Abstract
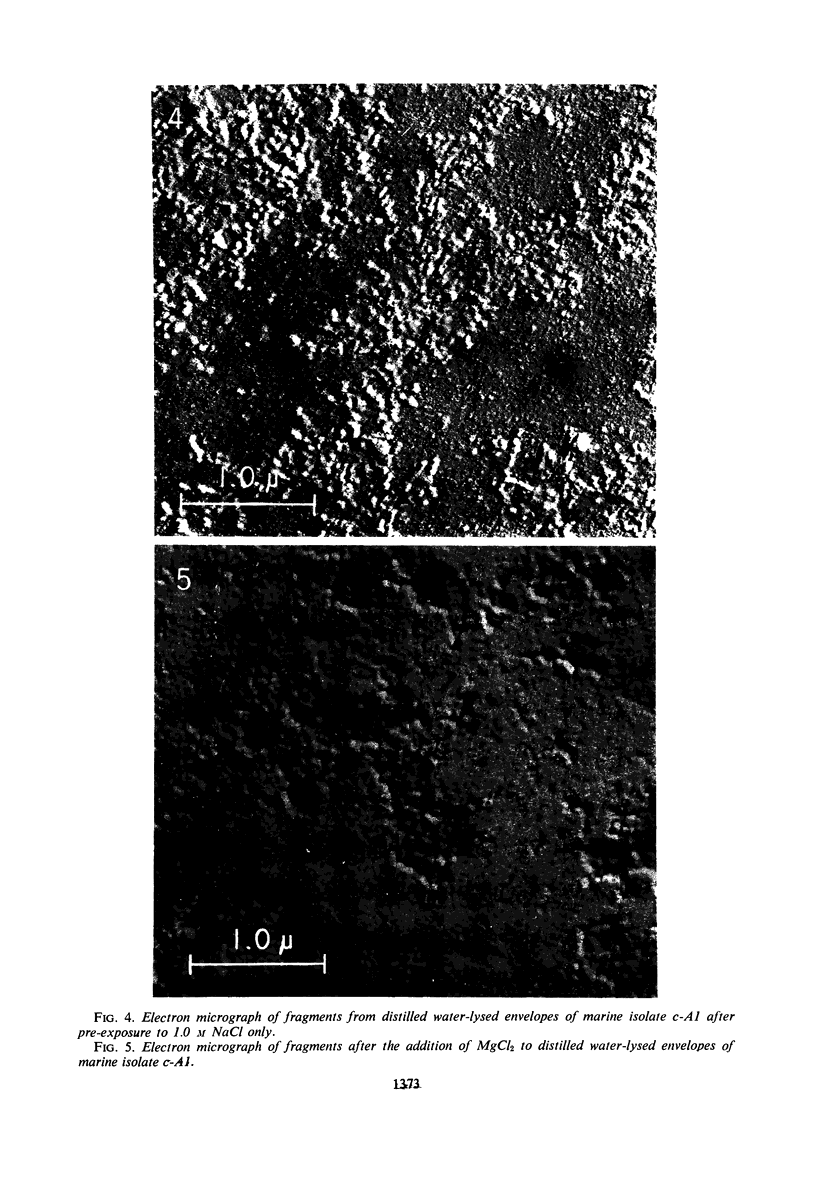
