Abstract
The title compound, C15H11Cl2NO, is approximately planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.062 Å) and contains a single C=C double bond in a trans (E) configuration. The crystal packing is stabilized by intermolecular N—H⋯N and N—H⋯O intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Related literature
For related flavonoids, see: Bargellini & Marini-Bettolo (1940 ▶). For isoflavonoids, see: Nógrádi & Szöllösy (1996 ▶). For the biological activities of chalcones, see: Go et al. (2005 ▶); Hans et al. (2010 ▶); Trivedi et al. (2007 ▶); Nielsen et al. (2004 ▶). For antimalarial activity, see: Mishra et al. (2008 ▶). For antifilarial activity, see: Awasthi, Mishra, Dixit et al. (2009 ▶). For other chalcone crystal structures and small molecules, see: Fun et al. (2008 ▶); Li et al. (2009 ▶); Singh et al. (2011 ▶). For the synthesis, see: Migrdichian (1957 ▶); Awasthi, Mishra, Kumar et al. (2009 ▶). For intermolecular N—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonding, see: Fonar et al. (2001 ▶).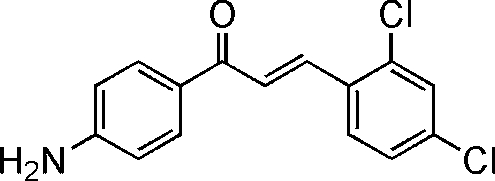
Experimental
Crystal data
C15H11Cl2NO
M r = 292.15
Monoclinic,
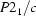
a = 22.771 (2) Å
b = 3.9889 (5) Å
c = 14.7848 (18) Å
β = 92.401 (12)°
V = 1341.7 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.47 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.23 × 0.11 × 0.08 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Sapphire3 diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.597, T max = 1.000
5765 measured reflections
2625 independent reflections
1733 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.047
Standard reflections: 0
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.057
wR(F 2) = 0.159
S = 0.98
2625 reflections
216 parameters
All H-atom parameters refined
Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis PRO (Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis PRO; data reduction: CrysAlis PRO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: Mercury (Macrae et al., 2006 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811020460/zj2011sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811020460/zj2011Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811020460/zj2011Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1N1⋯O1i | 0.78 (3) | 2.210 | 2.977 (4) | 171 (3) |
| N1—H2N1⋯N1ii | 0.76 (4) | 2.469 | 3.134 (5) | 147 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 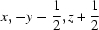 ; (ii)
; (ii) 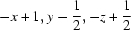 .
.
Acknowledgments
SKA is thankful to the University Grants Commission (UGC) [scheme F. No. 37-410/2009(SR)] and the University of Delhi, India, for financial assistance. The authors are highly thankful to the University Sophisticated Instrument Center (USIC), University of Delhi, India, for providing the single-crystal X-ray diffractometer facility.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
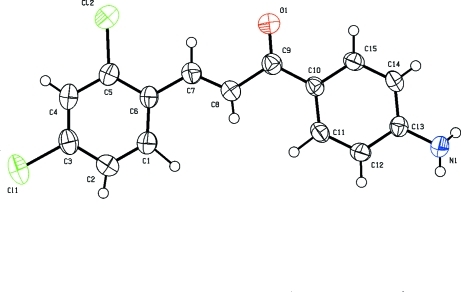
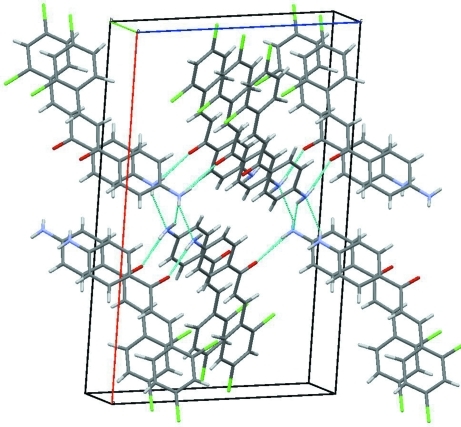
