Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, C5H2Cl2N2O2, consists of two crystallographically independent molecules. The pyridine ring in each molecule is essentially planar, with maximum deviations of 0.004 (4) and 0.007 (4) Å. Short Cl⋯O [3.09 (3) and 3.13 (4) Å] and Cl⋯Cl [3.38 (12) Å] contacts were observed. No significant intermolecular interactions were observed in the crystal packing.
Related literature
For the role of the nitropyridine nucleus in the development of medicinal agents and in the field of agrochemicals, see: Davis et al. (1996 ▶). For the properties and use of pyridine derivatives, see: Vacher et al. (1998 ▶); Olah et al. (1980 ▶); Bare et al. (1989 ▶). For standard bond lengths, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). For the melting point, see: Johnson et al. (1967 ▶). 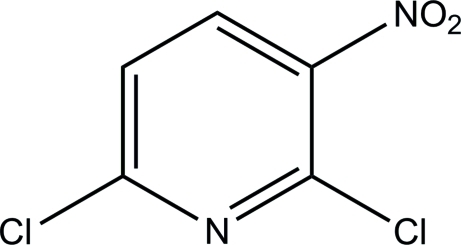
Experimental
Crystal data
C5H2Cl2N2O2
M r = 192.99
Monoclinic,

a = 7.9021 (8) Å
b = 19.166 (2) Å
c = 11.0987 (9) Å
β = 122.072 (5)°
V = 1424.4 (2) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.85 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.40 × 0.27 × 0.24 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.727, T max = 0.821
16845 measured reflections
4817 independent reflections
2323 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.060
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.067
wR(F 2) = 0.180
S = 1.08
4817 reflections
199 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.55 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.42 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811023683/ng5183sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811023683/ng5183Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811023683/ng5183Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) for the Research University Grant (1001/PFIZIK/811160). SA thanks the Malaysian Government and USM for the award of a research scholarship. AMI thanks the Department of Atomic Energy, Board for Research in Nuclear Sciences, Government of India for a Young Scientist award.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Nitropyridine nucleus played a pivotal role in the development of different medicinal agents and in the field of agrochemicals (Davis et al., 1996). It is seen from the current literature that pyridine derivatives have been developed and used as insecticidal agents (Vacher et al., 1998). Nitrated pyridines and their derivatives are important intermediates in synthesis of heterocyclic compounds in dyes and pharmaceutical products (Olah et al., 1980). Fused heterocycles containing nitropyridine systems have been associated with several biological and medicinal activities including antiolytic (Olah et al., 1980), antiviral and anti-inflammatory (Bare et al., 1989) profiles.
The asymmetric unit of the tittle compound (Fig. 1), consists of two crystallographically independent molecules A and B. The pyridine rings (N1/C1–C5) for molecules A and B are essentially planar with maximum deviations of 0.004 (4) Å at atom C1A and 0.007 (4) Å at atom C3B, respectively. The bond lengths (Allen et al., 1987) and angles are within normal ranges. In addition, short Cl···O [Cl1A···O2A (1 - x, -1/2 + y, 1/2 - z) = 3.093 (3) Å and Cl2A···O2A (1 - x, 2 - y, -z) = 3.132 (4) Å] and Cl···Cl [Cl2A···Cl2A (1 - x, 2 - y, -z) = 3.3839 (12) Å] contacts were observed.
The crystal packing is shown in Fig. 2. No significant intermolecular interactions were observed in the crystal packing.
Experimental
2,6-Dichloropyridine (5 g, 0.033 mol) was added lotwise to mixture of concentrated H2SO4 (25 ml) and fuming nitric acid (10 ml) at 0 °C. After the addition, the reaction mixture was heated to 65 °C for 2 h. After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and quenched with ice water. The solid that separated out was filtered and dried under vacuum. The crude product was purified by column chromatography using silica gel 60–120 mesh size and petroleum ether: ethyl acetate as eluent to afford title compound as a pale yellow solid. Yield: 3.0 g, 46.0%. M.p.: 333–338 K (Johnson et al., 1967).
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned geometrically [C–H = 0.93 Å] and refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C). There is no pseudo-symmetry in the crystal structure.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing the two independent molecules with atom labels and 30% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of the title compound.
