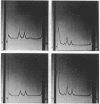
Abstract
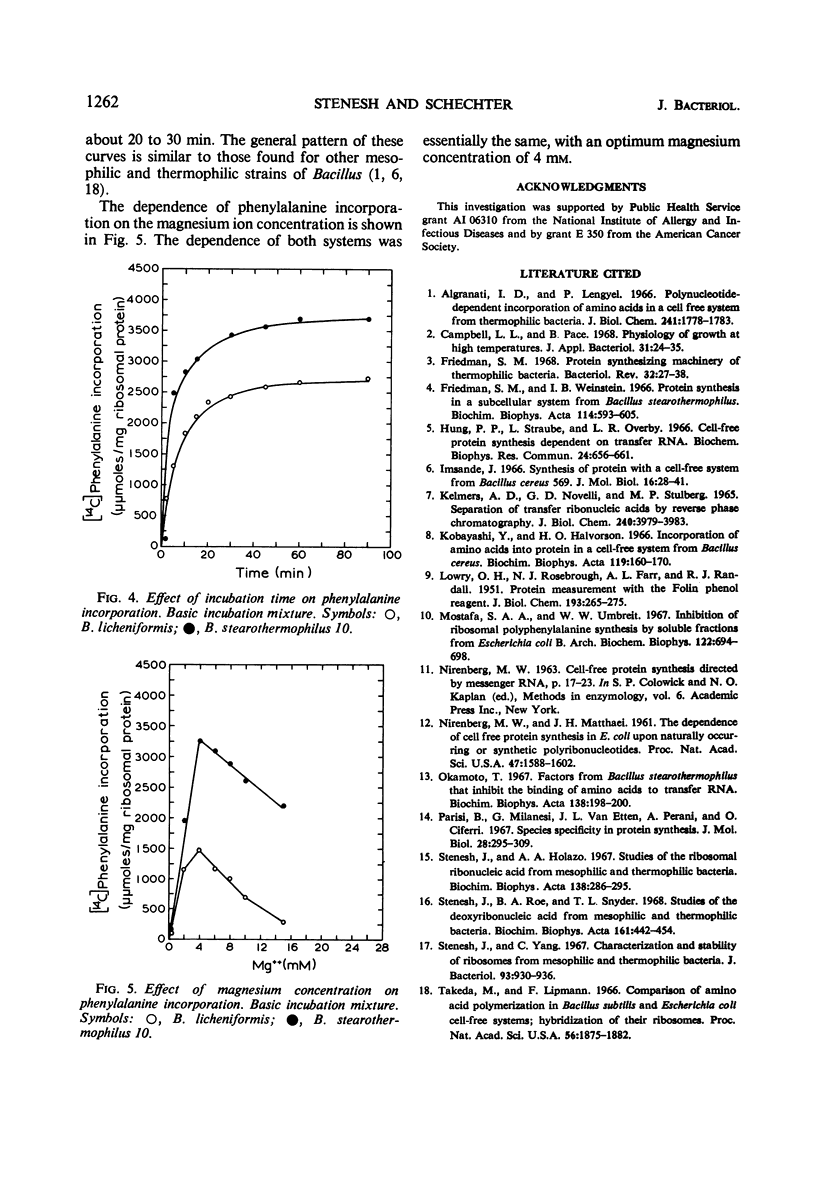
Cell-free amino acid-incorporating systems were prepared from log-phase cells of Bacillus licheniformis and B. stearothermophilus 10. No differences were observed between the two systems with respect to the types and relative amounts of the ribosomes, the time dependence of incorporation, and the optimal magnesium ion concentration (4 mm). The B. licheniformis system showed greater dependence on added transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) and was less stimulated by polyuridylic acid (poly U) than the B. stearothermophilus 10 system. Neither system was saturated at a level of 450 μg of poly U per incubation mixture. The S-100 fraction and the isolated tRNA inhibited incorporation in the B. stearothermophilus 10 system at 55 C but not at 37 C. No such inhibition was observed in the B. licheniformis system at either temperature. The tRNA prepared from B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, or B. stearothermophilus 10 could be used interchangeably in the two cell-free systems.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Algranati I. D., Lengyel P. Polynucleotide-dependent incorporation of amino acids in a cell-free system from thermophilic bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 25;241(8):1778–1783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L. L., Pace B. Physiology of growth at high temperatures. J Appl Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;31(1):24–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1968.tb00338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. M. Protein-synthesizing machinery of thermophilic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Mar;32(1):27–38. doi: 10.1128/br.32.1.27-38.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S. M., Weinstein I. B. Protein synthesis in a subcellular system from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 21;114(3):593–605. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung P. P., Straube L., Overby L. R. Cell-free protein synthesis dependent on transfer RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Sep 8;24(5):656–661. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90374-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imsande J., Caston J. D. Synthesis of protein with a cell-free system from Bacillus cereus 569. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):28–41. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80260-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelmers A. D., Novelli G. D., Stulberg M. P. Separation of transfer ribonucleic acids by reverse phase chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3979–3983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Halvorson H. O. Incorporation of amino acids into protein in a cell-free system from Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 18;119(1):160–170. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIRENBERG M. W., MATTHAEI J. H. The dependence of cell-free protein synthesis in E. coli upon naturally occurring or synthetic polyribonucleotides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1588–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto T. Factors from Bacillus stearothermophilus that inhibit the binding of amino acids to transfer RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Mar 29;138(1):198–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90603-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi B., Milanesi G., Van Etten J. L., Perani A., Ciferri O. Species specificity in protein synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1967 Sep 14;28(2):295–309. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(67)80011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenesh J., Holazo A. A. Studies of the ribosomal ribonucleic acid from mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Apr 18;138(2):286–295. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90489-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenesh J., Roe B. A., Snyder T. L. Studies of the deoxyribonucleic acid from mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Jul 23;161(2):442–454. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steneshi J., Yang C. Characterization and stability of ribosomes from mesophilic and thermophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):930–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.930-936.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda M., Lipmann F. Comparison of amino Acid polymerization in B. Subtilis and e. Coli cell-free systems; hybridization of their ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1875–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]