Chalcones (trans-1,3-diphenyl-2-propen-1-ones) are precursor of various natural products such as flavonoids (Bargellini & Marini-Bettolo, 1940), isoflavanoids (Nógrádi & Szöllösy, 1996) and key intermediates for synthesis of various heterocyclic scaffolds. Chalcone consists of two aromatic rings joined together by a three carbon α, β-unsaturated carbonyl system (Figure 1). These compounds have broad range of biological activities such as anticancer (Go et al., 2005), antimalarial activity (Mishra et al. 2008), anti-TB activity (Hans et al. 2010), antiviral (Trivedi et al., 2007), antibacterial (Nielsen et al., 2004) and more recently antifilarial activity (Awasthi, Mishra, Dixit et al. 2009) etc. Further, SAR on substituted chalcones reveal that presence of α, β-unsaturated ketone is critical for activity in which double bond is in a trans (E)-configuration (Li et al., 2009). The crystal structures of few substituted chalcones have been recently reported (Fun et al., 2008; Li et al., 2009). As a part of our ongoing research work on antimicrobial activities of substituted chalcones and crystal structure analysis of small molecules (Singh et al., 2011), we further explored the possibility of characterization of chalcone in the solid state. We crystallized substituted chalcone (2E)-1-(4-aminophenyl)-4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl) but-2-en-1-one,in the mixture of methanol and acetone at room temperature. In this paper, we report the single-crystal X-ray structure of the title compound and possible role of hydrogen bonding in the structure stabilization. The crystal packing is stabilized by intermolecular hydrogen bonding between N1-H2N1···N1 and N1-H1N1···O1(Fonar et al., 2001).as shown in packing diagram along b axis(figure 2, table 1).The torsion angle between atom C7—C8 - C9—C10 is 177.8 (3)°. The aminophenyl ring, dichlorophenyl ring and central ketone group are in the same plane, thus molecule is planer. The CCDC No. of the crystal is 797089.
Experimental
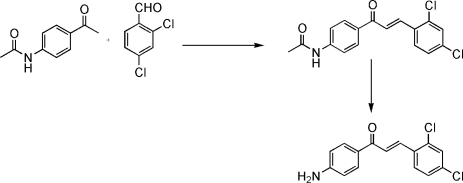
The synthesis of the title compound was carried out according to the published procedure (Migrdichian 1957; Awasthi, Mishra, Kumar et al., 2009). Briefly, an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide (10%, 10 ml) was added to a solution of acetlylated 4-aminoacetophenone (1.77 g m, 10 mmol) and 2, 4-dichlorobenzaldehyde (1.73 g m, 10 mmol) in minimum amount of methanol (3–5 ml) at ice cooled flask. The reaction mixture was allowed to draw closer to room temperature and stirred for 18–20 hrs yielded a yellow solid. The completion of the reaction was monitored by thin layer chromatography. After completion of the reaction, the mixture was neutralized with 10% hydrochloric acid in water. The acetyl group was removed by refluxing with HCl/C2H5OH for 4hrs. The product was recrystallized from dry methanol and acetone in 1:1 ratio. After few weeks, light yellow single crystals were obtained. Yield 70%. Rf = 0.64 (CHCl3: MeOH, 99:1). MS (Macromass G) m/z = 292.16 (M+). Elemental analysis (Perkin Elmer): Calcd. for C15 H11 Cl2 NO: C 61.67, H 3.79, Cl 24.26, N 4.79, O 5.48%. Found C 61.70, H 3.81, Cl 24.23, N 4.83, O 5.44%. IR (Perkin Elmer Fourier transform Spectrometer with KBr pellets (cm-1): 3462.18–3369.75 (–NH2), 2925.42- 2851.54 (aromatic), 1704.23 (C=O in conjugation C=C), 1656.19 (C=C str aromatic), 1584.94 (C=C str in conjugation CO—C=C), 1269.49 (C—N str), 1018.68–1105.40 (C—O—C str), C—Cl (867.02–814.49). 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz): δ 186.66, 152.16, 136.54, 135.27, 135.13, 131.78, 130.75, 130.22, 129.38, 128.07, 127.03, 126.46, 124.75, 113.20, 113.00. 1HNMR (Brucker AMX, 300 MHz, CDCl3): δ 4. 196 (s, 2H, NH2), δ 6.7 (d, 2H, H2 and H6, J = 8.7 Hz), δ 7.92 (d, 2H, H3 and H5, J = 8.4 Hz), δ 7.46 (d, 1H, Hα, J = 15.6 Hz), δ 8.06 (d, 1H, Hβ, J = 15.6 Hz), δ 7.463 (s, 1H, H'3), δ 7.29 (d, 1H, H'5, J = 6.9 Hz), δ 7.67 (d, 1H, H'6, J = 8.4 Hz).
