Abstract
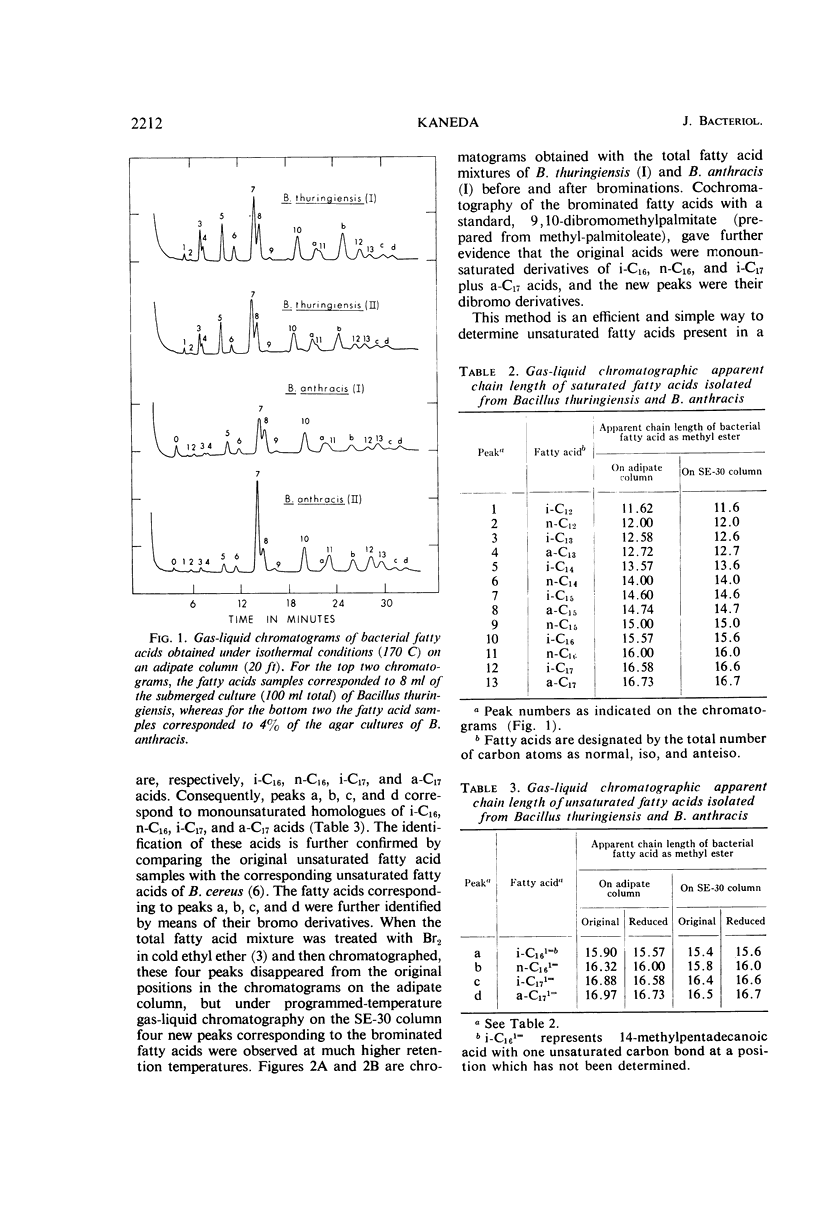
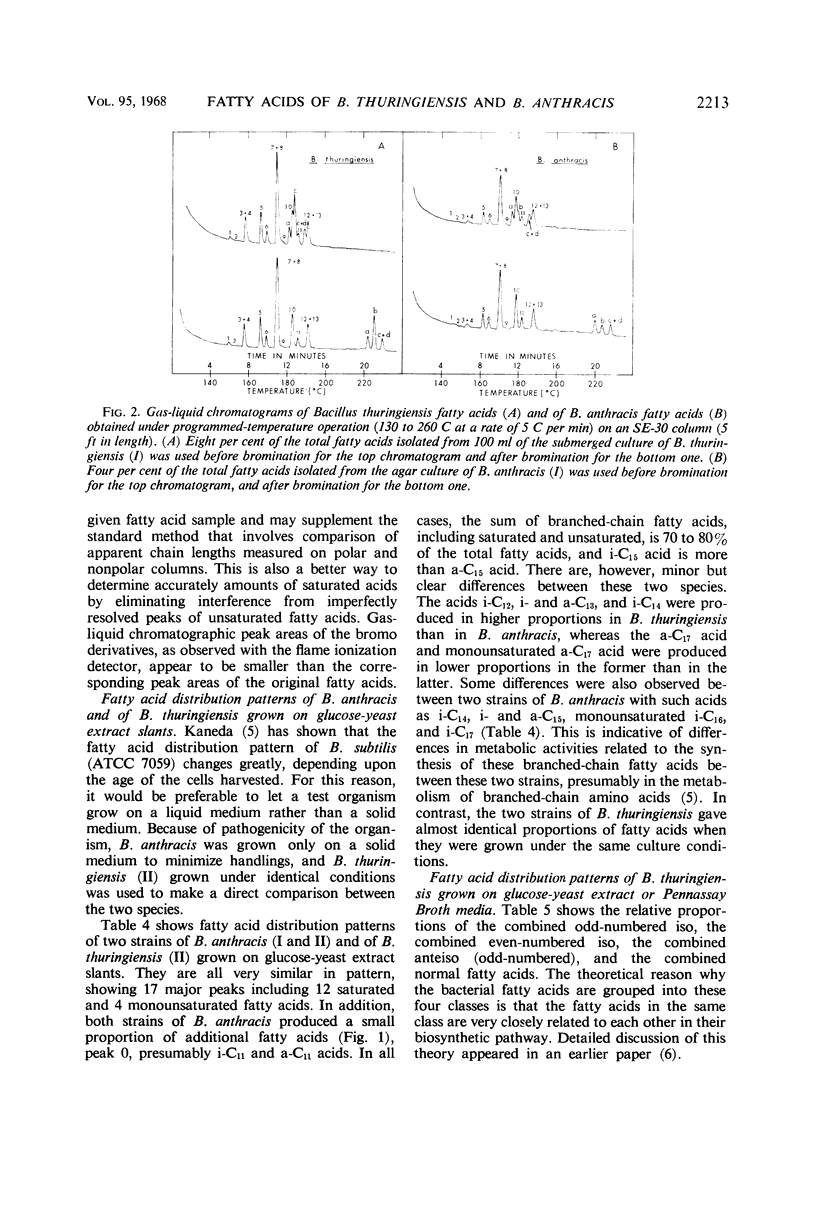
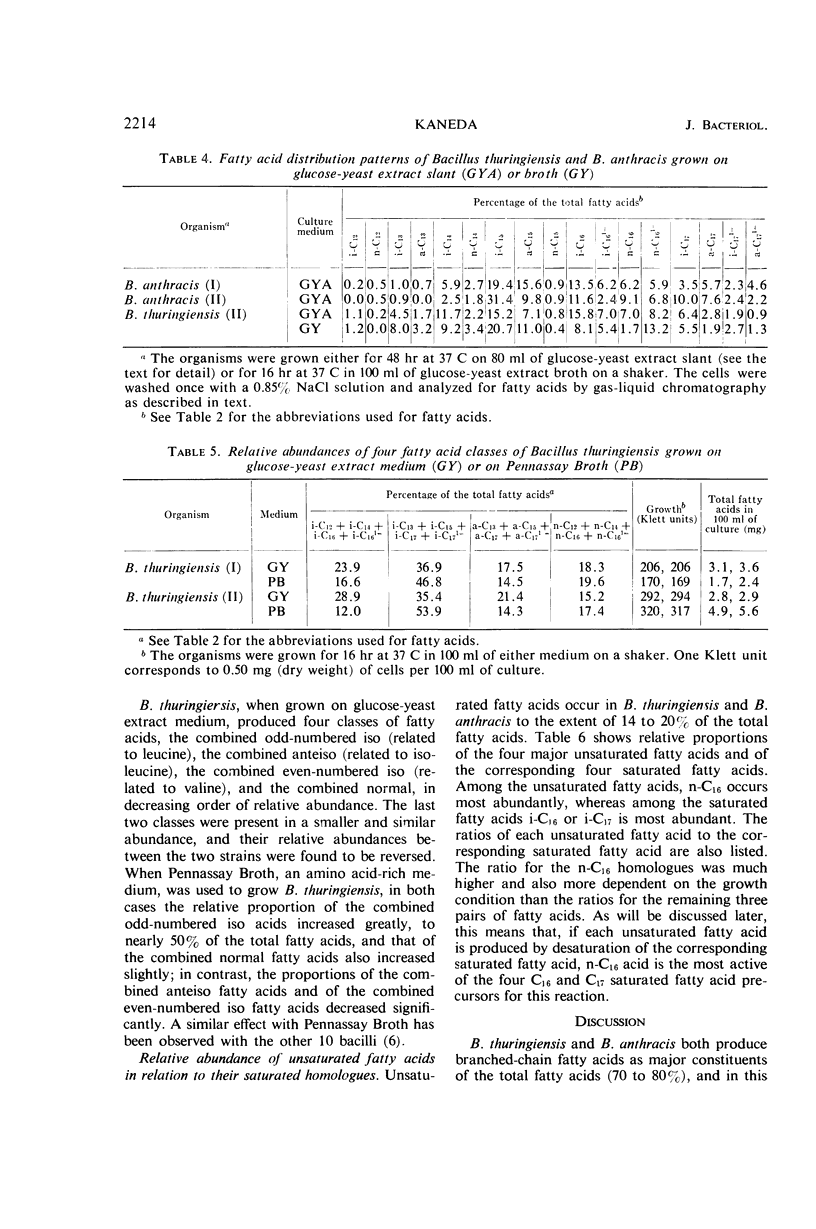
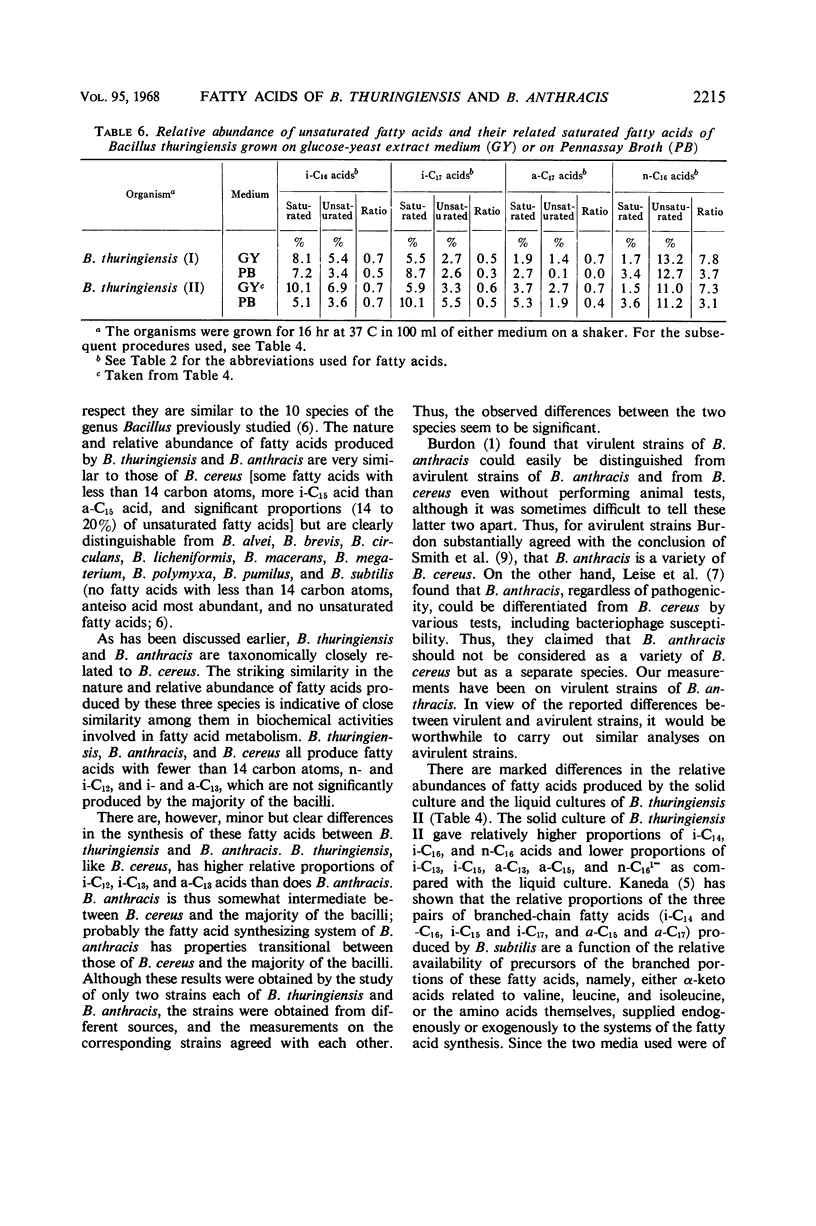
The nature and relative abundance of fatty acids produced by two strains each of Bacillus thuringiensis and of B. anthracis were studied by gas-liquid chromatography on a 12,000 theoretical plate polyester column capable of partially resolving iso- and anteiso-fatty acids with the same number of carbon atoms. Unsaturated fatty acids as the bromo derivatives were separated from the saturated acids and resolved in a short SE-30 column by use of programmed-temperature gas chromatography. All four strains produced 16 major fatty acids: 9 branched (i-C12, i-C13, i-C14, i-C15, i-C16, i-C17, a-C13, a-C15, and a-C17), 3 normal (n-C14, n-C15, and n-C16), and 4 monounsaturated (i-C161=, i-C171=, a-C171=, and n-C161=), in addition to some minor fatty acids. In all cases, 12 branched acids, including saturated and monounsaturated, made up over 70% of the total fatty acids, and iso-C15 acid was most abundant. These fatty acid distribution patterns were very similar to those of B. cereus and B. cereus var. mycoides. There were, however, minor but clear differences between the fatty acid distribution patterns of B. thuringiensis and B. anthracis. B. thuringiensis, like B. cereus, produced higher proportions of i-C13, a-C13, and i-C14 fatty acids than did B. anthracis. This difference between these two species could be useful as a supplemental criterion in their differentiation. Indications are that the enzyme systems for monounsaturated fatty acid synthesis in B. thuringiensis and B. anthracis prefer normal fatty acids as substrates rather than branched-chain fatty acids.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURDON K. L. Useful criteria for the identification of Bacillus anthracis and related species. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jan;71(1):25–42. doi: 10.1128/jb.71.1.25-42.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERWIN J., BLOCH K. BIOSYNTHESIS OF UNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS IN MICROORGANISMS. Science. 1964 Mar 6;143(3610):1006–1012. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3610.1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMES A. T. Qualitative and quantitative determination of the fatty acids by gas-liquid chromatography. Methods Biochem Anal. 1960;8:1–59. doi: 10.1002/9780470110249.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda T. Biosynthesis of branched-chain fatty acids. IV. Factors affecting relative abundance of fatty acids produced by Bacillus subtilis. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Jun;12(3):501–514. doi: 10.1139/m66-073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda T. Fatty acids in the genus Bacillus. I. Iso- and anteiso-fatty acids as characteristic constituents of lipids in 10 species. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):894–903. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.894-903.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEISE J. M., CARTER C. H., FRIEDLANDER H., FREED S. W. Criteria for the identification of Bacillus anthracis. J Bacteriol. 1959 May;77(5):655–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.5.655-660.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



