Abstract
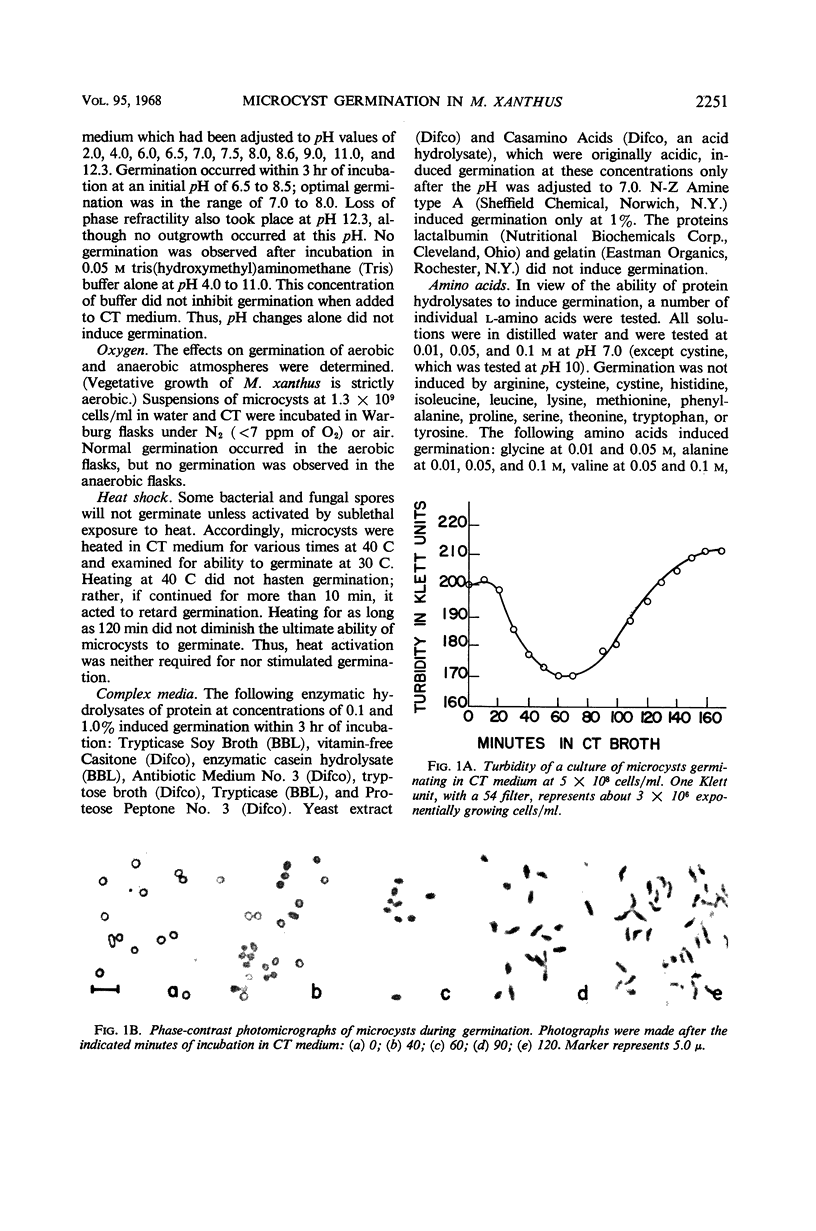
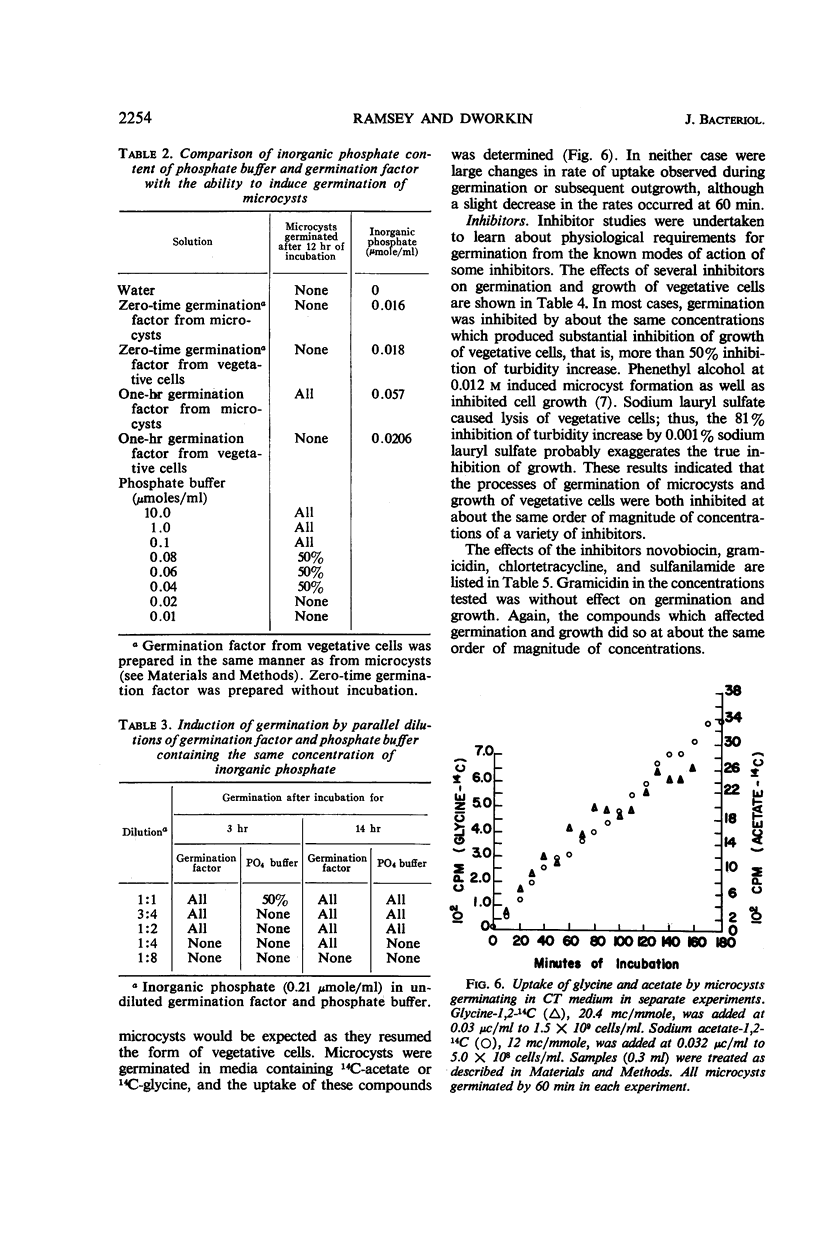
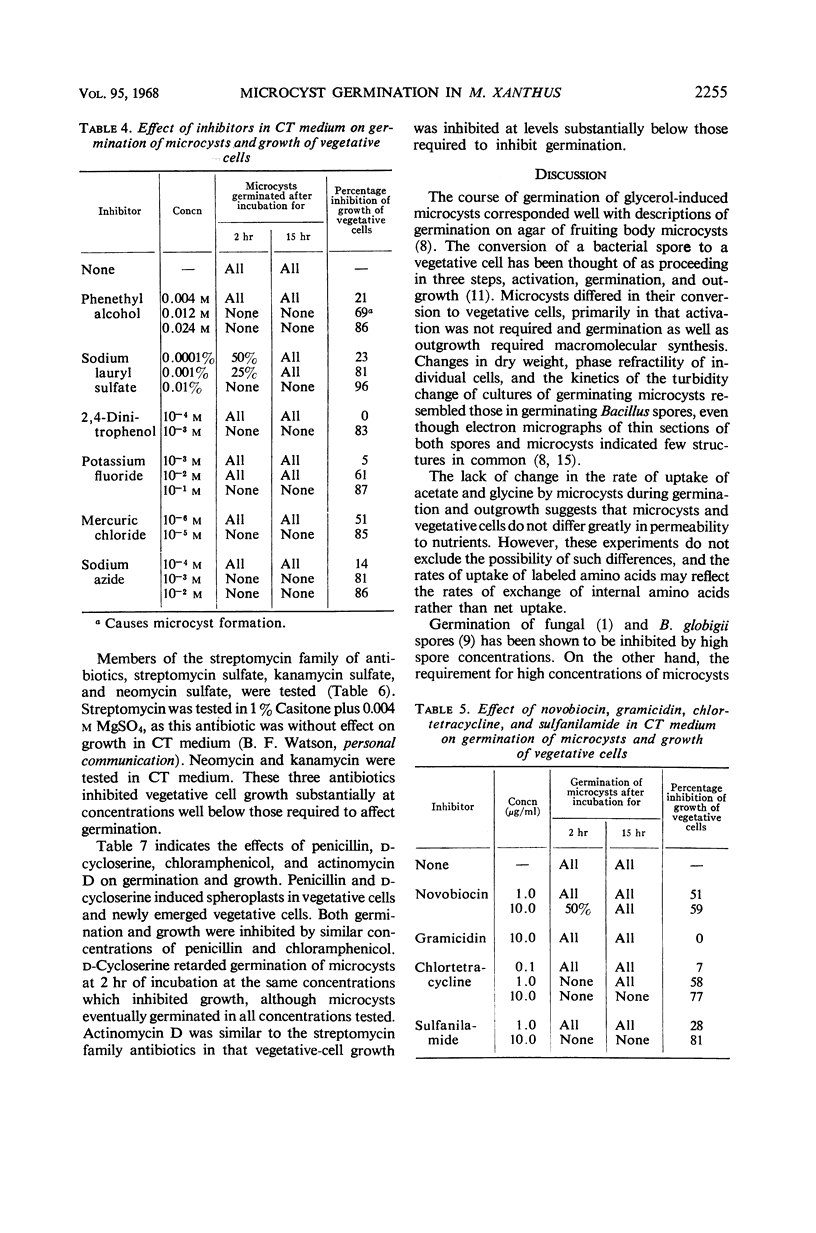
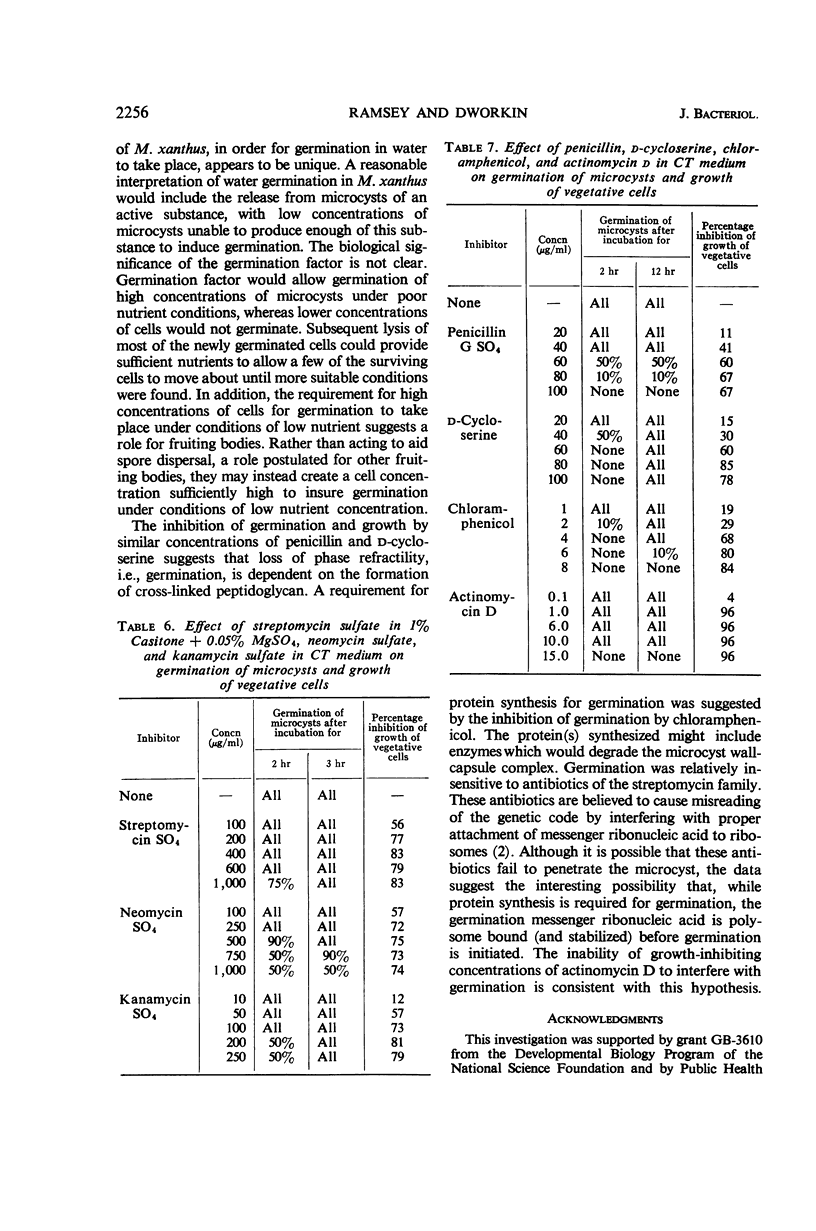
Germination of glycerol-prepared microcysts of Myxococcus xanthus was studied. The sequence of morphological events during germination resembled that of germinating fruiting body-microcysts. The turbidity drop of a culture of germinating microcysts could be described by McCormick's formula derived for germinating Bacillus spores. The rate of uptake of labeled glycine and acetate did not change during germination. Temperature, aeration, and pH optima for germination were the same as for vegetative cell growth. Germination was induced by protein hydrolysates and the individual amino acids glycine, alanine, valine, aspartic acid, and glutamic acid. A number of organic compounds, including sugars, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, organic acids, and chelating agents, did not induce germination. The inorganic ions HPO42−, Mg++, Ca++, and NH4+ induced germination, although ionic strength was not a factor. Microcysts incubated in distilled water at concentrations greater than about 109 cells/ml germinated; supernatant fluid from such suspensions (germination factor) induced germination of less concentrated suspensions. The activity of germination factor was resistant to boiling, but