Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, C26H16F6O2, contains one half of the molecule situated on an inversion centre. In the rod-like molecule, the two terminal benzene rings form a dihedral angle of 71.9 (1)° with the central benzene ring. The trifluoromethyl group is rotationally disordered over two orientations in a 0.53 (1):0.47 (1) ratio. The crystal packing exhibits no classical intermolecular interactions.
Related literature
For applications and details of the synthesis of (arylene)ethynylene derivatives, see: Dirk et al. (2001 ▶); Miljanić et al. (2005 ▶); Morin et al. (2007 ▶). For the crystal structure of a related 1,4-bis(p-tolylethynyl)benzene, see: Filatov & Petrukhina (2005 ▶).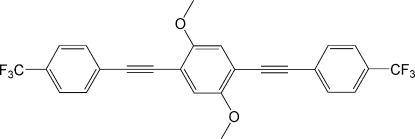
Experimental
Crystal data
C26H16F6O2
M r = 474.39
Monoclinic,

a = 11.1473 (4) Å
b = 13.0795 (6) Å
c = 7.5875 (4) Å
β = 97.467 (3)°
V = 1096.88 (9) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.13 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.22 × 0.20 × 0.19 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.973, T max = 0.977
9899 measured reflections
2484 independent reflections
1753 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.022
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.117
S = 1.04
2484 reflections
184 parameters
30 restraints
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: XP in SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681102099X/cv5093sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681102099X/cv5093Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681102099X/cv5093Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for financial support from the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (grant No. Q2008B02) and the Science Foundation of the Ministry of Education of China (grant No. 200804221009).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Recently, the synthesis and applications of new aryleneethynylene derivatives were reported (Dirk et al., 2001; Miljanić et al., 2005; Morin et al., 2007). To make our own contribution in this field of material science, herewith we report the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound, (I), which can be used as luminescent material.
In (I) (Fig. 1), all bond lengths and angles are normal and correspond to those reported for 1,4-bis(p-tolylethynyl)benzene (Filatov & Petrukhina, 2005). The asymmetric unit of (I) contains a half of the rod-like molecule. The centroid of the central benzene ring is situated on an inversion centre. The central benzene ring and C2–C7 ring form a dihedral angle of 71.9 (1)°. The crystal packing exhibits no classical intermolecular interactions.
Experimental
1,4-Dimethoxy-2,5-diethynylbenzene (93 mg, 0.5 mmol), Pd(PPh3)2Cl2 (17.5 mg)and CuI (9.5 mg) were added to triethylamine (3 ml) and tetrahydrofuran (9 ml)in a Schlenk flask under N2 atmosphere. The mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. Then the solution was cooled to room temperature and the solvent was removed in vacuum. CH2Cl2 (15 ml) was added and the suspension was filtered. The filtrate was washed with HCl (1 mol l-1), ammonium chloride solution and water. Then organic phase was dried with MgSO4 and concentrated. The crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica gel to afford the title compound (185.3 mg, 78%). Crystals suitable for X-ray structure analysis were obtained by slowly evaporating dichloromethane solution of the title compound at room temperature.
Refinement
All the H atoms were treated as riding atoms in geometrically idealized positions (C—H 0.93–0.96 Å), with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5Ueq(C). Trifluoromethyl fragment was treated as rotationally disordered over two orientations with the refined occupancies of 0.53 (1):0.47 (1), respectively.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) showing the atom-numbering scheme and 50% probabilty displacement ellipsoids. Unlabelled atoms are related with the labelled ones by symmetry operation (-x, 2 - y, 2 - z). For the disordered F atoms, only major parts are shown.