Crystal data
| C5H2Cl2N2O2 | F(000) = 768 |
| Mr = 192.99 | Dx = 1.800 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 3419 reflections |
| a = 7.9021 (8) Å | θ = 2.4–31.7° |
| b = 19.166 (2) Å | µ = 0.85 mm−1 |
| c = 11.0987 (9) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 122.072 (5)° | Block, yellow |
| V = 1424.4 (2) Å3 | 0.40 × 0.27 × 0.24 mm |
| Z = 8 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4817 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2323 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.060 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 31.8°, θmin = 2.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.727, Tmax = 0.821 | k = −28→28 |
| 16845 measured reflections | l = −16→16 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.067 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.180 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.08 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0527P)2 + 1.2999P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4817 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 199 parameters | Δρmax = 0.55 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.42 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1A | 0.51344 (18) | 0.68002 (5) | 0.26085 (12) | 0.0667 (3) | |
| Cl2A | 0.49627 (16) | 0.91466 (4) | 0.03753 (9) | 0.0540 (3) | |
| O1A | 0.6135 (4) | 1.00995 (14) | 0.4256 (3) | 0.0656 (8) | |
| O2A | 0.4472 (5) | 1.01996 (13) | 0.1975 (3) | 0.0641 (8) | |
| N1A | 0.5042 (4) | 0.80475 (13) | 0.1709 (3) | 0.0411 (6) | |
| N2A | 0.5284 (4) | 0.98557 (14) | 0.3053 (3) | 0.0433 (6) | |
| C1A | 0.5404 (5) | 0.87035 (18) | 0.4058 (3) | 0.0445 (8) | |
| H1A | 0.5538 | 0.8926 | 0.4848 | 0.053* | |
| C2A | 0.5356 (5) | 0.79924 (18) | 0.3979 (4) | 0.0463 (8) | |
| H2A | 0.5436 | 0.7720 | 0.4701 | 0.056* | |
| C3A | 0.5182 (5) | 0.76941 (15) | 0.2786 (3) | 0.0397 (7) | |
| C4A | 0.5072 (5) | 0.87406 (15) | 0.1788 (3) | 0.0359 (7) | |
| C5A | 0.5251 (5) | 0.90936 (15) | 0.2945 (3) | 0.0351 (7) | |
| Cl1B | 1.01800 (19) | 0.67408 (5) | 0.25606 (12) | 0.0673 (3) | |
| Cl2B | 0.98563 (15) | 0.91167 (5) | 0.03234 (9) | 0.0532 (3) | |
| O1B | 0.9156 (5) | 1.00415 (15) | 0.3366 (3) | 0.0731 (9) | |
| O2B | 1.1216 (5) | 1.01192 (14) | 0.2658 (3) | 0.0663 (8) | |
| N1B | 1.0071 (4) | 0.79906 (13) | 0.1667 (3) | 0.0403 (6) | |
| N2B | 1.0196 (5) | 0.97918 (15) | 0.2975 (3) | 0.0470 (7) | |
| C1B | 1.0342 (5) | 0.86410 (18) | 0.4000 (3) | 0.0450 (8) | |
| H1B | 1.0422 | 0.8863 | 0.4773 | 0.054* | |
| C2B | 1.0342 (5) | 0.79259 (19) | 0.3928 (4) | 0.0481 (8) | |
| H2B | 1.0421 | 0.7650 | 0.4646 | 0.058* | |
| C3B | 1.0218 (5) | 0.76313 (16) | 0.2741 (3) | 0.0427 (8) | |
| C4B | 1.0086 (5) | 0.86795 (16) | 0.1754 (3) | 0.0356 (7) | |
| C5B | 1.0219 (5) | 0.90270 (16) | 0.2895 (3) | 0.0376 (7) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1A | 0.0972 (8) | 0.0347 (4) | 0.0768 (7) | 0.0060 (5) | 0.0521 (7) | 0.0129 (4) |
