Abstract
The title compound, C15H15NO, which was synthesized under solvent-free conditions by the reaction of acetoacetone and 2-naphthylamine, adopts a Z conformation about the C=C bond. The enamine–ketone fragment is approximately planar [maximum deviation = 0.026 (3) Å] and forms a dihedral angle of 39.78 (3)° with the naphthalene ring system. An intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond is observed.
Related literature
For our studies on the synthesis of β-enaminones and β-enamino esters, see: Harrad et al. (2010 ▶, 2011 ▶). For related structures, see: Shaheen et al. (2006 ▶); Arıcı et al. (1999 ▶).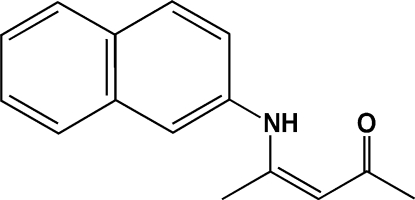
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H15NO
M r = 225.28
Orthorhombic,

a = 11.2417 (18) Å
b = 8.2532 (10) Å
c = 26.570 (4) Å
V = 2465.2 (6) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.08 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.48 × 0.34 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS, Bruker, 2008 ▶) T min = 0.660, T max = 0.746
9535 measured reflections
2221 independent reflections
1179 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.057
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.050
wR(F 2) = 0.142
S = 0.94
2221 reflections
159 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2008 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and SCHAKAL97 (Keller, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PARST95 (Nardelli, 1995 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811024494/ng5187sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811024494/ng5187Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811024494/ng5187Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1N⋯O1 | 0.92 (2) | 1.85 (2) | 2.657 (2) | 144 (2) |
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Universitá degli Studi di Parma is gratefully acknowledged.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
β-Enaminones and β-enaminoesters are useful precursors for the preparation of biologically active compounds such as β-enamino acids and γ-enamino alcohols, and many synthetic methods have been developed for the preparation of these compounds. As a continuation of our work on the synthesis and characterization of new β-enamino compounds (Harrad et al., 2010, 2011), we describe herein the crystal structure of title compound.
The title compound (Fig. 1) crystallizes in the keto-enamine form, as indicated by values of the C14═O1 and C13–C14 bond length of 1.252 (3) and 1.410 (3) Å, respectively. The bond lengths observed within the C13–C12–N1 chain (C12–C13 = 1.375 (3) Å; N1–C12 = 1.353 (3) Å) suggest some degree of electron delocalization of the imino and alkene double bonds. The molecule assumes a Z conformation about the C12═C13 bond. An S(6) ring motif is formed due to an intramolecular N—H···O hydrogen bond (Table 1). The enamino-ketone fragment (N1/C12/c13/C14/O1) is approximately planar (maximum deviation 0.026 (3) Å for atom C14) and is twisted by 39.78 (3)° with respect to the naphthalene ring. This value is comparable with those of 32.06 (9) and 44.71 (7)° found in (Z)-4-anilinopent-3-en-2-one (Shaheen et al., 2006) and 4-chloro-2-(4-oxopent-2-en-2-ylamino)phenol (Arıcı et al., 1999), respectively. The crystal packing (Fig. 2) is governed only by van der Waals interactions. No C—H···π or π···π interactions are observed.
Experimental
A mixture of acetoacetone (5 mmol), 2-naphthylamine (5 mmol) and Ca(CF3CO2)2 (0.05 mmol) was stirred at room temperature for 1 h under solvent-free conditions. After completion of the reaction, the mixture was diluted with H2O (10 ml), extracted with EtOAc (2 × 10 ml) and dried over Na2SO4. The title compound was isolated as a white powder by column chromatography on silica gel using ethyl acetate/n-hexane (1:1 v/v) as eluent (yield 62%; m. p.= 395 K). Colourless single crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow evaporation at room temperature of an n-hexane solution. 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz) δ: 1.9 (s; 3H), 2.2 (s, 3H), 3.1 (s, 1H); 7.2–7.7 (m, 7H, Ar), 12.6 (bs, 1H, HN); 13C NMR (CDCl3, 75 MHz) δ: 19.96, 30.53, 97.04, 127.95, 130.10, 132.50, 135.14, 126.61, 125.23; 124.63, 122.81; 120.58; 159.25, 195.23. EIMS (m/z) 226.1 (M+). HRMS calcd for C15H15NO: 225.1154; found 225.1163.
Refinement
The amine H atom was located in a difference Fourier map and refined freely. All other H atoms were fixed geometrically and treated as riding, with C–H = 0.93–0.96 Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C) or 1.5 Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms. A rotating group model was used for the methyl groups. Four low-angle reflections [2 0 0 (θ = 3.62°), 1 1 1 (θ = 3.16°), 1 0 2 (θ = 2.37°) and 1 1 2 (θ = 3.42°)] were omitted from the final cycles of refinement because their observed intensities were much lower than the calculated values as a result of being affected by the beam stop.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. The intramolecular hydrogen bond is shown as a dashed line.