was lost on charring and dialysis. Germination of microcysts and growth of vegetative cells was equally sensitive to a variety of metabolic inhibitors, including penicillin and chloramphenicol. Germination was more resistant than vegetative growth to inhibition by antibiotics of the streptomycin family and by actinomycin D.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DAVIES J., GILBERT W., GORINI L. STREPTOMYCIN, SUPPRESSION, AND THE CODE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 May;51:883–890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.5.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M., GIBSON S. M. A SYSTEM FOR STUDYING MICROBIAL MORPHOGENESIS: RAPID FORMATION OF MICROCYSTS IN MYXOCOCCUS XANTHUS. Science. 1964 Oct 9;146(3641):243–244. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3641.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M., NIEDERPRUEM D. J. ELECTRON TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN VEGETATIVE CELLS AND MICROCYSTS OF MYXOCOCCUS XANTHUS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:316–322. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.316-322.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M. NUTRITIONAL REGU.ATION OF MORPHOGENESIS IN MYXOCOCCUS XANTHUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:67–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.67-72.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M. Nutritional requirements for vegetative growth of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:250–257. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.250-257.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M., VOELZ H. The formation and germination of microcysts in Myxococcus xanthus. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Apr;28:81–85. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-1-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M., Sadler W. Induction of cellular morphogenesis in Myxococcus xanthus. I. General description. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1516–1519. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1516-1519.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEY G., GOULD G. W., HITCHINS A. D. IDENTIFICATION OF D-ALANINE AS THE AUTO-INHIBITOR OF GERMINATION OF BACILLUS GLOBIGII SPORES. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 May;35:229–236. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-2-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt M. C., Wyss O. Chelation effects on Azotobacter cells and cysts. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):120–124. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.120-124.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCORMICK N. G. KINETICS OF SPORE GERMINATION. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1180–1185. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1180-1185.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker L. T., Socolofsky M. D. Central body of the Azotobacter cyst. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):297–303. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.297-303.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner J. B. A METHOD FOR THE COLORIMETRIC DETERMINATION OF PHOSPHORUS. Science. 1944 Nov 3;100(2601):413–414. doi: 10.1126/science.100.2601.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VARY J. C., HALVORSON H. O. KINETICS OF GERMINATION OF BACILLUS SPORES. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1340–1347. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1340-1347.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOELZ H., DWORKIN M. Fine structure of Myxococcus xanthus during morphogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1962 Nov;84:943–952. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.5.943-952.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelz H. The fate of the cell envelopes of Myxococcus xanthus during microcyst germination. Arch Mikrobiol. 1966 Nov 11;55(2):110–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00418633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