| Cl2A | 0.0868 (7) | 0.0430 (4) | 0.0416 (5) | −0.0036 (4) | 0.0405 (5) | 0.0053 (3) |
| O1A | 0.085 (2) | 0.0609 (17) | 0.0551 (16) | −0.0130 (15) | 0.0404 (16) | −0.0206 (13) |
| O2A | 0.093 (2) | 0.0406 (13) | 0.0633 (17) | 0.0096 (13) | 0.0444 (17) | 0.0094 (12) |
| N1A | 0.0520 (18) | 0.0343 (12) | 0.0418 (15) | 0.0003 (12) | 0.0281 (14) | 0.0016 (11) |
| N2A | 0.0494 (17) | 0.0377 (13) | 0.0509 (17) | −0.0023 (12) | 0.0321 (15) | −0.0046 (12) |
| C1A | 0.049 (2) | 0.056 (2) | 0.0346 (17) | 0.0028 (16) | 0.0257 (17) | 0.0035 (14) |
| C2A | 0.050 (2) | 0.055 (2) | 0.0391 (18) | 0.0067 (16) | 0.0274 (17) | 0.0137 (15) |
| C3A | 0.0457 (19) | 0.0331 (14) | 0.0429 (18) | 0.0047 (13) | 0.0252 (17) | 0.0086 (13) |
| C4A | 0.0435 (19) | 0.0332 (14) | 0.0329 (16) | 0.0010 (13) | 0.0215 (15) | 0.0025 (11) |
| C5A | 0.0392 (18) | 0.0337 (14) | 0.0353 (16) | 0.0015 (13) | 0.0218 (14) | 0.0012 (12) |
| Cl1B | 0.0970 (9) | 0.0390 (5) | 0.0691 (7) | 0.0050 (5) | 0.0463 (6) | 0.0105 (4) |
| Cl2B | 0.0762 (7) | 0.0501 (5) | 0.0381 (4) | −0.0015 (4) | 0.0335 (5) | 0.0079 (3) |
| O1B | 0.084 (2) | 0.0648 (18) | 0.093 (2) | 0.0032 (15) | 0.062 (2) | −0.0159 (16) |
| O2B | 0.093 (2) | 0.0517 (15) | 0.0721 (18) | −0.0135 (15) | 0.0556 (18) | −0.0038 (13) |
| N1B | 0.0452 (16) | 0.0392 (14) | 0.0387 (15) | 0.0028 (12) | 0.0238 (13) | 0.0050 (11) |
| N2B | 0.0530 (18) | 0.0447 (15) | 0.0421 (16) | −0.0030 (14) | 0.0244 (15) | −0.0050 (12) |
| C1B | 0.051 (2) | 0.0542 (19) | 0.0355 (17) | −0.0033 (16) | 0.0268 (17) | −0.0007 (14) |
| C2B | 0.052 (2) | 0.059 (2) | 0.0369 (18) | −0.0006 (17) | 0.0255 (17) | 0.0104 (15) |
| C3B | 0.046 (2) | 0.0391 (16) | 0.0417 (19) | 0.0036 (14) | 0.0224 (17) | 0.0085 (14) |
| C4B | 0.0360 (18) | 0.0426 (16) | 0.0296 (15) | 0.0014 (13) | 0.0183 (14) | 0.0045 (12) |
| C5B | 0.0385 (18) | 0.0420 (16) | 0.0358 (16) | −0.0011 (14) | 0.0221 (15) | 0.0013 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1A—C3A | 1.723 (3) | Cl1B—C3B | 1.717 (3) |
| Cl2A—C4A | 1.711 (3) | Cl2B—C4B | 1.717 (3) |
| O1A—N2A | 1.224 (3) | O1B—N2B | 1.214 (4) |
| O2A—N2A | 1.209 (4) | O2B—N2B | 1.211 (4) |
| N1A—C4A | 1.331 (4) | N1B—C4B | 1.323 (4) |
| N1A—C3A | 1.326 (4) | N1B—C3B | 1.327 (4) |
| N2A—C5A | 1.465 (4) | N2B—C5B | 1.469 (4) |
| C1A—C2A | 1.365 (5) | C1B—C2B | 1.373 (5) |
| C1A—C5A | 1.393 (4) | C1B—C5B | 1.391 (4) |
| C1A—H1A | 0.9300 | C1B—H1B | 0.9300 |
| C2A—C3A | 1.381 (5) | C2B—C3B | 1.389 (5) |
| C2A—H2A | 0.9300 | C2B—H2B | 0.9300 |
| C4A—C5A | 1.391 (4) | C4B—C5B | 1.385 (4) |
| C4A—N1A—C3A | 117.4 (3) | C4B—N1B—C3B | 117.3 (3) |
| O2A—N2A—O1A | 124.5 (3) | O2B—N2B—O1B | 125.5 (3) |
| O2A—N2A—C5A | 119.0 (3) | O2B—N2B—C5B | 117.9 (3) |
| O1A—N2A—C5A | 116.5 (3) | O1B—N2B—C5B | 116.6 (3) |
| C2A—C1A—C5A | 119.5 (3) | C2B—C1B—C5B | 118.8 (3) |
| C2A—C1A—H1A | 120.2 | C2B—C1B—H1B | 120.6 |
| C5A—C1A—H1A | 120.2 | C5B—C1B—H1B | 120.6 |
| C1A—C2A—C3A | 117.4 (3) | C1B—C2B—C3B | 117.3 (3) |