Refinement
All the H atoms were located from difference Fourier map [range of C—H = 0.81 (4) - 1.10 (3) Å] and N–H = 0.76 (4)–0.78 (4)] and allowed to refine freely.
Figures
Fig. 1.
ORTEP diagram of the molecule with thermal ellipsoids drawn at 50% probability level Color code: White: C; red: O; blue: N; white: H; Green: Cl; Green: F
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of molecule viewed through b plane showing Intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
Fig. 3.
The formation of the title compound.
Crystal data
| C15H11Cl2NO | F(000) = 600 |
| Mr = 292.15 | Dx = 1.446 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 1458 reflections |
| a = 22.771 (2) Å | θ = 3.0–29.0° |
| b = 3.9889 (5) Å | µ = 0.47 mm−1 |
| c = 14.7848 (18) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 92.401 (12)° | Rod, yellow |
| V = 1341.7 (3) Å3 | 0.23 × 0.11 × 0.08 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur Sapphire3 diffractometer | 2625 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1733 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.047 |
| ω scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 3.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis PRO; Oxford Diffraction, 2009) | h = −25→28 |
| Tmin = 0.597, Tmax = 1.000 | k = −3→4 |
| 5765 measured reflections | l = −17→18 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.057 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.159 | All H-atom parameters refined |
| S = 0.98 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0919P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2625 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.003 |
| 216 parameters | Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.29 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.85377 (14) | 0.5099 (8) | 0.5485 (2) | 0.0466 (8) | |
| C2 | 0.91136 (15) | 0.6162 (9) | 0.5505 (2) | 0.0496 (8) | |
| C3 | 0.93472 (13) | 0.7698 (8) | 0.6273 (2) | 0.0454 (8) | |
| C4 | 0.90165 (14) | 0.8197 (8) | 0.7010 (2) | 0.0465 (8) | |
| C5 | 0.84351 (14) | 0.7060 (8) | 0.6984 (2) | 0.0440 (7) | |
| C6 | 0.81845 (12) | 0.5488 (7) | 0.62200 (19) | 0.0376 (7) | |
| C7 | 0.75725 (13) | 0.4285 (8) | 0.6200 (2) | 0.0434 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.72868 (14) | 0.2879 (9) | 0.5517 (2) | 0.0452 (8) | |
| C9 | 0.66735 (13) | 0.1629 (7) | 0.5571 (2) | 0.0403 (7) | |
| C10 | 0.63905 (12) | −0.0047 (7) | 0.47851 (18) | 0.0334 (6) | |
| C11 | 0.66507 (13) | −0.0353 (8) | 0.3948 (2) | 0.0408 (7) | |
| C12 | 0.63760 (13) | −0.1948 (8) | 0.3229 (2) | 0.0421 (7) | |
| C13 | 0.58122 (12) | −0.3296 (7) | 0.33087 (19) | 0.0344 (7) | |
| C14 | 0.55456 (13) | −0.2959 (8) | 0.4125 (2) | 0.0384 (7) | |
| C15 | 0.58231 (13) | −0.1377 (8) | 0.4847 (2) | 0.0392 (7) | |
| N1 | 0.55305 (14) | −0.4825 (8) | 0.2576 (2) | 0.0443 (7) | |
| O1 | 0.64210 (10) | 0.1991 (6) | 0.62783 (15) | 0.0604 (7) | |
| Cl1 | 1.00725 (4) | 0.9059 (2) | 0.63141 (7) | 0.0648 (3) | |
| Cl2 | 0.80366 (5) | 0.7782 (3) | 0.79390 (6) | 0.0786 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.8413 (15) | 0.404 (8) | 0.482 (2) | 0.057 (9)* | |