Crystal data
| C26H16F6O2 | F(000) = 484 |
| Mr = 474.39 | Dx = 1.436 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 11.1473 (4) Å | θ = 2.4–27.4° |
| b = 13.0795 (6) Å | µ = 0.13 mm−1 |
| c = 7.5875 (4) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 97.467 (3)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1096.88 (9) Å3 | 0.22 × 0.20 × 0.19 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2484 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1753 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.022 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 27.4°, θmin = 2.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007) | h = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.973, Tmax = 0.977 | k = −15→16 |
| 9899 measured reflections | l = −9→9 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.117 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0488P)2 + 0.235P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2484 reflections | Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3 |
| 184 parameters | Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3 |
| 30 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.011 (3) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R-factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| C1 | 0.75647 (18) | 0.83209 (17) | 0.5592 (3) | 0.0718 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.63855 (14) | 0.85402 (14) | 0.6275 (2) | 0.0527 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.54917 (16) | 0.78099 (15) | 0.6153 (3) | 0.0588 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.5617 | 0.7178 | 0.5647 | 0.071* | |
| C4 | 0.44076 (15) | 0.80134 (14) | 0.6781 (2) | 0.0562 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.3805 | 0.7518 | 0.6697 | 0.067* | |
| C5 | 0.42165 (13) | 0.89548 (14) | 0.7537 (2) | 0.0473 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.51220 (16) | 0.96868 (14) | 0.7635 (3) | 0.0589 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.4999 | 1.0322 | 0.8131 | 0.071* | |
| C7 | 0.62038 (16) | 0.94824 (15) | 0.7003 (3) | 0.0608 (5) | |
| H7 | 0.6806 | 0.9978 | 0.7069 | 0.073* | |
| C8 | 0.31058 (14) | 0.91755 (14) | 0.8243 (2) | 0.0525 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.22045 (14) | 0.93931 (13) | 0.8846 (2) | 0.0497 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.10877 (13) | 0.96910 (12) | 0.9454 (2) | 0.0452 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.03456 (14) | 1.03921 (12) | 0.8455 (2) | 0.0477 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.0584 | 1.0656 | 0.7417 | 0.057* | |
| C12 | 0.07381 (13) | 0.92971 (12) | 1.1021 (2) | 0.0455 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.1199 (2) | 0.82346 (18) | 1.3576 (3) | 0.0769 (6) | |
| H13A | 0.1109 | 0.8791 | 1.4372 | 0.115* | |
| H13B | 0.1823 | 0.7782 | 1.4105 | 0.115* | |
| H13C | 0.0449 | 0.7867 | 1.3348 | 0.115* | |
| O1 | 0.15207 (10) | 0.86246 (10) | 1.19450 (17) | 0.0605 (4) | |
| F1 | 0.7461 (6) | 0.8553 (4) | 0.3877 (5) | 0.0928 (16) | 0.530 (10) |
| F2 | 0.8484 (5) | 0.8832 (9) | 0.6296 (14) | 0.183 (5) | 0.530 (10) |
| F3 | 0.7807 (6) | 0.7351 (3) | 0.5523 (9) | 0.125 (3) | 0.530 (10) |
| F1' | 0.7695 (6) | 0.7396 (4) | 0.5079 (11) | 0.136 (4) | 0.470 (10) |
| F2' | 0.8458 (4) | 0.8398 (6) | 0.6905 (7) | 0.0953 (18) | 0.470 (10) |