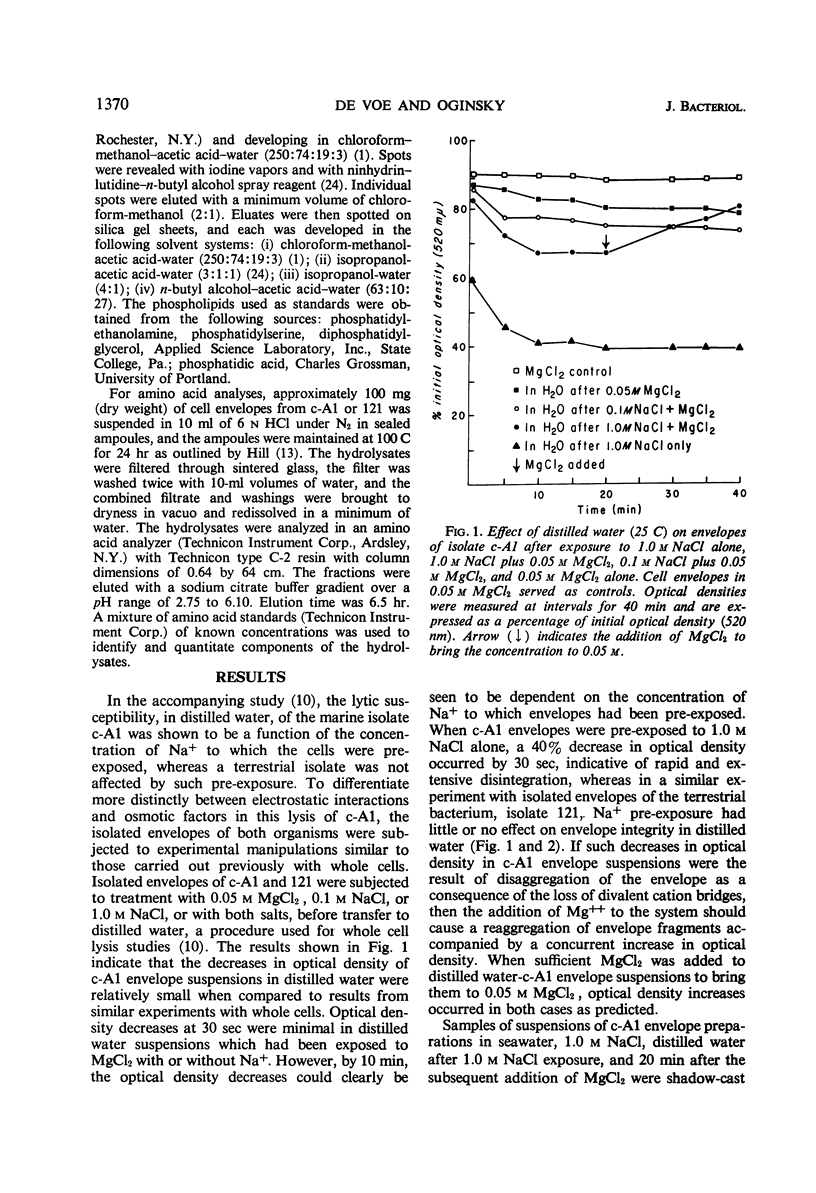
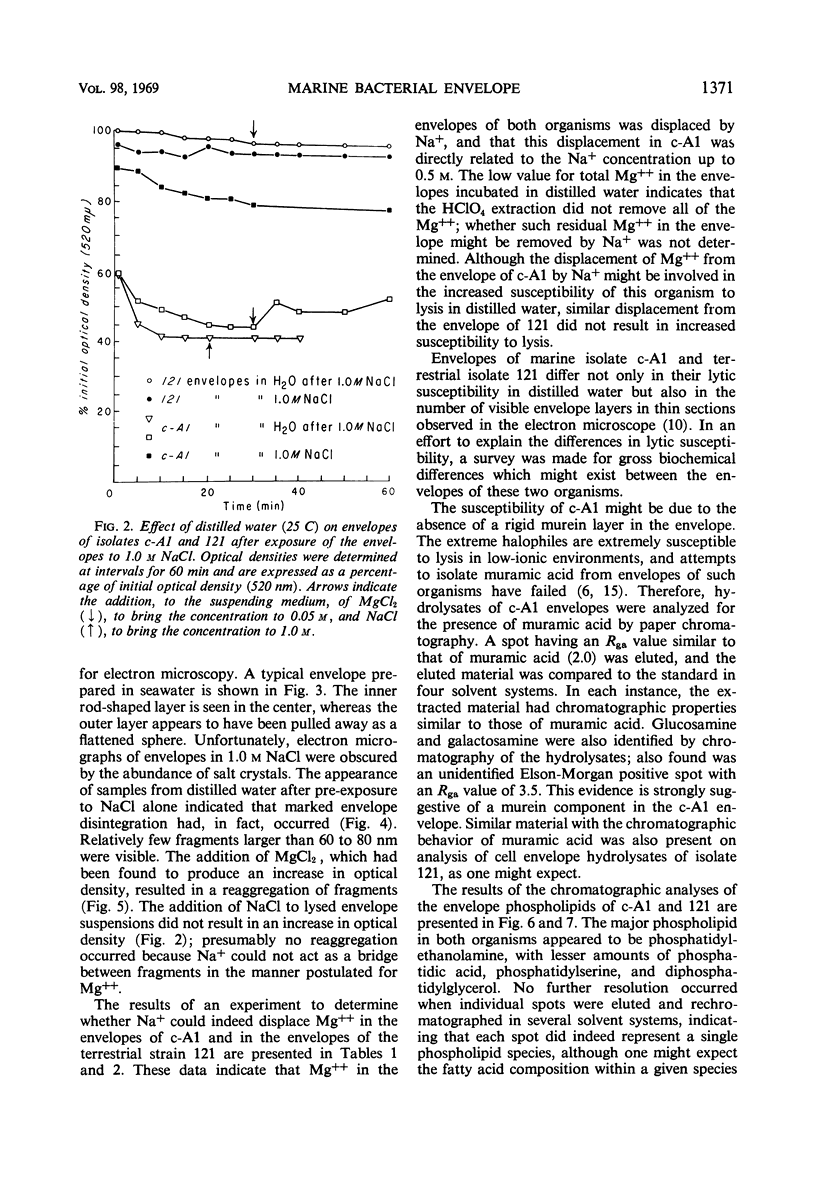