| H1N1 | 0.5731 (15) | −0.545 (9) | 0.220 (2) | 0.041 (10)* | |
| H2 | 0.9359 (16) | 0.602 (9) | 0.509 (2) | 0.058 (10)* | |
| H2N1 | 0.5329 (19) | −0.618 (10) | 0.275 (3) | 0.067 (15)* | |
| H4 | 0.9136 (16) | 0.923 (9) | 0.749 (3) | 0.065 (11)* | |
| H7 | 0.7369 (18) | 0.430 (10) | 0.674 (3) | 0.078 (12)* | |
| H8 | 0.7462 (17) | 0.234 (9) | 0.505 (3) | 0.065 (12)* | |
| H11 | 0.7039 (18) | 0.068 (10) | 0.384 (3) | 0.075 (11)* | |
| H12 | 0.6574 (14) | −0.213 (7) | 0.271 (2) | 0.042 (8)* | |
| H14 | 0.5245 (17) | −0.397 (9) | 0.422 (2) | 0.060 (11)* | |
| H15 | 0.5611 (13) | −0.119 (7) | 0.537 (2) | 0.038 (8)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0408 (17) | 0.055 (2) | 0.0431 (18) | −0.0017 (16) | −0.0039 (14) | −0.0028 (16) |
| C2 | 0.0424 (18) | 0.056 (2) | 0.051 (2) | −0.0029 (16) | 0.0079 (16) | −0.0013 (17) |
| C3 | 0.0372 (15) | 0.0416 (17) | 0.056 (2) | −0.0002 (14) | −0.0094 (15) | 0.0068 (15) |
| C4 | 0.0461 (18) | 0.0424 (19) | 0.050 (2) | −0.0059 (15) | −0.0119 (16) | −0.0010 (16) |
| C5 | 0.0446 (17) | 0.0468 (18) | 0.0400 (16) | −0.0010 (15) | −0.0043 (14) | −0.0017 (14) |
| C6 | 0.0349 (15) | 0.0369 (16) | 0.0403 (16) | −0.0002 (13) | −0.0054 (13) | 0.0005 (13) |
| C7 | 0.0380 (16) | 0.0498 (19) | 0.0424 (17) | −0.0030 (15) | −0.0007 (14) | −0.0002 (15) |
| C8 | 0.0368 (16) | 0.057 (2) | 0.0421 (18) | −0.0077 (15) | 0.0036 (15) | −0.0031 (16) |
| C9 | 0.0370 (15) | 0.0422 (18) | 0.0414 (17) | 0.0001 (14) | −0.0004 (14) | 0.0033 (14) |
| C10 | 0.0268 (13) | 0.0373 (16) | 0.0361 (15) | 0.0007 (12) | −0.0003 (11) | 0.0033 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0286 (14) | 0.0513 (19) | 0.0426 (17) | −0.0049 (14) | 0.0017 (13) | 0.0028 (15) |
| C12 | 0.0338 (15) | 0.057 (2) | 0.0362 (16) | 0.0001 (15) | 0.0057 (13) | −0.0007 (15) |
| C13 | 0.0303 (14) | 0.0349 (16) | 0.0374 (15) | 0.0042 (12) | −0.0043 (12) | 0.0009 (12) |
| C14 | 0.0275 (15) | 0.0425 (18) | 0.0452 (17) | −0.0054 (14) | 0.0007 (13) | 0.0031 (14) |
| C15 | 0.0333 (15) | 0.0470 (19) | 0.0378 (16) | 0.0013 (14) | 0.0068 (13) | 0.0016 (14) |
| N1 | 0.0372 (15) | 0.054 (2) | 0.0409 (16) | −0.0038 (15) | −0.0023 (13) | −0.0097 (15) |
| O1 | 0.0515 (13) | 0.0868 (19) | 0.0436 (13) | −0.0177 (13) | 0.0096 (11) | −0.0133 (12) |
| Cl1 | 0.0387 (5) | 0.0691 (6) | 0.0857 (7) | −0.0114 (4) | −0.0079 (4) | 0.0039 (5) |
| Cl2 | 0.0705 (6) | 0.1094 (9) | 0.0565 (6) | −0.0218 (6) | 0.0104 (5) | −0.0299 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.377 (5) | C9—O1 | 1.223 (4) |
| C1—C6 | 1.388 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.466 (4) |
| C1—H1 | 1.10 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.399 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.377 (5) | C10—C15 | 1.403 (4) |
| C2—H2 | 0.85 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.368 (4) |
| C3—C4 | 1.365 (5) | C11—H11 | 0.99 (4) |
| C3—Cl1 | 1.737 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.401 (4) |
| C4—C5 | 1.399 (5) | C12—H12 | 0.91 (3) |
| C4—H4 | 0.86 (4) | C13—C14 | 1.381 (4) |
| C5—C6 | 1.393 (4) | C13—N1 | 1.378 (4) |
| C5—Cl2 | 1.734 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.371 (4) |
| C6—C7 | 1.473 (4) | C14—H14 | 0.81 (4) |