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of the title compound approximately viewed along the a axis.
Crystal data
| C15H15NO | F(000) = 960 |
| Mr = 225.28 | Dx = 1.214 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 1094 reflections |
| a = 11.2417 (18) Å | θ = 3.1–19.4° |
| b = 8.2532 (10) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| c = 26.570 (4) Å | T = 296 K |
| V = 2465.2 (6) Å3 | Plate, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.48 × 0.34 × 0.12 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2221 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1179 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.057 |
| ω and φ scans | θmax = 25.3°, θmin = 1.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS, Bruker, 2008) | h = −13→8 |
| Tmin = 0.660, Tmax = 0.746 | k = −9→9 |
| 9535 measured reflections | l = −31→31 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.050 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.142 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0749P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 0.94 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2221 reflections | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 159 parameters | Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.011 (2) |
Special details
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.37331 (17) | 0.7158 (2) | 0.48799 (6) | 0.0702 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.3060 (2) | 0.5679 (2) | 0.57214 (7) | 0.0544 (6) | |
| H1N | 0.359 (2) | 0.602 (3) | 0.5479 (9) | 0.081 (9)* | |
| C1 | 0.3453 (2) | 0.5091 (3) | 0.61903 (8) | 0.0468 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.2893 (2) | 0.5426 (3) | 0.66352 (8) | 0.0526 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.2212 | 0.6066 | 0.6633 | 0.063* | |
| C3 | 0.3326 (2) | 0.4819 (2) | 0.70984 (8) | 0.0465 (6) | |
| C4 | 0.2751 (2) | 0.5120 (3) | 0.75613 (9) | 0.0616 (7) | |
| H4 | 0.2051 | 0.5722 | 0.7566 | 0.074* | |
| C5 | 0.3207 (3) | 0.4541 (3) | 0.80021 (9) | 0.0713 (8) | |
| H5 | 0.2816 | 0.4749 | 0.8304 | 0.086* | |
| C6 | 0.4261 (3) | 0.3634 (3) | 0.80025 (10) | 0.0714 (8) | |
| H6 | 0.4565 | 0.3241 | 0.8304 | 0.086* | |
| C7 | 0.4840 (2) | 0.3327 (3) | 0.75657 (10) | 0.0646 (7) | |
| H7 | 0.5540 | 0.2727 | 0.7571 | 0.077* | |
| C8 | 0.4395 (2) | 0.3907 (2) | 0.71006 (8) | 0.0489 (6) | |
| C9 | 0.4972 (2) | 0.3633 (3) | 0.66390 (9) | 0.0573 (7) | |
| H9 | 0.5681 | 0.3050 | 0.6635 | 0.069* | |
| C10 | 0.4518 (2) | 0.4200 (2) | 0.61962 (8) | 0.0546 (6) | |
| H10 | 0.4917 | 0.3996 | 0.5896 | 0.065* | |
| C11 | 0.0924 (2) | 0.5082 (3) | 0.58249 (9) | 0.0661 (7) | |
| H11A | 0.0820 | 0.5612 | 0.6143 | 0.099* | |
| H11B | 0.1095 | 0.3956 | 0.5879 | 0.099* | |
| H11C | 0.0209 | 0.5183 | 0.5630 | 0.099* | |
| C12 | 0.1937 (2) | 0.5854 (3) | 0.55465 (8) | 0.0517 (6) | |
| C13 | 0.1742 (2) | 0.6647 (3) | 0.50990 (8) | 0.0563 (7) | |
| H13 | 0.0958 | 0.6769 | 0.4993 | 0.068* | |
| C14 | 0.2644 (3) | 0.7286 (3) | 0.47888 (9) | 0.0574 (7) | |
| C15 | 0.2277 (3) | 0.8137 (3) | 0.43102 (9) | 0.0835 (9) | |
| H15A | 0.2948 | 0.8702 | 0.4172 | 0.125* | |
| H15B | 0.1654 | 0.8897 | 0.4383 | 0.125* | |
| H15C | 0.1995 | 0.7353 | 0.4071 | 0.125* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0617 (13) | 0.0837 (12) | 0.0651 (11) | −0.0036 (10) | 0.0047 (10) | 0.0057 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0499 (14) | 0.0651 (12) | 0.0481 (12) | −0.0006 (11) | 0.0026 (12) | 0.0017 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0438 (15) | 0.0486 (12) | 0.0481 (15) | 0.0001 (11) | 0.0000 (11) | −0.0053 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0497 (16) | 0.0521 (14) | 0.0560 (15) | 0.0084 (11) | −0.0038 (12) | −0.0073 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0450 (15) | 0.0457 (12) | 0.0488 (14) | −0.0069 (11) | 0.0007 (12) | −0.0071 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0576 (17) | 0.0708 (15) | 0.0563 (16) | −0.0027 (13) | 0.0031 (14) | −0.0120 (12) |
| C5 | 0.076 (2) | 0.0848 (19) | 0.0529 (17) | −0.0202 (17) | 0.0030 (16) | −0.0073 (13) |
| C6 | 0.073 (2) | 0.0849 (18) | 0.0559 (17) | −0.0205 (16) | −0.0149 (16) | 0.0106 (14) |
| C7 | 0.0530 (16) | 0.0665 (15) | 0.0742 (18) | −0.0044 (12) | −0.0118 (15) | 0.0069 (13) |
| C8 | 0.0447 (15) | 0.0463 (12) | 0.0556 (14) | −0.0030 (11) | −0.0065 (12) | −0.0001 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0422 (15) | 0.0607 (14) | 0.0690 (17) | 0.0057 (11) | 0.0001 (13) | −0.0026 (13) |
| C10 | 0.0479 (16) | 0.0594 (14) | 0.0563 (15) | −0.0002 (12) | 0.0105 (12) | −0.0080 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0552 (17) | 0.0758 (15) | 0.0673 (16) | −0.0156 (14) | 0.0013 (13) | −0.0088 (13) |