| F3' | 0.7830 (9) | 0.8979 (10) | 0.4453 (17) | 0.205 (6) | 0.470 (10) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0550 (12) | 0.0973 (17) | 0.0678 (14) | 0.0107 (11) | 0.0252 (10) | −0.0029 (13) |
| C2 | 0.0413 (8) | 0.0727 (12) | 0.0462 (9) | 0.0070 (8) | 0.0135 (7) | −0.0022 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0545 (10) | 0.0638 (12) | 0.0603 (11) | 0.0052 (8) | 0.0152 (8) | −0.0127 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0465 (9) | 0.0623 (11) | 0.0613 (11) | −0.0033 (8) | 0.0128 (8) | −0.0070 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0374 (8) | 0.0606 (10) | 0.0454 (9) | 0.0062 (7) | 0.0118 (7) | 0.0025 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0543 (10) | 0.0562 (11) | 0.0703 (12) | 0.0008 (8) | 0.0239 (9) | −0.0095 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0468 (9) | 0.0697 (12) | 0.0696 (12) | −0.0083 (8) | 0.0213 (9) | −0.0073 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0438 (9) | 0.0616 (11) | 0.0542 (10) | 0.0045 (8) | 0.0146 (7) | 0.0039 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0409 (8) | 0.0552 (10) | 0.0552 (10) | 0.0014 (7) | 0.0142 (7) | 0.0028 (8) |
| C10 | 0.0354 (7) | 0.0494 (9) | 0.0531 (9) | −0.0011 (7) | 0.0144 (7) | −0.0027 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0422 (8) | 0.0532 (10) | 0.0503 (9) | −0.0016 (7) | 0.0162 (7) | 0.0039 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0379 (8) | 0.0464 (9) | 0.0532 (10) | 0.0014 (6) | 0.0099 (7) | 0.0029 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0759 (13) | 0.0846 (15) | 0.0732 (14) | 0.0208 (11) | 0.0207 (11) | 0.0317 (12) |
| O1 | 0.0510 (7) | 0.0679 (8) | 0.0653 (8) | 0.0144 (6) | 0.0170 (6) | 0.0167 (6) |
| F1 | 0.089 (3) | 0.120 (3) | 0.081 (2) | 0.005 (2) | 0.0551 (18) | 0.006 (2) |
| F2 | 0.056 (3) | 0.278 (10) | 0.228 (8) | −0.065 (5) | 0.068 (4) | −0.175 (8) |
| F3 | 0.119 (4) | 0.109 (4) | 0.168 (5) | 0.074 (3) | 0.095 (4) | 0.067 (4) |
| F1' | 0.071 (3) | 0.180 (8) | 0.163 (5) | 0.005 (3) | 0.031 (3) | −0.118 (6) |
| F2' | 0.0321 (19) | 0.142 (4) | 0.115 (3) | 0.0013 (19) | 0.0200 (17) | 0.000 (3) |
| F3' | 0.142 (8) | 0.247 (10) | 0.260 (10) | 0.105 (7) | 0.157 (8) | 0.190 (9) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—F2 | 1.281 (4) | C6—C7 | 1.380 (2) |
| C1—F3' | 1.281 (4) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| C1—F1' | 1.285 (4) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| C1—F3 | 1.300 (4) | C8—C9 | 1.191 (2) |
| C1—F2' | 1.318 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.437 (2) |
| C1—F1 | 1.327 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.391 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.502 (2) | C10—C12 | 1.397 (2) |
| C2—C3 | 1.375 (3) | C11—C12i | 1.381 (2) |
| C2—C7 | 1.376 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.381 (2) | C12—O1 | 1.3664 (19) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C12—C11i | 1.381 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.386 (2) | C13—O1 | 1.427 (2) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.386 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C5—C8 | 1.441 (2) | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| F2—C1—F3' | 71.9 (5) | C5—C4—H4 | 119.9 |
| F2—C1—F1' | 120.1 (5) | C6—C5—C4 | 119.06 (14) |
| F3'—C1—F1' | 112.5 (6) | C6—C5—C8 | 119.78 (16) |
| F2—C1—F3 | 111.5 (5) | C4—C5—C8 | 121.15 (16) |
