Abstract
The title compound, C16H19NO, was synthesized under solvent-free conditions by reaction of 7-oxa-bicyclo[4.1.0]heptane and naphthalen-1-amine in the presence of Ca(CF3COO)2 as catalyst. The cyclohexane ring adopts a chair conformation. In the crystal, molecules are linked by intermolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯π interactions into chains parallel to the c axis.
Related literature
For background to applications of β-aminoalcohols in organic synthesis, see: Rogers et al. (1989 ▶); O’Brien (1999 ▶); Ager et al. (1996 ▶). For the synthesis of β-aminoalcohols, see: Deyrup & Moyer (1969 ▶); Kamal, Ramu et al. (2005 ▶); Yarapathy et al. (2006 ▶); Yadav et al. (2003 ▶); Rafiee et al. (2004 ▶); Robin et al. (2007 ▶); Das et al. (2000 ▶); Kamal, Adil & Arifuddin (2005 ▶). For puckering parameters, see: Cremer & Pople (1975 ▶).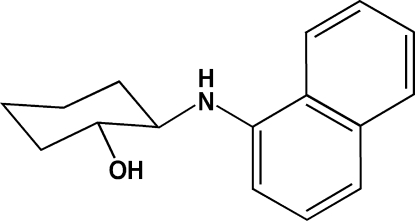
Experimental
Crystal data
C16H19NO
M r = 241.32
Orthorhombic,

a = 12.0278 (4) Å
b = 11.5910 (3) Å
c = 9.5566 (3) Å
V = 1332.33 (7) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 0.58 mm−1
T = 294 K
0.18 × 0.15 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Siemens AED diffractometer
4933 measured reflections
1353 independent reflections
1326 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.034
3 standard reflections every 100 reflections intensity decay: 0.0%
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.030
wR(F 2) = 0.087
S = 1.08
1353 reflections
169 parameters
1 restraint
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.14 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.13 e Å−3
Data collection: AED (Belletti et al., 1993 ▶); cell refinement: AED; data reduction: AED; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and SCHAKAL97 (Keller, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PARST95 (Nardelli, 1995 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811021714/zl2377sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811021714/zl2377Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811021714/zl2377Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the C7–C11/C16 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1N⋯O1i | 0.83 (3) | 2.30 (3) | 3.125 (2) | 171 (2) |
| C14—H14⋯Cg1i | 0.93 | 2.71 | 3.530 (3) | 148 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Universitá degli Studi di Parma is gratefully acknowledged.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
β-Amino alcohols are useful organic intermediates owing to their versatility as building blocks in the synthesis of several biologically active natural products (Rogers et al., 1989), unnatural amino acids (O'Brien, 1999) and chiral auxiliaries (Ager et al., 1996). These compounds are traditionally synthesized by direct treatment of epoxides with excessive amounts of amines at elevated temperatures (Deyrup & Moyer, 1969). Under such conditions, less reactive epoxides and sluggish amines react slowly and sensitive functional groups undergo undesirable side reactions. Many alterations were made in recent years to enhance the synthetic scope of this reaction by the use of Lewis acid catalysis (Kamal, Ramu et al., 2005), solid phase synthesis (Yarapathy et al., 2006), ionic liquids (Yadav et al., 2003), heteropolyacids (Rafiee et al., 2004), microwave irradiation (Robin et al., 2007), fluorinated solvents (Das et al., 2000), and ultrasound mediation (Kamal, Adil & Arifuddin, 2005). As a contribution to this widespread area, we describe here the synthesis and crystal structure of the title amino alcohol.
In the molecule of the title compound (Fig. 1), the cyclohexane ring adopts a chair conformation with puckering parameters (Cremer & Pople, 1975) Q = 0.5765 (19) Å, θ = 2.6 (2)° and φ = 31 (5)°. The hydroxy and amine substituent to the ring are equatorially oriented. In the crystal structure (Fig. 2), intermolecular N—H···O hydrogen bonds and C—H···π interactions (Table 1) link the molecules into chains running parallel to the c axis.
Experimental
In a screw capped vial equipped with a magnetic stirrer, Ca(CF3CO2)2 (0.03 g, 0.11 mmol) was added to naphthalen-1-amine (0.293 g, 2.04 mmol) and 7-oxa-bicyclo[4.1.0]heptane (0.481 g, 2.00 mmol), and the resulting mixture was left under vigorous stirring at 313 K (40°C) for 31 h. The mixture was extracted with AcOEt (3 × 10 ml), and the combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. The combined filtrates were concentrated under vacuum to afford the title product (276 mg, yield 56%). Crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow evaporation of a diethyl ether solution. M.p. 366–367 K.
