Abstract
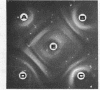
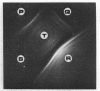
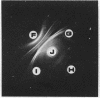
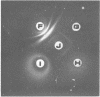
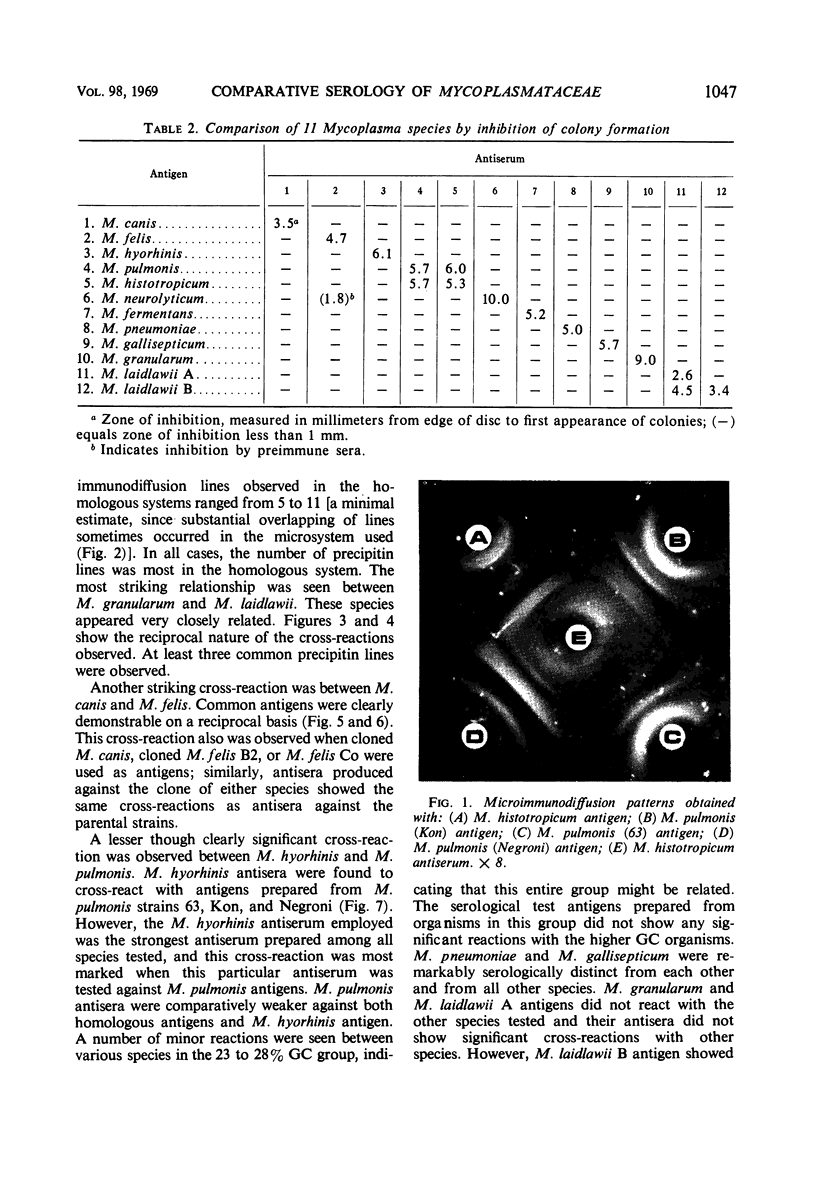
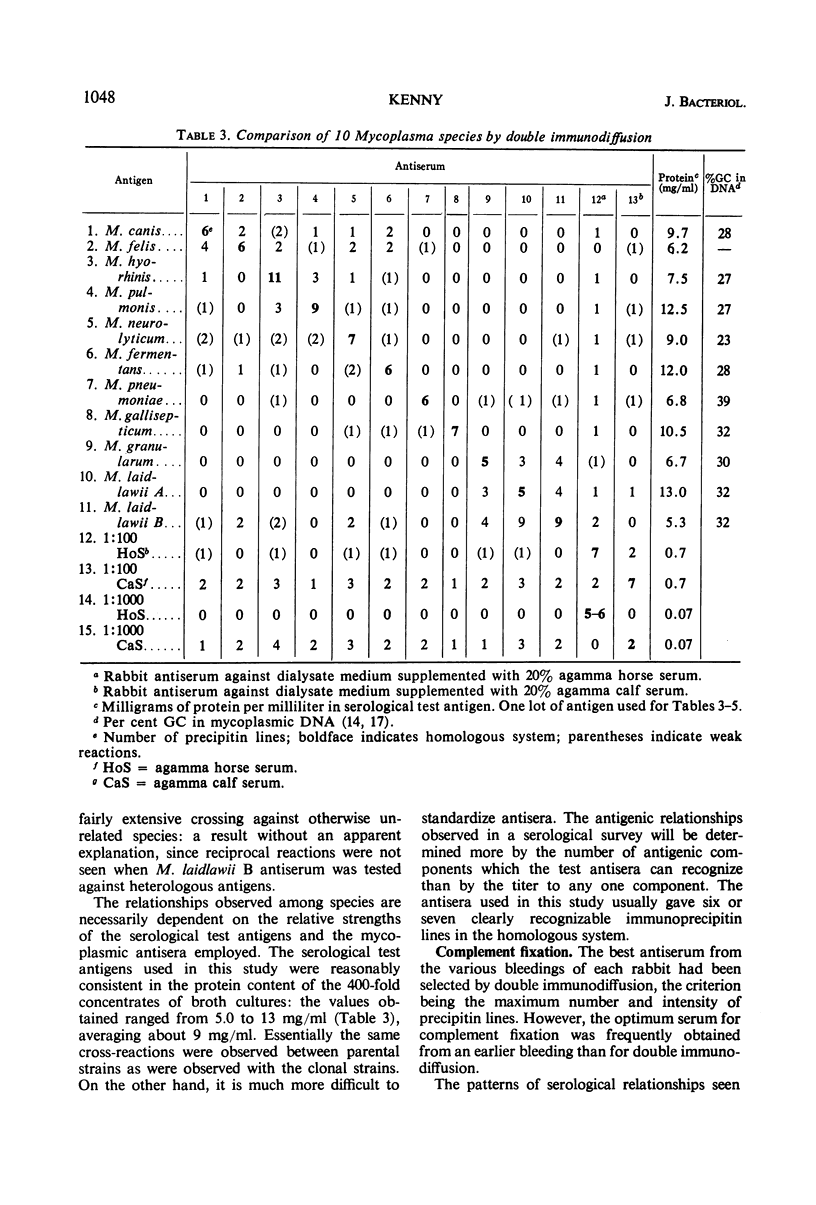
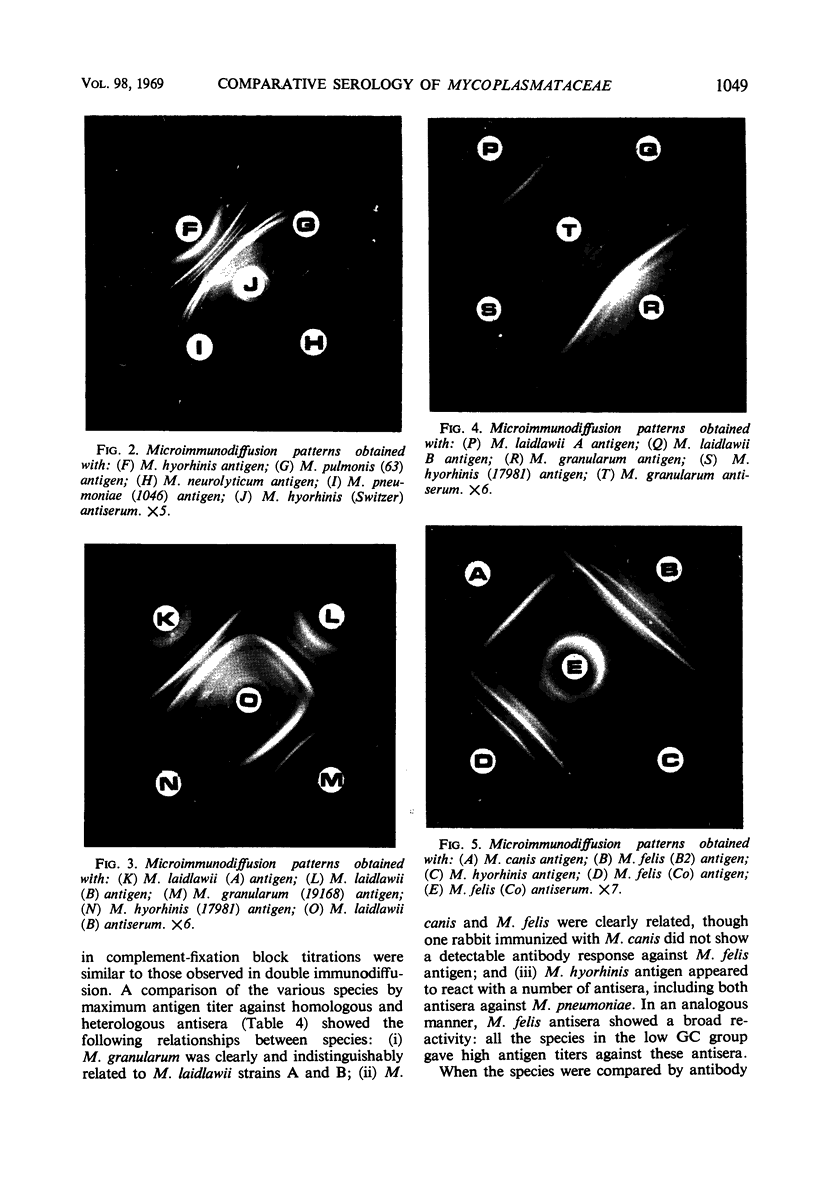
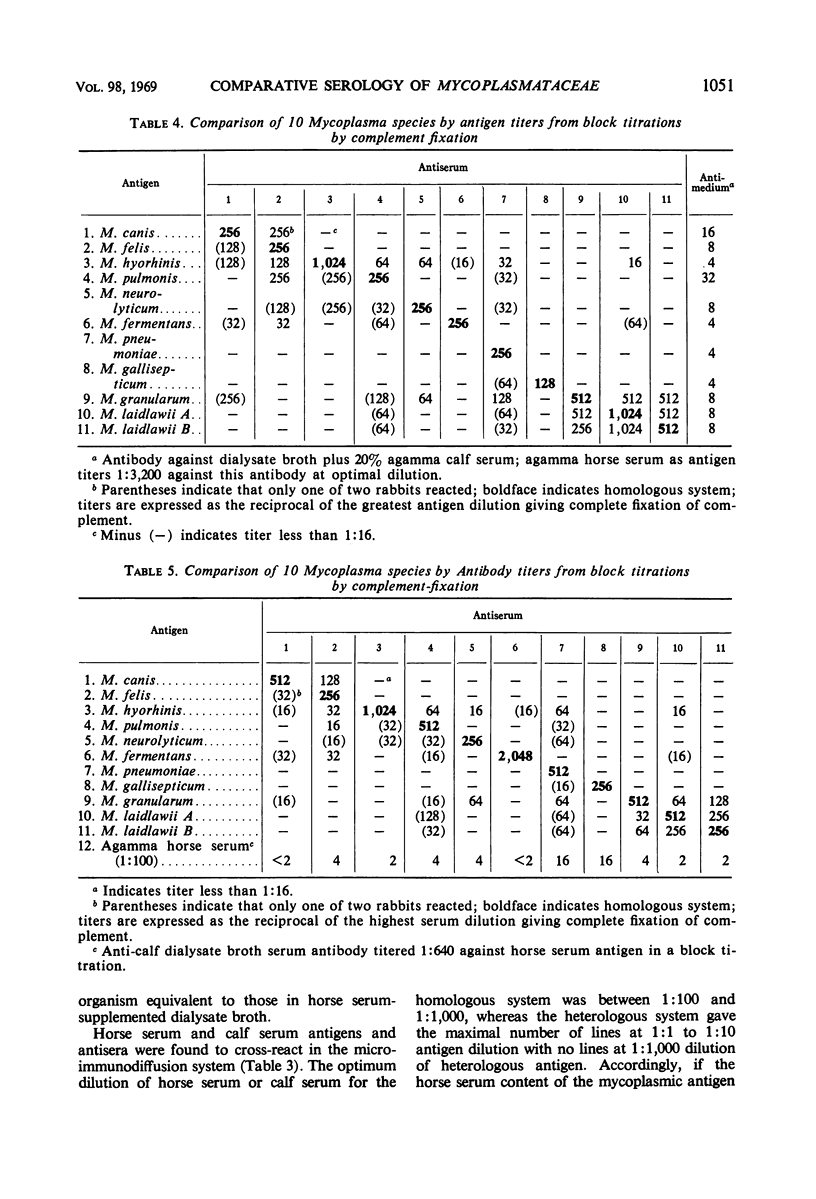
Seventeen strains of mycoplasmata representing 11 named species were compared serologically by three parameters: growth inhibition on agar, double immunodiffusion, and complement fixation. In growth-inhibition studies, a strain labeled Mycoplasma histotropicum was found related to and perhaps best classified as M. pulmonis, a relationship confirmed by double immuno-diffusion studies. A comparison of the remaining 10 species demonstrated that two pairs of species could be shown to be closely related by complement fixation and double immunodiffusion but not by growth inhibition; these were: M. granularum-M. laidlawii and M. felis-M. canis. M. pneumoniae and M. gallisepticum were the most serologically unique organisms in this study, showing very few cross-reactions with each other or other species. Overall, taxonomic groupings obtained by comparative serology appeared to correlate with the groupings obtained when the guanine plus cytosine contents of the deoxyribonucleic acid of mycoplasmata were employed as classification criteria. The group of organisms having a guanine plus cytosine content of 23 to 28% (M. canis, M. fermentans, M. hyorhinis, M. neurolyticum, and M. pulmonis) appeared to be generally serologically related. Thus the remarkable heterogeneity observed in the base composition of the deoxyribonucleic acid of order Mycoplasmatales is also reflected and apparently paralleled by a corresponding serological heterogeneity.