| C12 | 0.0499 (16) | 0.0519 (13) | 0.0532 (14) | −0.0027 (11) | −0.0009 (13) | −0.0139 (11) |
| C13 | 0.0505 (16) | 0.0678 (15) | 0.0506 (14) | 0.0000 (13) | −0.0048 (13) | −0.0079 (12) |
| C14 | 0.072 (2) | 0.0537 (14) | 0.0467 (14) | 0.0015 (13) | −0.0084 (15) | −0.0070 (11) |
| C15 | 0.110 (3) | 0.0807 (19) | 0.0595 (16) | −0.0019 (16) | −0.0137 (16) | 0.0079 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C14 | 1.252 (3) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C12 | 1.353 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.406 (3) |
| N1—C1 | 1.408 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.365 (3) |
| N1—H1N | 0.92 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.368 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C10 | 1.405 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.500 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.415 (3) | C11—H11A | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C11—H11B | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.412 (3) | C11—H11C | 0.9600 |
| C3—C8 | 1.418 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.375 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.365 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.410 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.401 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.510 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.354 (3) | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.416 (3) | ||
| C12—N1—C1 | 129.3 (2) | C10—C9—C8 | 121.6 (2) |
| C12—N1—H1N | 109.5 (16) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.2 |
| C1—N1—H1N | 121.1 (16) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.2 |
| C2—C1—C10 | 119.2 (2) | C9—C10—C1 | 120.5 (2) |
| C2—C1—N1 | 123.4 (2) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.7 |
| C10—C1—N1 | 117.24 (19) | C1—C10—H10 | 119.7 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 121.4 (2) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.3 | C12—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.3 | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 122.5 (2) | C12—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C8 | 118.6 (2) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C8 | 118.90 (19) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.9 (2) | N1—C12—C13 | 119.8 (2) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.5 | N1—C12—C11 | 119.6 (2) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.5 | C13—C12—C11 | 120.5 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.4 (2) | C12—C13—C14 | 124.7 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.8 | C12—C13—H13 | 117.7 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.8 | C14—C13—H13 | 117.7 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 120.3 (2) | O1—C14—C13 | 124.0 (2) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.8 | O1—C14—C15 | 118.0 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.8 | C13—C14—C15 | 118.0 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 121.0 (2) | C14—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.5 | C14—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.5 | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 122.9 (2) | C14—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C3 | 118.25 (19) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C3 | 118.8 (2) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1N···O1 | 0.92 (2) | 1.85 (2) | 2.657 (2) | 144 (2) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: NG5187).
References
- Arıcı, C., Tahir, M. N., Ülkü, D. & Atakol, O. (1999). Acta Cryst. C55, 1691–1692. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2008). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Harrad, M. A., Boualy, B., Ali, M. A., Firdoussi, L. E. & Rizzoli, C. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1269–o1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Harrad, M. A., Outtouch, R., Ait Ali, M., El Firdoussi, L., Karim, A. & Roucoux, A. (2010). Catal. Commun. 11, 442–446.
- Keller, E. (1997). SCHAKAL97 University of Freiburg, Germany.
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst. 28, 659.
- Shaheen, F., Marchio, L., Badshah, A. & Khosa, M. K. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o873–o874.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811024494/ng5187sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811024494/ng5187Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811024494/ng5187Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




