Abstract
Spores of all strains of Dictyostelium discoideum tested in this study germinated after a heat shock of 45 C for 30 min. Whereas the strains differed in their rates of germination, the rate for each strain was constant. A correlation existed between the rate of germination and the rate of vegetative growth when spores were inoculated into bacterial streaks. Heat shock clearly increased spore germination in D. purpureum, but the response was less dramatic than in D. discoideum. Enhancement also occurred in D. rosarium, but only in media containing peptone. Strains of D. mucoroides gave varied responses, and these could be divided into those which required mutrients for spore germination and those which did not. The spores of Polysphondylium pallidum were resistant to mild heat (45 C), but were not activated; peptone was required for germination. In contrast, the microcysts of this species were heat-labile and required no added nutrients for excystment.
Full text
PDF
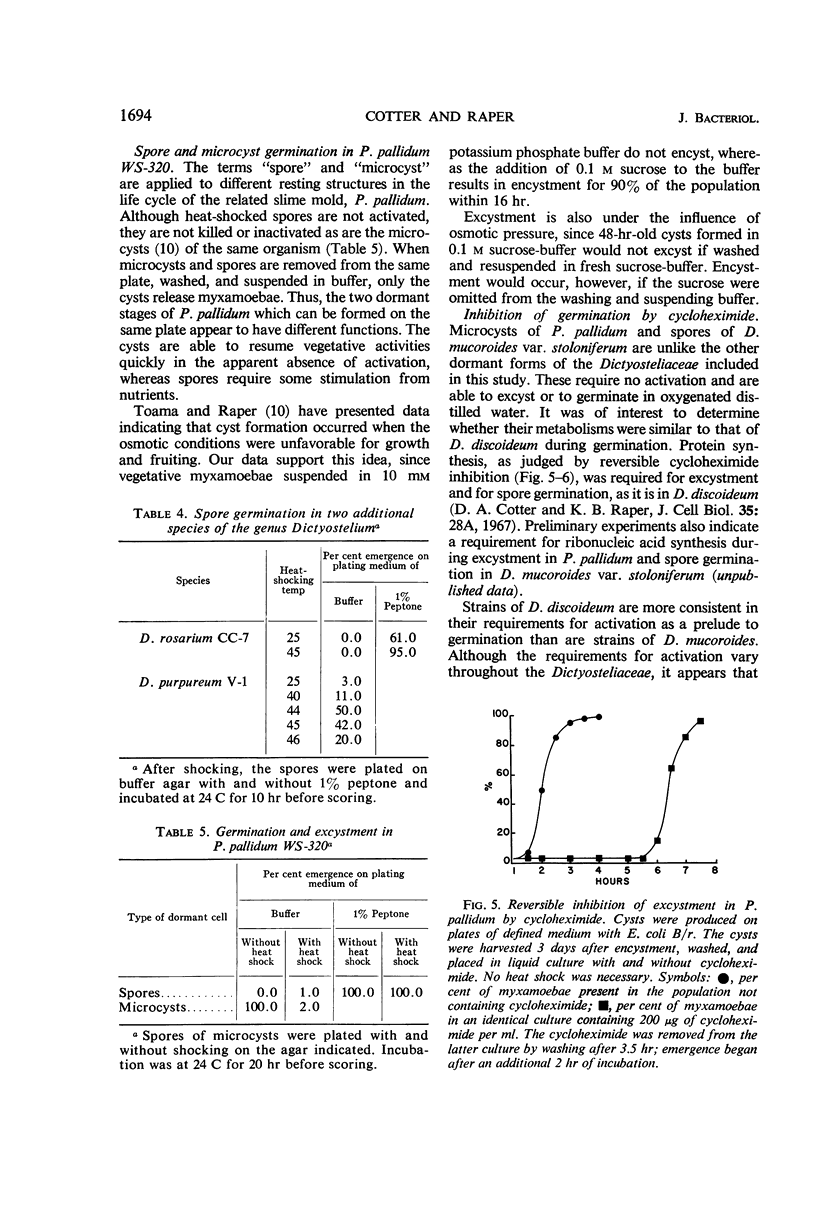
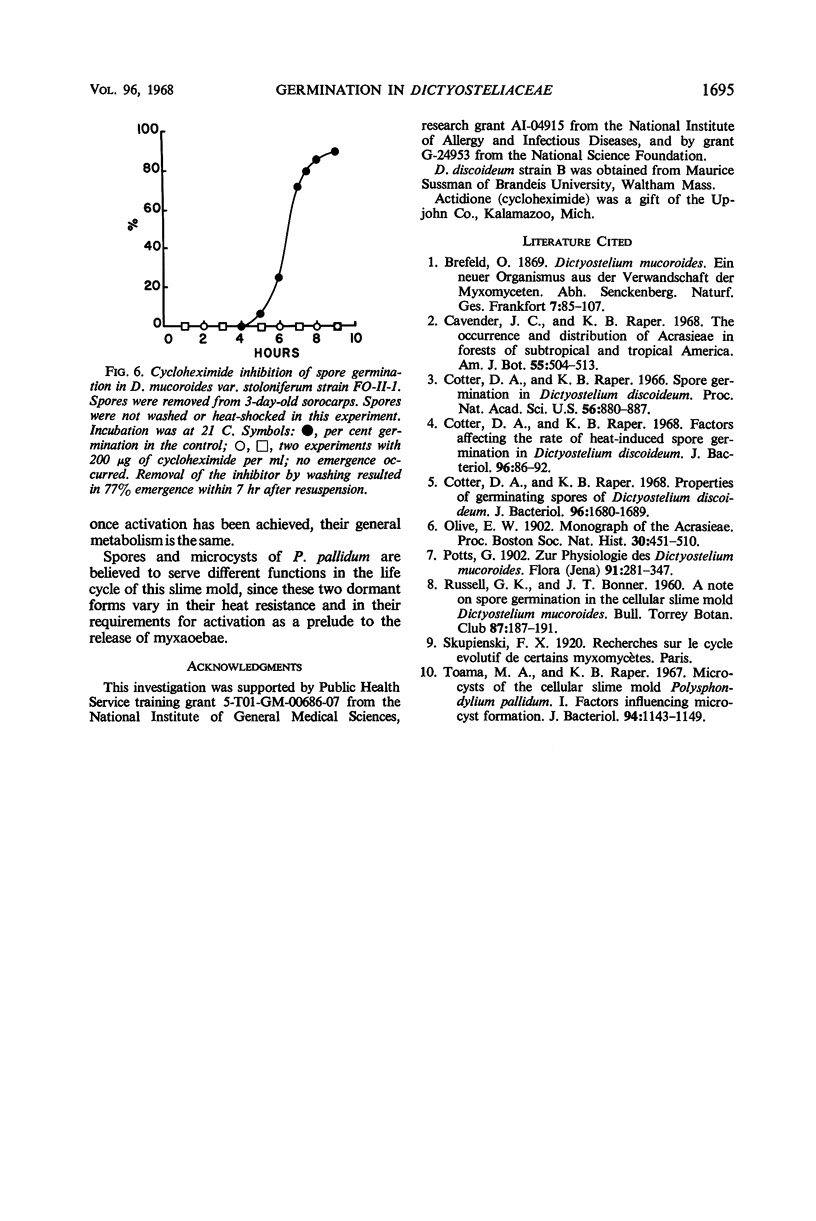
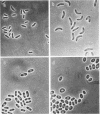
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cotter D. A., Raper K. B. Factors affecting the rate of heat-induced spore germination in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):86–92. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.86-92.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotter D. A., Raper K. B. Properties of germinating spores of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1680–1689. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1680-1689.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotter D. A., Raper K. B. Spore germination in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):880–887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toama M. A., Raper K. B. Microcysts of the cellular slime mold Polysphondylium pallidum. I. Factors influencing microcyst formation. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1143–1149. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1143-1149.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]