| C1A—C2A—H2A | 121.3 | C1B—C2B—H2B | 121.4 |
| C3A—C2A—H2A | 121.3 | C3B—C2B—H2B | 121.4 |
| N1A—C3A—C2A | 124.8 (3) | N1B—C3B—C2B | 124.7 (3) |
| N1A—C3A—Cl1A | 114.8 (2) | N1B—C3B—Cl1B | 115.0 (3) |
| C2A—C3A—Cl1A | 120.4 (2) | C2B—C3B—Cl1B | 120.2 (3) |
| N1A—C4A—C5A | 122.4 (3) | N1B—C4B—C5B | 122.7 (3) |
| N1A—C4A—Cl2A | 113.8 (2) | N1B—C4B—Cl2B | 115.3 (2) |
| C5A—C4A—Cl2A | 123.8 (2) | C5B—C4B—Cl2B | 122.0 (2) |
| C1A—C5A—C4A | 118.4 (3) | C4B—C5B—C1B | 119.1 (3) |
| C1A—C5A—N2A | 118.2 (3) | C4B—C5B—N2B | 122.5 (3) |
| C4A—C5A—N2A | 123.3 (3) | C1B—C5B—N2B | 118.4 (3) |
| C5A—C1A—C2A—C3A | 0.9 (5) | C5B—C1B—C2B—C3B | 0.0 (5) |
| C4A—N1A—C3A—C2A | 0.0 (5) | C4B—N1B—C3B—C2B | 1.5 (5) |
| C4A—N1A—C3A—Cl1A | −180.0 (3) | C4B—N1B—C3B—Cl1B | 179.7 (2) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A—N1A | −0.6 (6) | C1B—C2B—C3B—N1B | −1.1 (6) |
| C1A—C2A—C3A—Cl1A | 179.4 (3) | C1B—C2B—C3B—Cl1B | −179.2 (3) |
| C3A—N1A—C4A—C5A | 0.3 (5) | C3B—N1B—C4B—C5B | −0.9 (5) |
| C3A—N1A—C4A—Cl2A | 178.0 (2) | C3B—N1B—C4B—Cl2B | −179.1 (2) |
| C2A—C1A—C5A—C4A | −0.6 (5) | N1B—C4B—C5B—C1B | 0.0 (5) |
| C2A—C1A—C5A—N2A | 179.3 (3) | Cl2B—C4B—C5B—C1B | 178.1 (3) |
| N1A—C4A—C5A—C1A | 0.0 (5) | N1B—C4B—C5B—N2B | −178.8 (3) |
| Cl2A—C4A—C5A—C1A | −177.5 (3) | Cl2B—C4B—C5B—N2B | −0.7 (5) |
| N1A—C4A—C5A—N2A | −179.9 (3) | C2B—C1B—C5B—C4B | 0.5 (5) |
| Cl2A—C4A—C5A—N2A | 2.6 (5) | C2B—C1B—C5B—N2B | 179.3 (3) |
| O2A—N2A—C5A—C1A | −153.8 (3) | O2B—N2B—C5B—C4B | −44.8 (5) |
| O1A—N2A—C5A—C1A | 25.6 (4) | O1B—N2B—C5B—C4B | 135.7 (4) |
| O2A—N2A—C5A—C4A | 26.1 (5) | O2B—N2B—C5B—C1B | 136.4 (3) |
| O1A—N2A—C5A—C4A | −154.5 (3) | O1B—N2B—C5B—C1B | −43.0 (5) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: NG5183).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bare, T. M., McLaren, C. D., Campbell, D. J. B., Firor, J. W., Resch, J. F., Walters, C. P., Salama, A. I., Meiners, B. A. & Patel, J. B. (1989). J. Med. Chem. 32, 2561–2573. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2009). SADABS, APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Davis, L., Olsen, G. E., Klein, J. T., Kapples, K. J., Huger, F. P., Smith, C. P., Petko, W. W., Cornfeldt, M. & Effland, R. C. (1996). J. Med. Chem. 39, 582–587. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C. D., Katritzky, A. R., Ridgewell, B. J. & Viney, M. (1967). J. Chem. Soc. B. pp. 1204–1210.
- Olah, G. A., Narang, S. C., Olah, J. A., Pearson, R. L. & Cupas, C. A. (1980). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 102, 3507–3510.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Vacher, B., Bonnaud, B., Funes, P., Jubault, N., Koek, W., Assié, M.-B. & Cosi, C. (1998). J. Med. Chem. 41, 5070–5083. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811023683/ng5183sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811023683/ng5183Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811023683/ng5183Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