| C7—C8 | 1.305 (4) | C15—H15 | 0.93 (3) |
| C7—H7 | 0.94 (4) | N1—H1N1 | 0.78 (4) |
| C8—C9 | 1.488 (4) | N1—H2N1 | 0.76 (4) |
| C8—H8 | 0.84 (4) | ||
| C2—C1—C6 | 122.1 (3) | O1—C9—C10 | 121.7 (3) |
| C2—C1—H1 | 110.2 (18) | O1—C9—C8 | 118.8 (3) |
| C6—C1—H1 | 127.6 (18) | C10—C9—C8 | 119.5 (3) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.3 (3) | C11—C10—C15 | 116.7 (3) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 113 (2) | C11—C10—C9 | 123.5 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 128 (2) | C15—C10—C9 | 119.7 (3) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.1 (3) | C12—C11—C10 | 122.1 (3) |
| C4—C3—Cl1 | 118.8 (2) | C12—C11—H11 | 117 (2) |
| C2—C3—Cl1 | 120.1 (3) | C10—C11—H11 | 121 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.0 (3) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.2 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 125 (3) | C11—C12—H12 | 117.7 (19) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 116 (3) | C13—C12—H12 | 122.0 (19) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.5 (3) | C14—C13—N1 | 121.6 (3) |
| C6—C5—Cl2 | 121.6 (2) | C14—C13—C12 | 118.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—Cl2 | 116.8 (2) | N1—C13—C12 | 120.1 (3) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 117.0 (3) | C15—C14—C13 | 121.4 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 121.8 (3) | C15—C14—H14 | 117 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.2 (3) | C13—C14—H14 | 120 (3) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 126.6 (3) | C14—C15—C10 | 121.2 (3) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 114 (2) | C14—C15—H15 | 116.4 (18) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119 (2) | C10—C15—H15 | 122.4 (18) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 122.8 (3) | C13—N1—H1N1 | 116 (2) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120 (3) | C13—N1—H2N1 | 109 (3) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 116 (3) | H1N1—N1—H2N1 | 113 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.8 (5) | C7—C8—C9—O1 | 1.5 (5) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.4 (5) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −177.5 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—Cl1 | 180.0 (2) | O1—C9—C10—C11 | 176.4 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 1.3 (5) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −4.6 (4) |
| Cl1—C3—C4—C5 | −179.1 (2) | O1—C9—C10—C15 | −2.1 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.2 (5) | C8—C9—C10—C15 | 176.8 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—Cl2 | −179.8 (2) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | −1.8 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.9 (5) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 179.7 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −178.8 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 1.0 (5) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.1 (5) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.2 (4) |
| Cl2—C5—C6—C1 | 178.6 (2) | C11—C12—C13—N1 | 178.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 179.7 (3) | N1—C13—C14—C15 | −178.7 (3) |