Refinement
The amine H atom was located in a difference Fourier map and refined freely. All other H atoms were placed at calculated positions and refined using a riding model approximation, with C—H = 0.93–0.98 Å, O—H = 0.82 Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C) or 1.5 Ueq(C, O) for methyl and hydroxy H atoms. In the absence of significant anomalous scattering effects, 460 Friedel pairs were merged in the last cycles of refinement.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of the title compound showing the formation of molecular chains along the a axis via intermolecular N—H···O hydrogen bonds (red dashed lines) and C—H···π interactions (green dashed lines).
Crystal data
| C16H19NO | F(000) = 520 |
| Mr = 241.32 | Dx = 1.203 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pca21 | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2c -2ac | Cell parameters from 48 reflections |
| a = 12.0278 (4) Å | θ = 16.7–36.3° |
| b = 11.5910 (3) Å | µ = 0.58 mm−1 |
| c = 9.5566 (3) Å | T = 294 K |
| V = 1332.33 (7) Å3 | Block, pale-blue |
| Z = 4 | 0.18 × 0.15 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Siemens AED diffractometer | Rint = 0.034 |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | θmax = 69.9°, θmin = 3.8° |
| graphite | h = −14→13 |
| θ/2θ scans | k = −14→13 |
| 4933 measured reflections | l = −11→5 |
| 1353 independent reflections | 3 standard reflections every 100 reflections |
| 1326 reflections with I > 2σ(I) | intensity decay: 0.0% |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.030 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.087 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0541P)2 + 0.0897P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.08 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 1353 reflections | Δρmax = 0.14 e Å−3 |
| 169 parameters | Δρmin = −0.13 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Extinction correction: SHELXL |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0102 (11) |
Special details
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.27577 (13) | −0.01165 (12) | 0.00639 (19) | 0.0690 (4) | |
| H1O | 0.2788 | 0.0522 | 0.0431 | 0.104* | |
| N1 | 0.14586 (12) | 0.08201 (12) | 0.21600 (17) | 0.0491 (3) | |
| H1N | 0.1730 (16) | 0.0622 (17) | 0.292 (3) | 0.054 (5)* | |
| C1 | 0.20467 (14) | −0.08488 (14) | 0.08667 (19) | 0.0471 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.2464 | −0.1137 | 0.1675 | 0.057* | |
| C2 | 0.16883 (16) | −0.18640 (16) | −0.0013 (2) | 0.0572 (4) | |
| H2A | 0.2339 | −0.2284 | −0.0331 | 0.069* | |
| H2B | 0.1288 | −0.1591 | −0.0829 | 0.069* | |
| C3 | 0.09482 (17) | −0.26593 (17) | 0.0831 (3) | 0.0661 (6) | |
| H3A | 0.1366 | −0.2976 | 0.1609 | 0.079* | |
| H3B | 0.0706 | −0.3296 | 0.0246 | 0.079* | |
| C4 | −0.00636 (18) | −0.20139 (19) | 0.1385 (3) | 0.0747 (7) | |
| H4A | −0.0500 | −0.2527 | 0.1969 | 0.090* | |
| H4B | −0.0525 | −0.1774 | 0.0605 | 0.090* | |
| C5 | 0.02757 (15) | −0.09561 (16) | 0.2233 (2) | 0.0577 (5) | |
| H5A | −0.0384 | −0.0529 | 0.2503 | 0.069* | |
| H5B | 0.0651 | −0.1202 | 0.3081 | 0.069* | |
| C6 | 0.10412 (13) | −0.01752 (13) | 0.13964 (18) | 0.0458 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.0628 | 0.0107 | 0.0582 | 0.055* | |
| C7 | 0.08882 (12) | 0.18703 (14) | 0.22162 (18) | 0.0431 (3) | |
| C8 | −0.01028 (14) | 0.20562 (15) | 0.1532 (2) | 0.0500 (4) | |
| H8 | −0.0435 | 0.1456 | 0.1040 | 0.060* | |
| C9 | −0.06185 (15) | 0.31447 (17) | 0.1569 (2) | 0.0583 (5) | |
| H9 | −0.1284 | 0.3253 | 0.1091 | 0.070* | |
| C10 | −0.01684 (16) | 0.40383 (17) | 0.2286 (3) | 0.0609 (5) | |
| H10 | −0.0527 | 0.4749 | 0.2303 | 0.073* | |
| C11 | 0.08457 (15) | 0.38906 (15) | 0.3007 (2) | 0.0530 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.1337 (2) | 0.47978 (17) | 0.3771 (3) | 0.0687 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.0984 | 0.5511 | 0.3805 | 0.082* | |
| C13 | 0.2316 (2) | 0.46537 (17) | 0.4458 (3) | 0.0744 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.2618 | 0.5261 | 0.4968 | 0.089* | |
| C14 | 0.28733 (17) | 0.35946 (17) | 0.4400 (3) | 0.0630 (5) | |
| H14 | 0.3550 | 0.3504 | 0.4859 | 0.076* | |
| C15 | 0.24238 (16) | 0.26941 (14) | 0.3671 (2) | 0.0508 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.2803 | 0.1995 | 0.3636 | 0.061* | |
