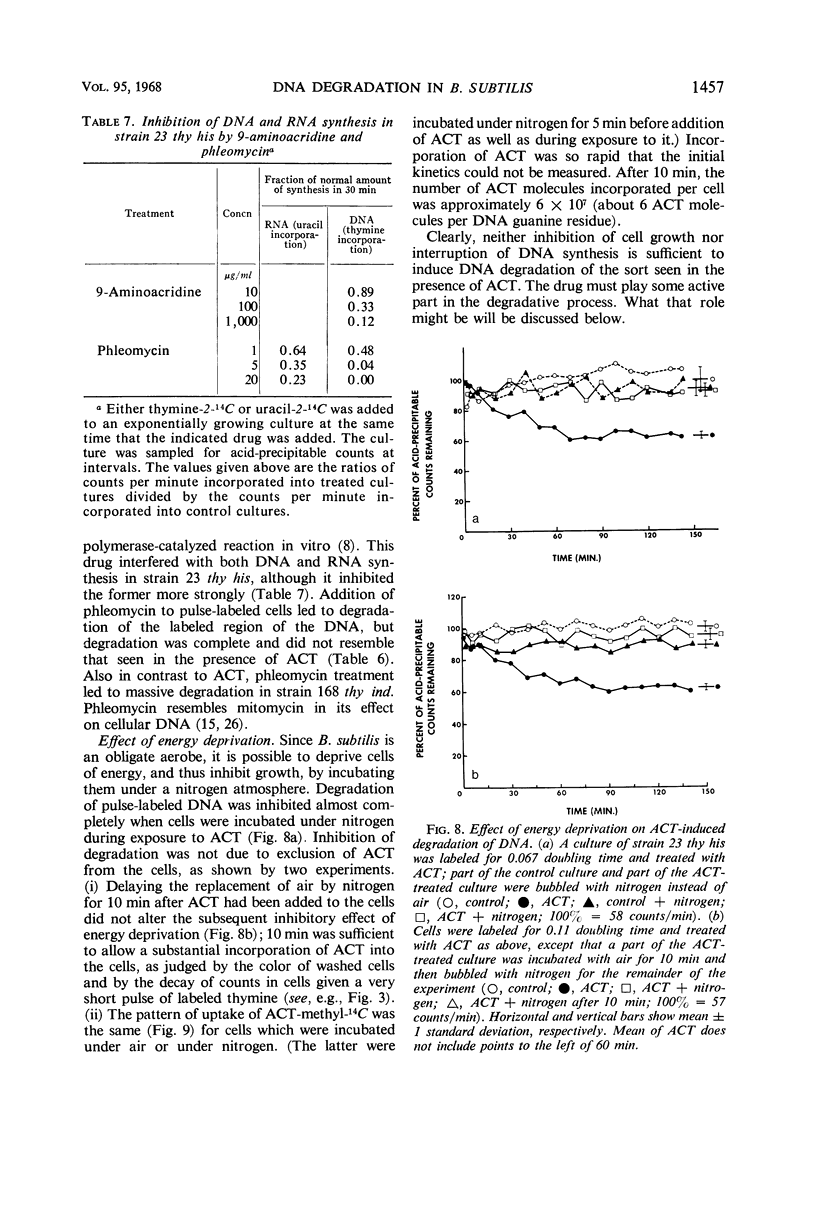
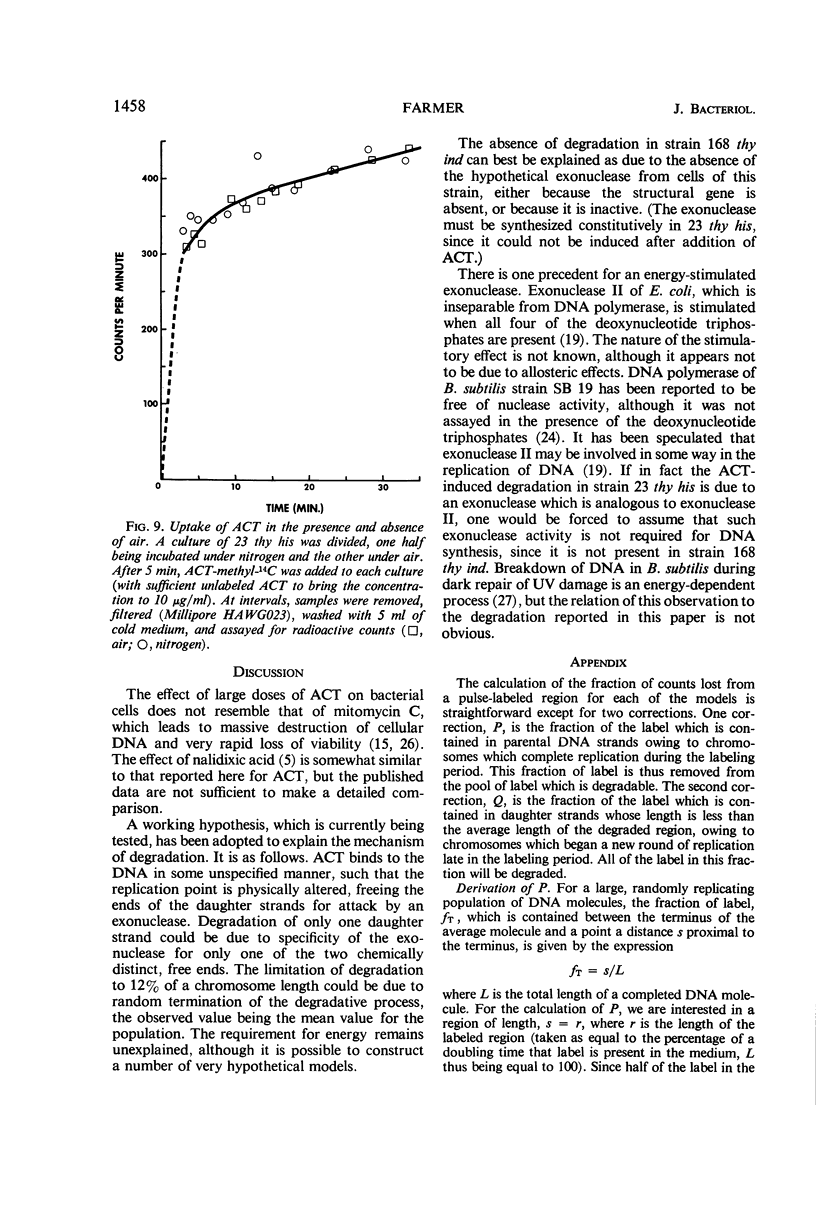
At high concentrations (10 μg/ml), actinomycin D inhibited deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. Inhibition occurred quickly (in less than 1 min) and was complete. In strain 23 thy his, inhibition of DNA synthesis by actinomycin D was followed by partial degradation of one of the two daughter strands to acid-soluble products. Degradation began at the replication point and proceeded over a distance equal to about 12% of a chromosome in length. Actinomycin D played some essential part in degradation, since exposure of the cells to other treatments or agents which inhibit growth did not lead to the above result.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVALIERI L. F., NEMCHIN R. G. THE MODE OF INTERACTION OF ACTINOMYCIN D WITH DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Aug 12;87:641–652. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerami A., Reich E., Ward D. C., Goldberg I. H. The interaction of actinomycin with DNA: requirement for the 2-amino group of purines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):1036–1042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. S., Barner H. D. STUDIES ON UNBALANCED GROWTH IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1954 Oct;40(10):885–893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.40.10.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook T. M., Brown K. G., Boyle J. V., Goss W. A. Bactericidal action of nalidixic acid on Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1510–1514. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1510-1514.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott W. H. The effects of antimicrobial agents on deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. Biochem J. 1963 Mar;86(3):562–567. doi: 10.1042/bj0860562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eron L. J., McAuslan B. R. Inhibition of deoxyribonuclease action by actinomycin D and ethidium bromide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 21;114(3):633–636. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FALASCHI A., KORNBERG A. ANTIMETABOLITES AFFECTING PROTEIN OR NUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS. PHLEOMYCIN, AN INHIBITOR OF DNA POLYMERASE. Fed Proc. 1964 Sep-Oct;23:940–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARMER J. L., ROTHMAN F. TRANSFORMABLE THYMINE-REQUIRING MUTANT OF BACILLUS SUBTILS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:262–263. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.262-263.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELLERT M., SMITH C. E., NEVILLE D., FELSENFELD G. ACTINOMYCIN BINDING TO DNA: MECHANISM AND SPECIFICITY. J Mol Biol. 1965 Mar;11:445–457. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBERG I. H., RABINOWITZ M., REICH E. Basis of actinomycin action. I. DNA binding and inhibition of RNA-polymerase synthetic reactions by actinomycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Dec 15;48:2094–2101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.12.2094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMILTON L. D., FULLER W., REICH E. X-ray diffraction and molecular model building studies of the interaction of actinomycin with nucleic acids. Nature. 1963 May 11;198:538–540. doi: 10.1038/198538b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ J., FURTH J. J., MALAMY M., ALEXANDER M. The role of deoxyribonucleic acid in ribonucleic acid synthesis. III. The inhibition of the enzymatic synthesis of ribonucleic acid and deoxyribonucleic acid by actinomycin D and proflavin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jul 15;48:1222–1230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.7.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERSTEN H., RAUEN H. M. Degradation of deoxyribonucleic acid in Escherichia coli cells treated with mitomycin C. Nature. 1961 Jun 24;190:1195–1196. doi: 10.1038/1901195a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersten W., Kersten H., Szybalski W. Physicochemical properties of complexes between deoxyribonucleic acid and antibiotics which affect ribonucleic acid synthesis (actinomycin, daunomycin, cinerubin, nogalamycin, chormomycin, mithramycin, and olivomycin). Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):236–244. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEITH J. D., Jr ACRIDINE ORANGE AND ACRIFLAVIN INHIBIT DEOXYRIBONUCLEASE ACTION. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 20;72:643–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIERSCH M., HARTMANN G. DIE BINDUNG VON PROFLAVIN UND ACTINOMYCIN AN DESOXYRIBONUCLEINSAEURE I. DER EINFLUSS DER IONENSTAERKE UND DES PH SOWIE DIE WIRKUNG VON HARNSTOFF AUF DIE BINDUNG. Biochem Z. 1964 Sep 28;340:390–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labouret T., Pouyet J., Fromageot P. Note sur l'interaction entre actinomycine C-1 et DNA. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1965;47(8):1579–1590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lark K. G. Regulation of chromosome replication and segregation in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Mar;30(1):3–32. doi: 10.1128/br.30.1.3-32.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liersch M., Hartmann G. Die Bindung von Proflavin und Actinomycin an Desoxyribonucleinsäure. II. Die Bindung an denaturierte und einsträngige DNA, Apyrimidinsäure und Apurinsäure. Biochem Z. 1965 Nov 5;343(1):16–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKAZAKI T., KORNBERG A. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. XV. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF A POLYMERASE FROM BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Jan;239:259–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REICH E. ACTINOMYCIN: CORRELATION OF STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF ITS COMPLEXES WITH PURINES AND DNA. Science. 1964 Feb 14;143(3607):684–689. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3607.684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter H., Strauss B., Marone R., Robbins M. Actinomycin D inhibition of UV-dark repair in Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 22;24(6):892–898. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90333-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolfe R. On the mechanism of thymineless death in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jan;57(1):114–121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar N. K. Effects of actinomycin D and mitomycin C on the degradation of deoxyribonucleic acid and polydeoxyribonucleotide by deoxyribonucleases and venom phosphodiesterase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 22;145(1):174–177. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90669-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soska J., Lark K. G. Regulation of nucleic acid synthesis in Lactobacillus acidophilus R-26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 22;119(3):526–539. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


