Abstract
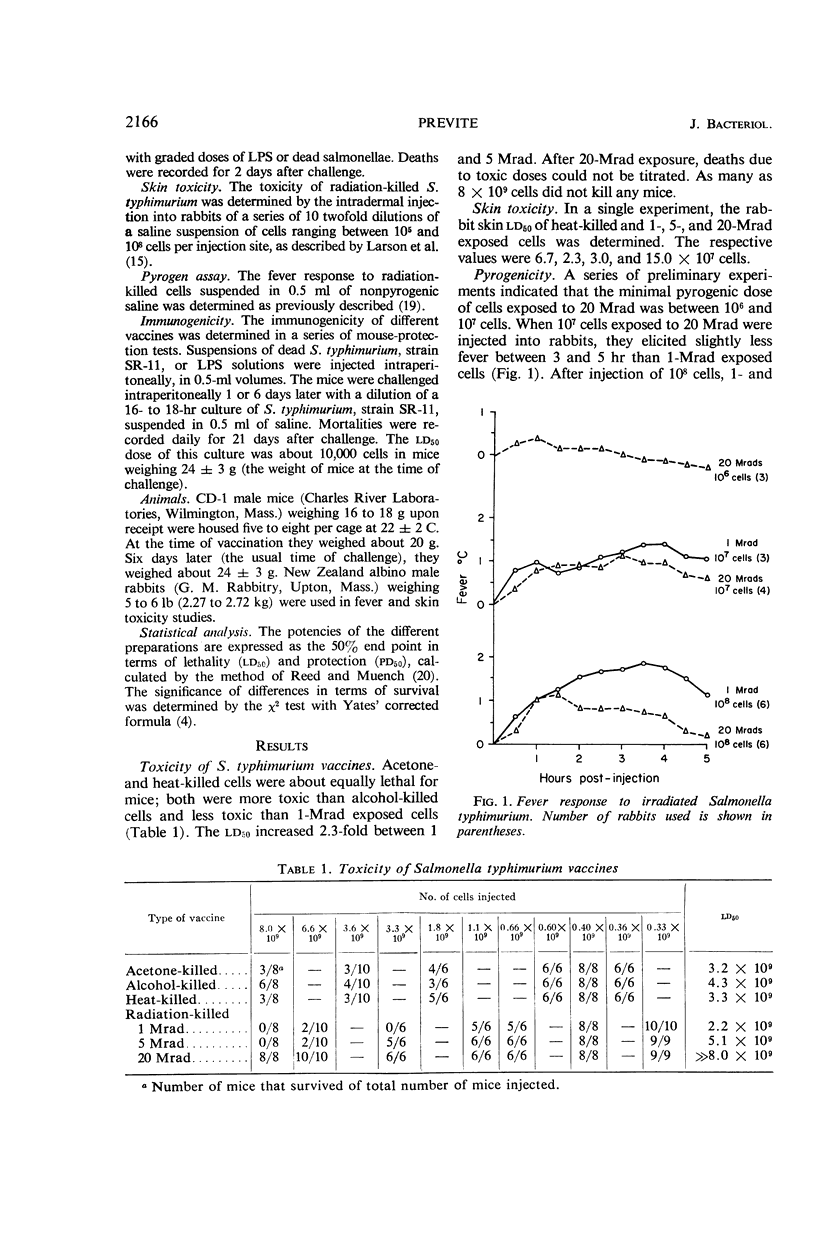
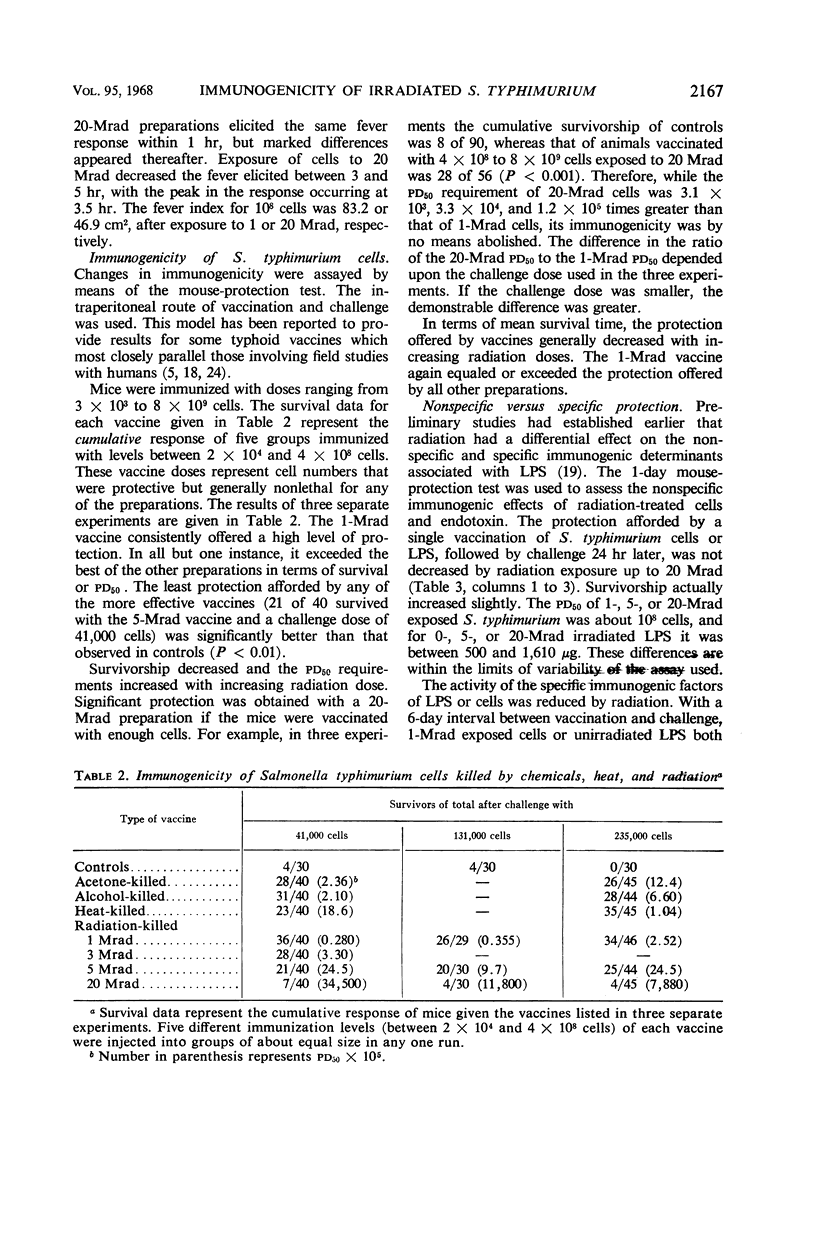
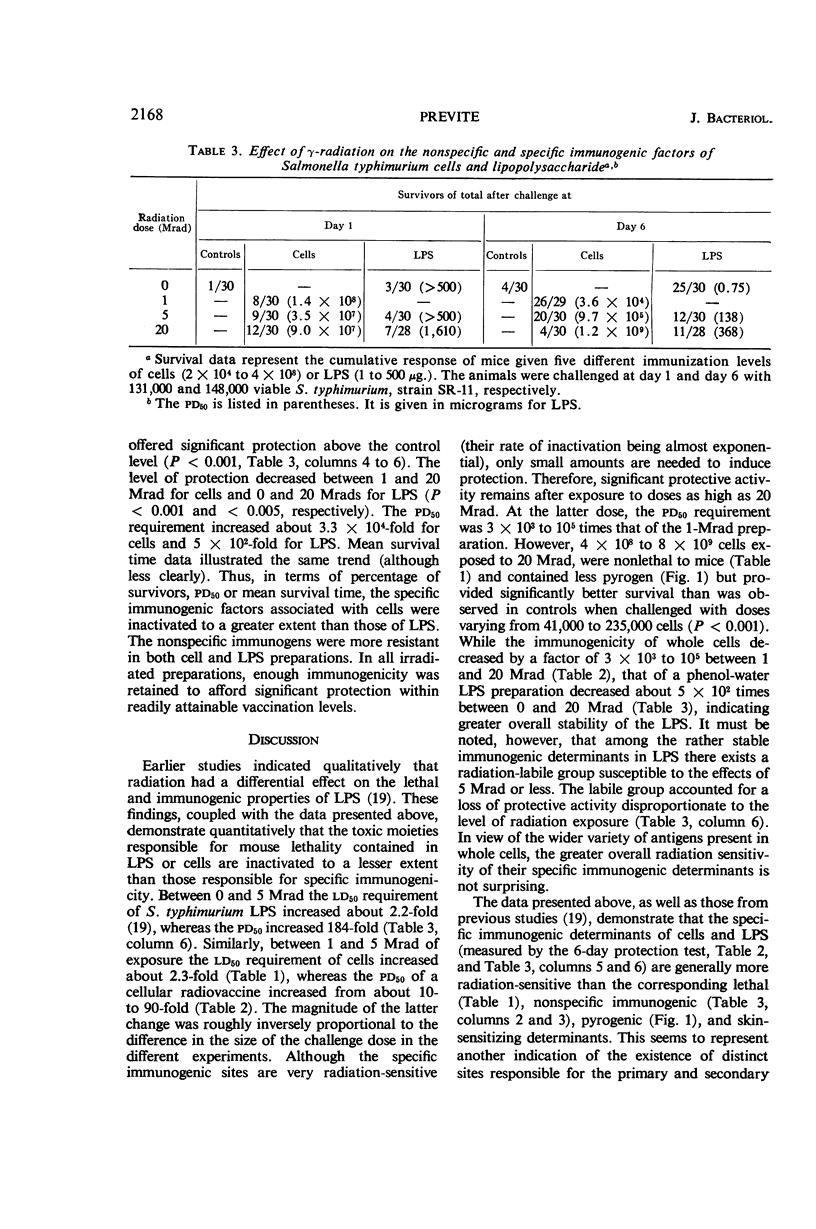
The effects of high doses of radiation (1, 5, or 20 Mrad) on the toxicity, pyrogenicity, and immunogenicity of Salmonella typhimurium cells and endotoxin were studied. Toxicity decreased progressively after exposure to 1, 5, or 20 Mrad. The lethal effect of 1-Mrad exposed cells was greater than that of heat-, acetone-, or alcohol-killed preparations. An amount of 5 Mrad is about a 50% end point in terms of inactivation of the lethal lipopolysaccharide or cell-associated determinants. The fever response to radiation-killed salmonellae decreased between 1- and 20-Mrad exposure. The immunogenicity of 1-Mrad-treated cells usually exceeded that of nonirradiated preparations in mouse-protection tests. With increasing radiation doses, there was a dramatic decrease in, but not an abolition of, immunogenicity. Preparations exposed to 20 Mrad which were nonlethal afforded significant protection. The results are interpreted as a reflection of a dissociation of the primary and secondary toxic determinants of endotoxin after irradiation. The data indicate the potential value of radiation sterilization as a means of production of Salmonella vaccine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARON L. S., FORMAL S. B. Immunization studies with living vaccine of Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Aug-Sep;104:565–567. doi: 10.3181/00379727-104-25909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Infection-immunity in experimental salmonellosis. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):601–619. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Milne M. Heat-labile antigens of Salmonella enteritidis. II. Mouse-protection studies. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):549–557. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.549-557.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDEBO L., HOLME T. PREPARATION OF BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE FRACTIONS OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. 3. EXTRACTION OF IMMUNOGENIC COMPONENTS. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;63:228–234. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.63.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON M., DONALDSON D. M., WRIGHT G. G. IMMUNIZATION OF MICE WITH IRRADIATED PASTEURELLA TULARENSIS. J Infect Dis. 1964 Dec;114:435–440. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.5.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKIN C. R., ROWLEY D. PARTIAL PURIFICATION OF THE "PROTECTIVE" ANTIGEN OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM AND ITS DISTRIBUTION AMONGST VARIOUS STRAINS OF BACTERIA. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1965 Feb;43:65–78. doi: 10.1038/icb.1965.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami M., Osawa N., Mitsuhashi S. Experimental salmonellosis. VII. Comparison of the immunizing effect of live vaccine and materials extracted from Salmonella enteritidis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;92(6):1585–1589. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.6.1585-1589.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny K., Herzberg M. Early antibody response in mice to either infection or immunization with Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):773–778. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.773-778.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. B., Watson D. W. Biologically active endotoxins from Salmonella mutants deficient in O- and R-polysaccharides and heptose. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1320–1326. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1320-1326.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurashige S., Osawa N., Kawakami M., Mitsuhashi S. Experimental salmonellosis. X. Cellular immunity and its antibody in mouse mononuclear phagocytes. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):902–906. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.902-906.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARSON C. L., RIBI E., MILNER K. C., LIEBERMAN J. E. A method for titrating endotoxic activity in the skin of rabbits. J Exp Med. 1960 Jan 1;111:1–20. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi S., Saito K., Osawa N., Kurashige S. Expermental salmonellosis. XI. Induction of cellular immunity and formation of antibody by transfer agent of mouse mononuclear phagocytes. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):907–913. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.907-913.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa N., Kawakami M., Kurashige S., Mitsuhashi S. Experimental salmonellosis. 8. Postinfective immunity and its significance for conferring cellular immunity. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1534–1540. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1534-1540.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman M., Bohner H. J. Laboratory assays of different types of field trial typhoid vaccines and relationship to efficacy in man. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1713–1723. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1713-1723.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Previte J. J., Chang Y., el-Bisi H. M. Detoxification of Salmonella typhimurium lipopolysaccharide by ionizing radiation. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1607–1614. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1607-1614.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M. Infectivity and antigenicity of streptomycin-dependent Salmonella typhosa. J Infect Dis. 1967 Feb;117(1):101–107. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEDOVA Ts. O VLIIANII IONIZIRUIUSHCHE I RADIATSII NA BRUISHNOTIFOZNYE O AND VI-ANTIGENY. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol. 1964 Jan;41:10–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiba D., Nakae T., Akiyama T., Kishimoto Y. Characterization of "clearance" factor and "cell-bound" antibody in experimental typhoid. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):1705–1712. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.1705-1712.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON D. W., KIM Y. B. MODIFICATION OF HOST RESPONSES TO BACTERIAL ENDOTOXINS. I. SPECIFICITY OF PYROGENIC TOLERANCE AND THE ROLE OF HYPERSENSITIVITY IN PYROGENICITY, LETHALITY, AND SKIN REACTIVITY. J Exp Med. 1963 Sep 1;118:425–446. doi: 10.1084/jem.118.3.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