| C16 | 0.13946 (13) | 0.28016 (13) | 0.29679 (17) | 0.0443 (4) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0746 (9) | 0.0685 (8) | 0.0640 (9) | −0.0070 (7) | 0.0230 (8) | 0.0016 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0558 (8) | 0.0455 (7) | 0.0460 (8) | 0.0049 (6) | −0.0107 (7) | −0.0054 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0484 (8) | 0.0510 (8) | 0.0419 (8) | 0.0012 (7) | 0.0005 (7) | 0.0008 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0614 (10) | 0.0588 (9) | 0.0513 (10) | 0.0102 (8) | −0.0018 (8) | −0.0113 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0658 (11) | 0.0534 (10) | 0.0793 (14) | −0.0043 (8) | 0.0012 (11) | −0.0181 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0556 (10) | 0.0691 (13) | 0.0995 (19) | −0.0144 (9) | 0.0103 (12) | −0.0260 (13) |
| C5 | 0.0532 (9) | 0.0604 (10) | 0.0595 (11) | −0.0051 (8) | 0.0087 (9) | −0.0113 (9) |
| C6 | 0.0478 (7) | 0.0490 (8) | 0.0407 (9) | 0.0029 (6) | −0.0057 (7) | −0.0039 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0445 (7) | 0.0460 (8) | 0.0389 (8) | 0.0010 (6) | 0.0033 (7) | 0.0017 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0462 (8) | 0.0537 (9) | 0.0501 (10) | −0.0019 (7) | −0.0029 (7) | 0.0006 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0486 (9) | 0.0647 (10) | 0.0616 (11) | 0.0069 (8) | −0.0053 (9) | 0.0068 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0596 (10) | 0.0545 (10) | 0.0684 (12) | 0.0133 (8) | 0.0016 (10) | 0.0020 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0580 (9) | 0.0501 (8) | 0.0508 (10) | 0.0029 (7) | 0.0059 (8) | −0.0026 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0814 (13) | 0.0501 (9) | 0.0747 (15) | 0.0058 (9) | −0.0010 (12) | −0.0125 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0828 (15) | 0.0594 (10) | 0.0811 (15) | −0.0082 (10) | −0.0099 (13) | −0.0226 (12) |
| C14 | 0.0622 (10) | 0.0653 (10) | 0.0616 (11) | −0.0076 (9) | −0.0105 (9) | −0.0066 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0516 (8) | 0.0516 (8) | 0.0491 (9) | −0.0001 (8) | −0.0023 (8) | −0.0023 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0478 (8) | 0.0466 (8) | 0.0385 (8) | −0.0007 (6) | 0.0044 (7) | −0.0003 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C1 | 1.428 (2) | C6—H6 | 0.9800 |
| O1—H1O | 0.8200 | C7—C8 | 1.377 (2) |
| N1—C7 | 1.398 (2) | C7—C16 | 1.433 (2) |
| N1—C6 | 1.454 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.406 (2) |
| N1—H1N | 0.83 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.509 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.355 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.526 (2) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1 | 0.9800 | C10—C11 | 1.411 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.514 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9700 | C11—C12 | 1.410 (3) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9700 | C11—C16 | 1.425 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.523 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.359 (4) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9700 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3B | 0.9700 | C13—C14 | 1.399 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.526 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9700 | C14—C15 | 1.367 (3) |
| C4—H4B | 0.9700 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.519 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.414 (3) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9700 | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5B | 0.9700 | ||
| C1—O1—H1O | 109.5 | N1—C6—C1 | 107.38 (13) |
| C7—N1—C6 | 122.71 (14) | C5—C6—C1 | 110.50 (13) |
| C7—N1—H1N | 113.6 (15) | N1—C6—H6 | 108.0 |
| C6—N1—H1N | 110.9 (14) | C5—C6—H6 | 108.0 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 109.60 (16) | C1—C6—H6 | 108.0 |
| O1—C1—C6 | 110.40 (13) | C8—C7—N1 | 122.87 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 110.94 (14) | C8—C7—C16 | 119.24 (15) |
| O1—C1—H1 | 108.6 | N1—C7—C16 | 117.81 (14) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 108.6 | C7—C8—C9 | 120.67 (17) |
| C6—C1—H1 | 108.6 | C7—C8—H8 | 119.7 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 110.28 (17) | C9—C8—H8 | 119.7 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.6 | C10—C9—C8 | 121.51 (17) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 109.6 | C10—C9—H9 | 119.2 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.6 | C8—C9—H9 | 119.2 |