| Cl2—C5—C6—C7 | −1.7 (4) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.6 (4) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −2.6 (5) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | −0.2 (5) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 177.8 (3) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 1.4 (4) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 177.8 (3) | C9—C10—C15—C14 | 180.0 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1N1···O1i | 0.78 (3) | 2.210 | 2.977 (4) | 171 (3) |
| N1—H2N1···N1ii | 0.76 (4) | 2.469 | 3.134 (5) | 147 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y−1/2, z+1/2; (ii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: ZJ2011).
References
- Awasthi, S. K., Mishra, N., Dixit, S. K., Singh, A., Yadav, M., Yadav, S. S. & Rathaur, S. (2009). Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg 80, 764–768. [PubMed]
- Awasthi, S. K., Mishra, N., Kumar, B., Sharma, M., Bhattacharya, A., Mishra, L. C. & Bhasin, V. K. (2009). Med. Chem. Res. 18, 407–420.
- Bargellini, G. & Marini-Bettolo, G. B. (1940). Gazz. Chim. Ital. 70, 170–178.
- Fonar, M. S., Simonov, Yu. A., Kravtsov, V. H., Lipkowski, J., Javolowski, A. A. & Ganin, É. V. (2001). J. Struct. Chem. 42, 459–469.
- Fun, H.-K., Patil, P. S., Dharmaprakash, S. M. & Chantrapromma, S. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Go, M. L., Wu, X. & Liu, X. L. (2005). Curr. Med. Chem. 12, 483–499.
- Hans, R. H., Guantai, E. M., Lategan, C., Smith, P. J., Wan, B., Franzblau, S. G., Gut, J., Rosenthal, P. J. & Chibale, K. (2010). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 20, 942–944. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Li, H., Kamath, K. P., Narayana, B., Yathirajan, H. S. & Harrison, W. T. A. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o1915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- Migrdichian, V. (1957). Organic Synthesis, Vol. 1, pp.171–173. New York: Reinhold Publishing Co.
- Mishra, N., Arora, P., Kumar, B., Mishra, L. C., Bhattacharya, A., Awasthi, S. K. & Bhasin, V. K. (2008). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 43, 1530–1535. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S. F., Bosen, T., Larsen, M., Schonning, K. & Kromann, H. (2004). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 12, 3047–3054. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Nógrádi, M. & Szöllösy, Á. (1996). Liebigs Ann. Chem. 10, 1651–1652.
- Oxford Diffraction (2009). CrysAlis PRO Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Yarnton, Oxfordshire, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Singh, M. K., Agarwal, A., Mahawar, C. & Awasthi, S. K. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, J. C., Bariwal, J. B., Upadhyay, K. D., Naliapara, Y. T., Soshi, S. K., Pannecouque, C. C., De Clercq, E. & Shah, A. K. (2007). Tetrahedron Lett. 48, 8472–8474.
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811020460/zj2011sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811020460/zj2011Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811020460/zj2011Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report