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barile M. F., Schimke R. T., Riggs D. B. Presence of the arginine dihydrolase pathway in Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):189–192. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.189-192.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole B. C., Golightly L., Ward J. R. Characterization of mycoplasma strains from cats. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1451–1458. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1451-1458.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deeb B. J., Kenny G. E. Characterizion of Mycoplasma pulmonis variants isolated from rabbits. II. Basis for differentiation of antigenic subtypes. J Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(4):1425–1429. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.4.1425-1429.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinter Z., Danielsson D., Bakos K. Differentiation of porcine Mycoplasma strains. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Oct;41(1):77–84. doi: 10.1099/00221287-41-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. G., FREUNDT E. A. The classification and nomenclature of organisms of the pleuropneumonia group. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Feb;14(1):197–207. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-1-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENNY G. E., GRAYSTON J. T. EATON PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISM (MYCOPLASMA PNEUMONIAE) COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN: EXTRACTION WITH ORGANIC SOLVENTS. J Immunol. 1965 Jul;95:19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Heat-lability and organic solvent-solubility of mycoplasma antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):676–681. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEMCKE R. M. A SEROLOGICAL COMPARISON OF VARIOUS SPECIES OF MYCOPLASMA BY AN AGAR GEL DOUBLE-DIFFUSION TECHNIQUE. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Jan;38:91–100. doi: 10.1099/00221287-38-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEMCKE R. M. THE SEROLOGICAL DIFFERENTIATION OF MYCOPLASMA STRAINS (PLEURO-PNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS) FROM VARIOUS SOURCES. J Hyg (Lond) 1964 Jun;62:199–219. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400039930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmion B. P., Plackett P., Lemcke R. M. Immunochemical analysis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. 1. Methods of extraction and reaction of fractions from M. pneumoniae and from M. mycoides with homologous antisera and with antisera against Streptococcus MG. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1967 Apr;45(2):163–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Rogul M., Wittler R. G. Molecular genetic studies of relationships among mycoplasma, L-forms and bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):21–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morowitz H. J., Bode H. R., Kirk R. G. The nucleic acids of mycoplasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):110–114. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neimark H. Heterogeneity among the mycoplasma and relationships to bacteria. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):31–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27640.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Mycoplasma taxonomy studiedy electrophoresis of cell proteins. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):687–694. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.687-694.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B. THE FILTRABLE MICROORGANISMS OF THE PLEUROPNEUMONIA GROUP. Bacteriol Rev. 1941 Mar;5(1):1–67. doi: 10.1128/br.5.1.1-67.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer W. P. Swine mycoplasmosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):281–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR-ROBINSON D., SOMERSON N. L., TURNER H. C., CHANOCK R. M. SEROLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS AMONG HUMAN MYCOPLASMAS AS SHOWN BY COMPLEMENT-FIXATION AND GEL DIFFUSION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1261–1273. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1261-1273.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TULLY J. G. BIOCHEMICAL, MORPHOLOGICAL, AND SEROLOGICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF MYCOPLASMA OF MURINE ORIGIN. J Infect Dis. 1965 Apr;115:171–185. doi: 10.1093/infdis/115.2.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TULLY J. G., RUCHMAN I. RECOVERY, IDENTIFICATION, AND NEUROTOXICITY OF SABIN'S TYPE A AND C MOUSE MYCOPLASMA (PPLO) FROM LYOPHILIZED CULTURES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Feb;115:554–558. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-28966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Sobeslavský O., Chanock R. M. Relationship of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to other human Mycoplasma species studied by gel diffusion. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1432–1437. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1432-1437.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Razin S. Physiological and serological comparisons among strains of Mycoplasma granularum and Mycoplasma laidlawii. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1504–1512. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1504-1512.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]