| C3—C2—H2B | 109.6 | C9—C10—C11 | 119.97 (17) |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 108.1 | C9—C10—H10 | 120.0 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 110.83 (17) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.0 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 109.5 | C12—C11—C10 | 121.65 (17) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 109.5 | C12—C11—C16 | 118.67 (18) |
| C2—C3—H3B | 109.5 | C10—C11—C16 | 119.68 (16) |
| C4—C3—H3B | 109.5 | C13—C12—C11 | 121.47 (19) |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 108.1 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.3 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 111.45 (16) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.3 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 109.3 | C12—C13—C14 | 120.24 (19) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 109.3 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| C3—C4—H4B | 109.3 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| C5—C4—H4B | 109.3 | C15—C14—C13 | 120.04 (19) |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 108.0 | C15—C14—H14 | 120.0 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 111.16 (18) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.0 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 109.4 | C14—C15—C16 | 121.42 (17) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 109.4 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.3 |
| C6—C5—H5B | 109.4 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.3 |
| C4—C5—H5B | 109.4 | C15—C16—C11 | 118.12 (15) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 108.0 | C15—C16—C7 | 122.96 (14) |
| N1—C6—C5 | 114.69 (15) | C11—C16—C7 | 118.92 (15) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| Cg1 is the centroid of the C7–C11/C16 ring. |
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1N···O1i | 0.83 (3) | 2.30 (3) | 3.125 (2) | 171 (2) |
| C14—H14···Cg1i | 0.93 | 2.71 | 3.530 (3) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1/2, y, z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: ZL2377).
References
- Ager, D. J., Prakash, I. & Schaad, D. R. (1996). Chem. Rev. 96, 835–875. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 115–119.
- Belletti, D., Cantoni, A. & Pasquinelli, G. (1993). AED Internal Report 1/93. Centro di Studio per la Strutturistica Diffrattometrica del CNR, Parma, Italy.
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
- Das, U., Crousse, B., Kesavan, V., Bonnet-Delpon, D. & Begue, J. P. (2000). J. Org. Chem. 65, 6749–6751. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Deyrup, J. A. & Moyer, C. L. (1969). J. Org. Chem. 34, 175–179.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Kamal, A., Adil, S. F. & Arifuddin, M. (2005). Ultrason. Sonochem. 12, 429–431. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kamal, A., Ramu, R., Azhar, M. A. & Khanna, G. B. R. (2005). Tetrahedron Lett. 46, 2675–2677.
- Keller, E. (1997). SCHAKAL97 University of Freiburg, Germany.
- Nardelli, M. (1995). J. Appl. Cryst. 28, 659.
- O’Brien, P. (1999). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 38, 326–329.
- Rafiee, E., Tangestaninejad, S., Habibi, M. H. & Mirkhani, V. (2004). Synth. Commun. 34, 3673–3681.
- Robin, A., Brown, F., Bahamontes-Rosa, N., Wu, B., Beitz, E., Kun, J. F. J. & Flitsch, S. L. (2007). J. Med. Chem. 50, 4243–4249. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rogers, G. A., Parsons, S. M., Anderson, D. C., Nilsson, L. M., Bahr, B. A., Kornreich, W. D., Kaufman, R., Jacobs, R. S. & Kirtman, B. (1989). J. Med. Chem. 32, 1217–1230. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Yadav, J. S., Reddy, B. V. S., Basak, A. K. & Narsaiah, A. V. (2003). Tetrahedron Lett. 44, 1047–1050.
- Yarapathy, V. R., Mekala, S., Rao, B. V. & Tammishetti, S. (2006). Catal. Commun. 7, 466–471.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811021714/zl2377sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811021714/zl2377Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811021714/zl2377Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




