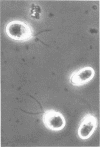
Abstract
Determinations of the salt sensitivity of enzymes extracted from the halophilic alga Dunaliella viridis revealed that pentose phosphate isomerase, ribulose diphosphate carboxylase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, and phosphohexose isomerase were inhibited by NaCl concentrations far lower than that in the growth medium (3.75 m). The inhibition was reversible and was not prevented by preparing the extracts in the presence of salt. Potassium, lithium, and cesium chlorides were equally inhibitory. In contrast, whole cells require rather high levels of NaCl for optimal growth, whereas growth is inhibited by low levels of the other cations. The results suggest a specific mechanism for the exclusion of sodium from the interior of the cell.
Full text
PDF
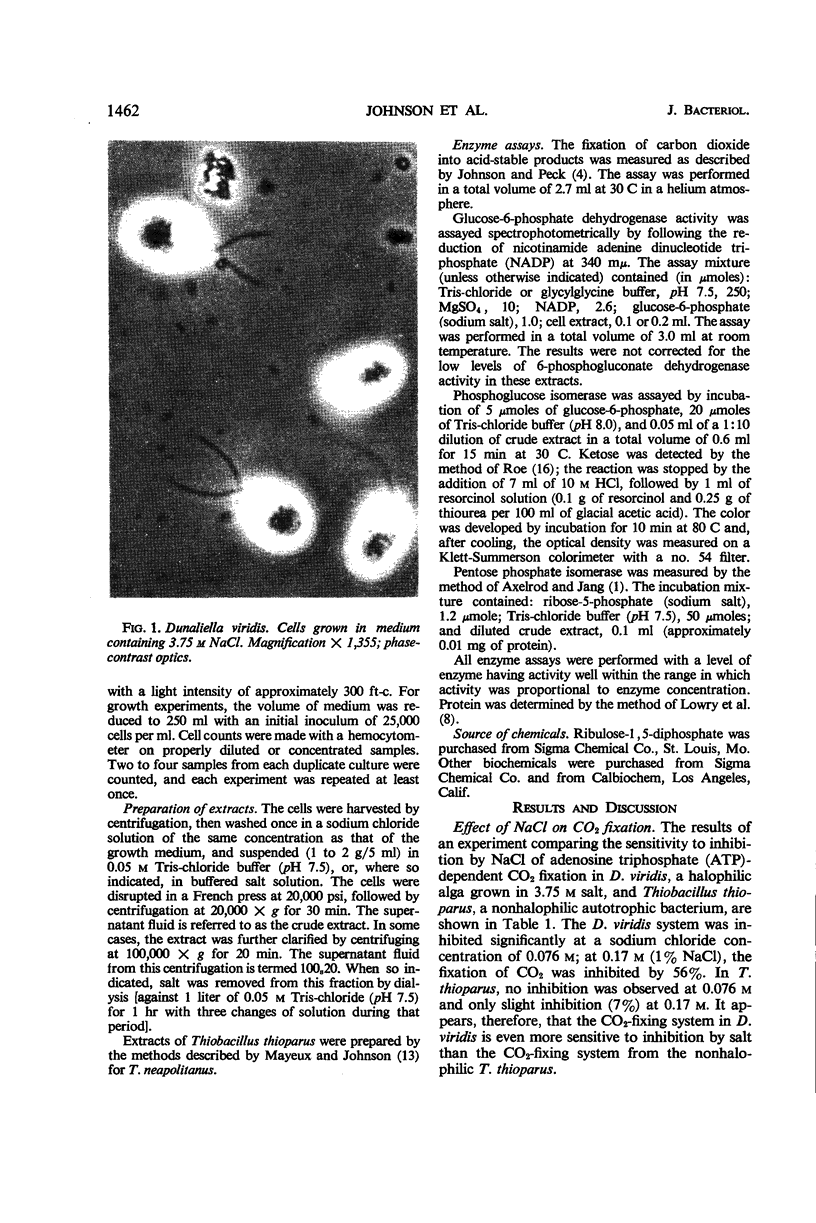
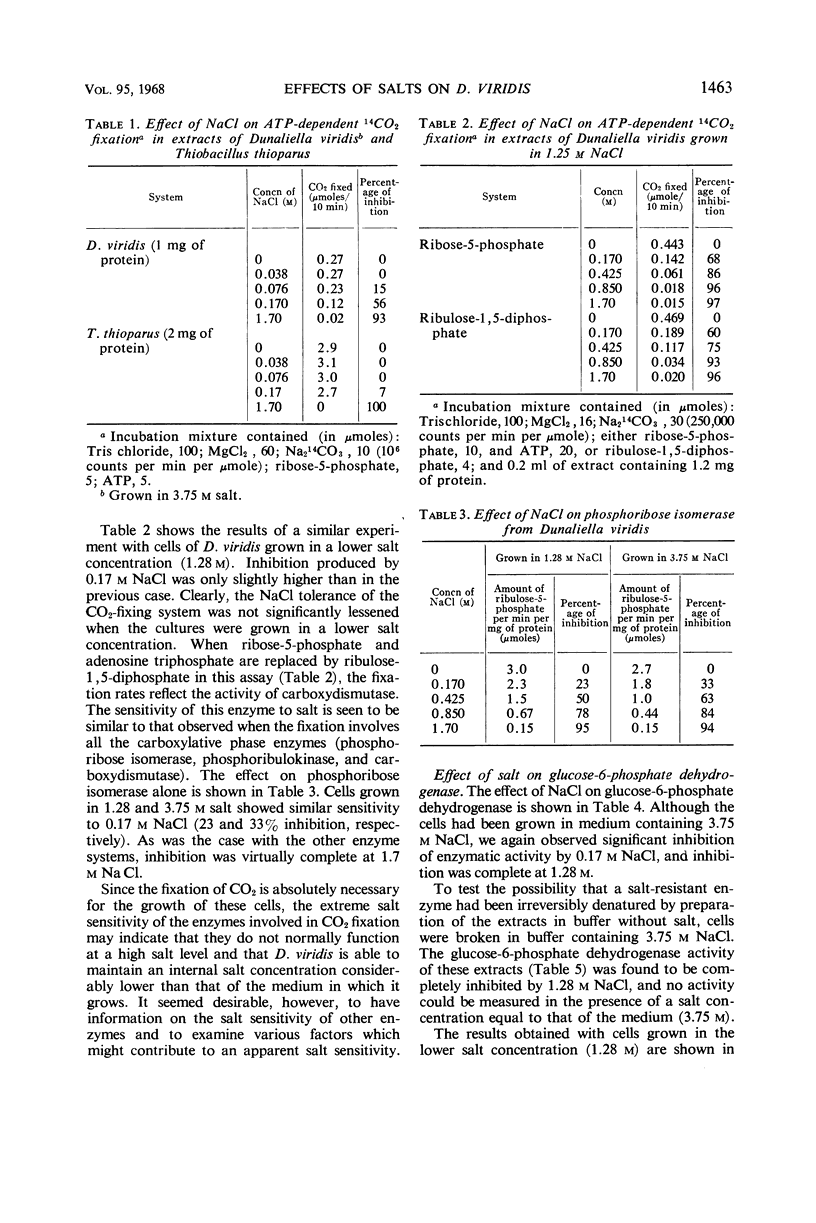
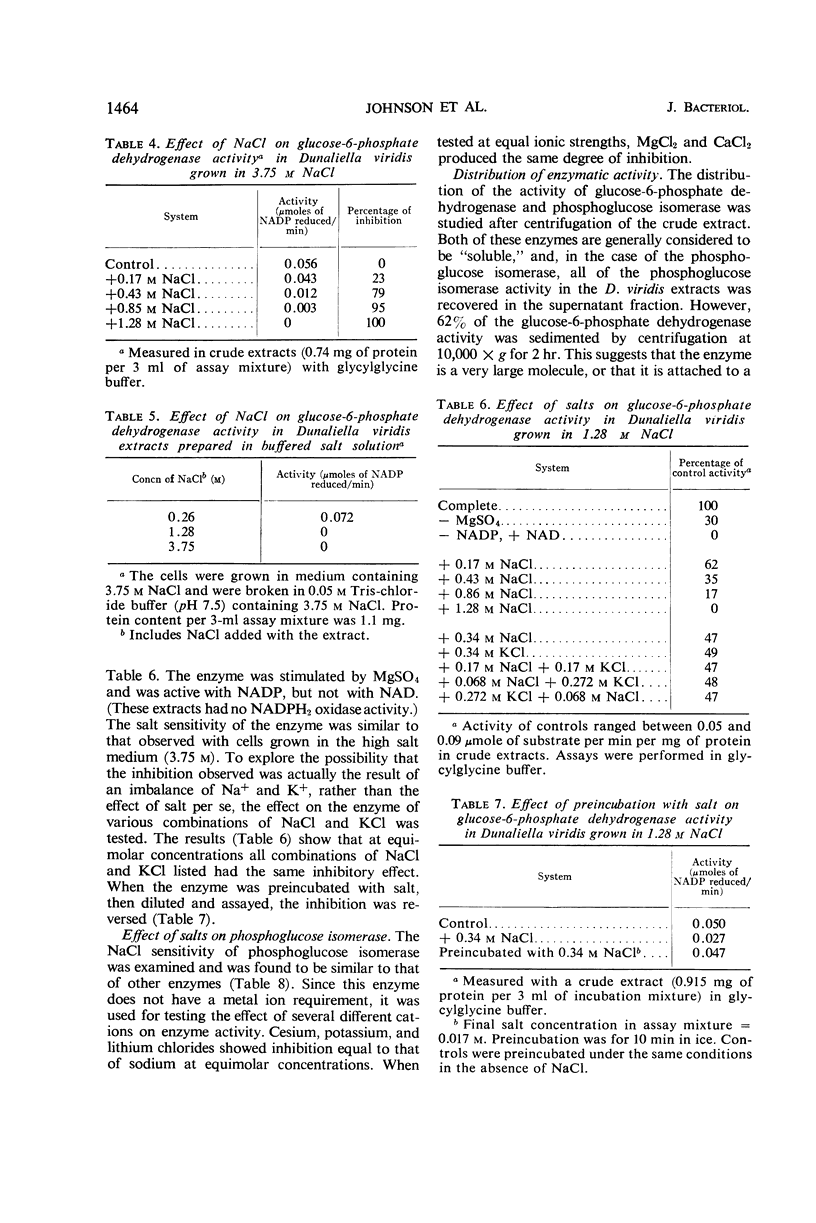