| F3'—C1—F3 | 124.1 (6) | C7—C6—C5 | 120.70 (17) |
| F1'—C1—F3 | 15.5 (5) | C7—C6—H6 | 119.6 |
| F2—C1—F2' | 32.8 (6) | C5—C6—H6 | 119.6 |
| F3'—C1—F2' | 103.9 (7) | C2—C7—C6 | 119.57 (17) |
| F1'—C1—F2' | 101.3 (4) | C2—C7—H7 | 120.2 |
| F3—C1—F2' | 87.9 (5) | C6—C7—H7 | 120.2 |
| F2—C1—F1 | 104.7 (6) | C9—C8—C5 | 177.5 (2) |
| F3'—C1—F1 | 35.2 (8) | C8—C9—C10 | 175.89 (19) |
| F1'—C1—F1 | 85.2 (4) | C11—C10—C12 | 119.64 (13) |
| F3—C1—F1 | 100.1 (4) | C11—C10—C9 | 118.86 (14) |
| F2'—C1—F1 | 133.2 (3) | C12—C10—C9 | 121.50 (15) |
| F2—C1—C2 | 116.4 (3) | C12i—C11—C10 | 121.18 (15) |
| F3'—C1—C2 | 113.2 (3) | C12i—C11—H11 | 119.4 |
| F1'—C1—C2 | 115.0 (4) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.4 |
| F3—C1—C2 | 113.4 (3) | O1—C12—C11i | 124.45 (15) |
| F2'—C1—C2 | 109.5 (3) | O1—C12—C10 | 116.37 (13) |
| F1—C1—C2 | 109.1 (3) | C11i—C12—C10 | 119.18 (15) |
| C3—C2—C7 | 120.41 (15) | O1—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.20 (17) | O1—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C7—C2—C1 | 119.38 (17) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.11 (17) | O1—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.14 (17) | C12—O1—C13 | 117.37 (13) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.9 | ||
| F2—C1—C2—C3 | −154.8 (8) | C8—C5—C6—C7 | 178.50 (18) |
| F3'—C1—C2—C3 | 124.7 (9) | C3—C2—C7—C6 | 0.9 (3) |
| F1'—C1—C2—C3 | −6.6 (5) | C1—C2—C7—C6 | −179.94 (18) |
| F3—C1—C2—C3 | −23.5 (4) | C5—C6—C7—C2 | −0.3 (3) |
| F2'—C1—C2—C3 | −119.9 (4) | C6—C5—C8—C9 | −1(5) |
| F1—C1—C2—C3 | 87.1 (3) | C4—C5—C8—C9 | 178 (100) |
| F2—C1—C2—C7 | 26.0 (8) | C5—C8—C9—C10 | 85 (5) |
| F3'—C1—C2—C7 | −54.5 (10) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −11 (3) |
| F1'—C1—C2—C7 | 174.2 (5) | C8—C9—C10—C12 | 169 (3) |
| F3—C1—C2—C7 | 157.3 (4) | C12—C10—C11—C12i | −0.4 (3) |
| F2'—C1—C2—C7 | 60.9 (4) | C9—C10—C11—C12i | 179.90 (16) |
| F1—C1—C2—C7 | −92.1 (3) | C11—C10—C12—O1 | −179.04 (15) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −0.8 (3) | C9—C10—C12—O1 | 0.6 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.95 (18) | C11—C10—C12—C11i | 0.4 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.0 (3) | C9—C10—C12—C11i | −179.92 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.6 (3) | C11i—C12—O1—C13 | −1.1 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C8 | −178.37 (17) | C10—C12—O1—C13 | 178.26 (17) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.5 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+2, −z+2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CV5093).
References
- Bruker (2007). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Dirk, S. M., Price, D. W., Chanteau, S., Kosynkin, D. V. & Tour, J. M. (2001). Tetrahedron, 57, 5109–5121.
- Filatov, A. S. & Petrukhina, M. A. (2005). Acta Cryst. C61, o193–o194. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Miljanić, O. Š., Holmes, D. & Vollhardt, K. P. C. (2005). Org. Lett. 7, 4001–4004. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Morin, J. F., Sasaki, T., Shirai, Y., Guerrero, J. M. & Tour, J. M. (2007). J. Org. Chem. 72, 9481–9490. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681102099X/cv5093sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681102099X/cv5093Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S160053681102099X/cv5093Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



