Abstract
Mutants defective either in the histidine permease (hisP) or in the aromatic permease (aroP) were isolated in Salmonella typhimurium and were characterized. The hisP locus had a 49% linkage to purF by phage transduction. The aroP locus was close to proA. Merozygotes diploid for the hisP gene were constructed by episomal transfer, and hisP+ was dominant over hisP. The properties of merozygotes are described and discussed. A method for the selection of revertants of hisP mutants was devised. By this method, one of the hisP mutants was characterized as an amber mutant. The specificity of the aromatic permease was investigated by using as substrates analogues of the aromatic amino acids and of histidine.
Full text
PDF

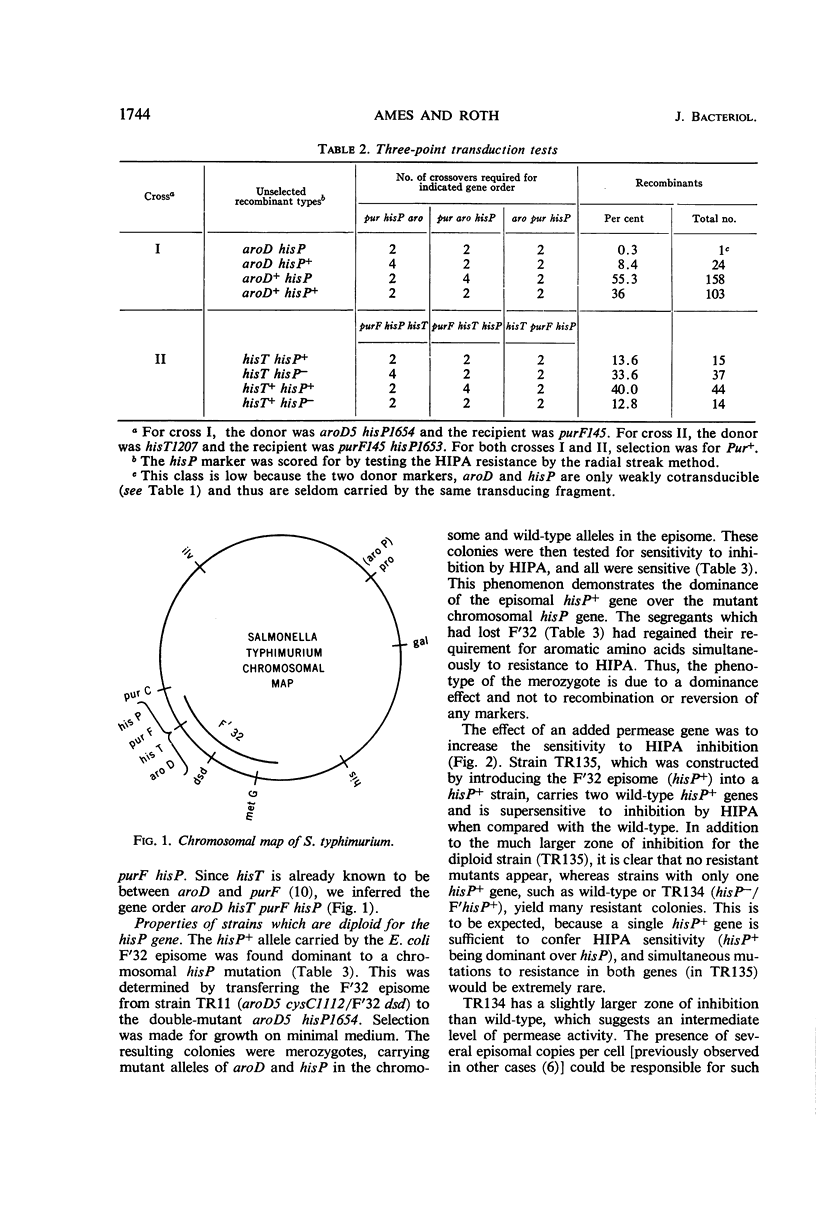



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES G. F. UPTAKE OF AMINO ACIDS BY SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1964 Jan;104:1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(64)80028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F. Lipids of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli: structure and metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):833–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.833-843.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antón D. N. Histidine regulatory mutants in Salmonella typhimurium. V. Two new classes histidine regulatory mutants. J Mol Biol. 1968 May 14;33(3):533–546. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90304-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkowitz D., Hushon J. M., Whitfield H. J., Jr, Roth J., Ames B. N. Procedure for identifying nonsense mutations. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):215–220. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.215-220.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus M., Halpern Y. S. Genetic analysis of glutamate transport and glutamate decarboxylase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1409–1415. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1409-1415.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFall E. Dominance studies with stable merodiploids in the D-serine deaminase system of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1982–1988. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1982-1988.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. R., Ames B. N. Histidine regulatory mutants in Salmonella typhimurium II. Histidine regulatory mutants having altered histidyl-tRNA synthetase. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. R., Antón D. N., Hartman P. E. Histidine regulatory mutants in Salmonella typhimurium. I. Isolation and general properties. J Mol Biol. 1966 Dec 28;22(2):305–323. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDERSON K. E., DEMEREC M. THE LINKAGE MAP OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Genetics. 1965 Jun;51:897–913. doi: 10.1093/genetics/51.6.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shifrin S., Ames B. N., FerroLuzzi-Ames G. Effect of the alpha-hydrazino analogue of histidine on histidine transport and arginine biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 25;241(14):3424–3429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sletzinger M., Firestone R. A., Reinhold D. F., Rooney C. S., Nicholson W. H. The alpha-hydrazino analog of histidine. J Med Chem. 1968 Mar;11(2):261–263. doi: 10.1021/jm00308a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL H. J., BONNER D. M. Acetylornithinase of Escherichia coli: partial purification and some properties. J Biol Chem. 1956 Jan;218(1):97–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield H. J., Jr, Martin R. G., Ames B. N. Classification of aminotransferase (C gene) mutants in the histidine operon. J Mol Biol. 1966 Nov 14;21(2):335–355. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]