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELROD B., JANG R. Purification and properties of phosphoribo-isomerase from alfalfa. J Biol Chem. 1954 Aug;209(2):847–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEMOSS R. D., GUNSALUS I. C., BARD R. C. A glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in Leuconostoc mesenteroides. J Bacteriol. 1953 Jul;66(1):10–16. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.1.10-16.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASER L., BROWN D. H. Purification and properties of d-glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1955 Sep;216(1):67–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON E. J., PECK H. D., Jr COUPLING OF PHOSPHORYLATION AND CARBON DIOXIDE FIXATION IN EXTRACTS OF THIOBACILLUS THIOPARUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1041–1050. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1041-1050.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeux J. V., Johnson E. J. Effect of adenosine monophosphate, adenosine diphosphate, and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide on adenosine triphosphate-dependent carbon dioxide fixation in the autotroph Thiobacillus neapolitanus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):409–414. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.409-414.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD W. A., SCHWERDT R. F. Carbohydrate oxidation by Pseudomonas fluorescens. II. Mechanism of hexose phosphate oxidation. J Biol Chem. 1954 Feb;206(2):625–635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMADA K., SHIMAZONO N. Recognition and solubilization of glucose 6-phosphate and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenases in the particle fractions of brain. J Biochem. 1962 Apr;51:242–245. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaheer N., Tewari K. K., Krishnan P. S. Mitochondrial forms of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconic acid dehydrogenase in rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Apr;120(1):22–34. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90593-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]