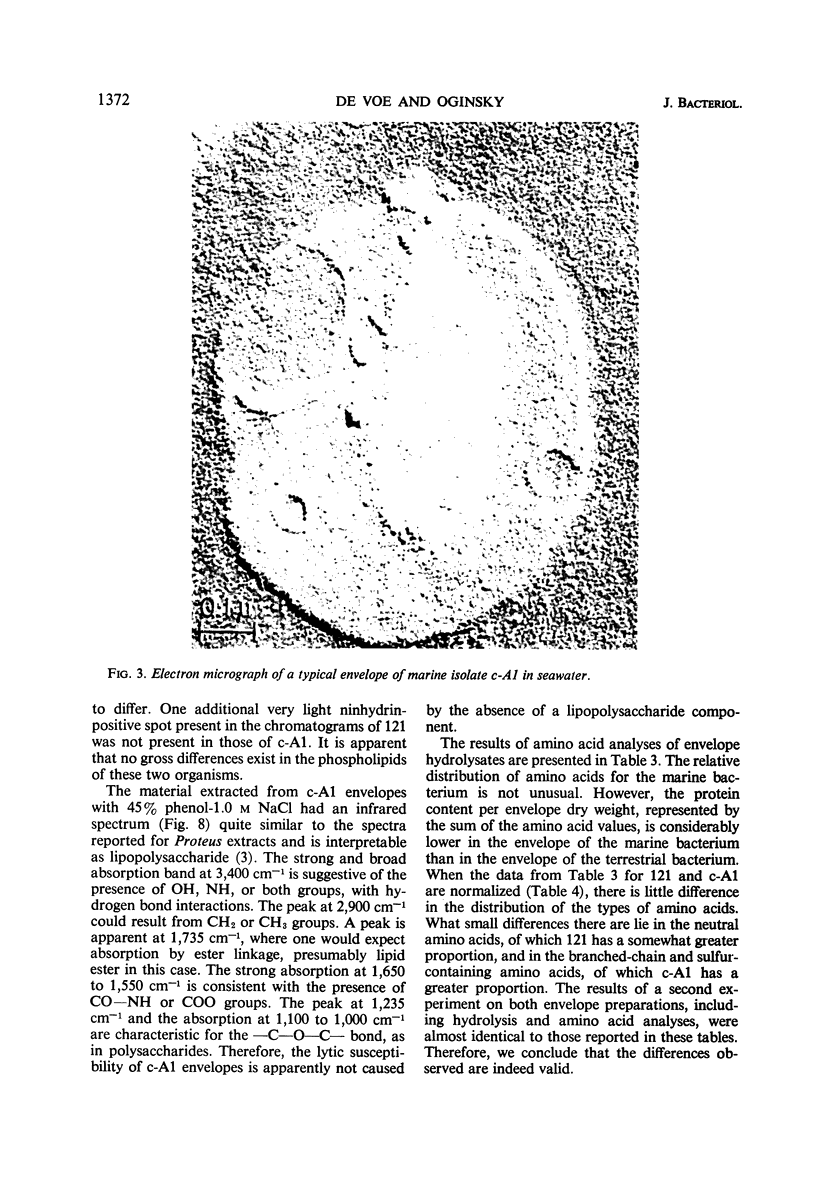
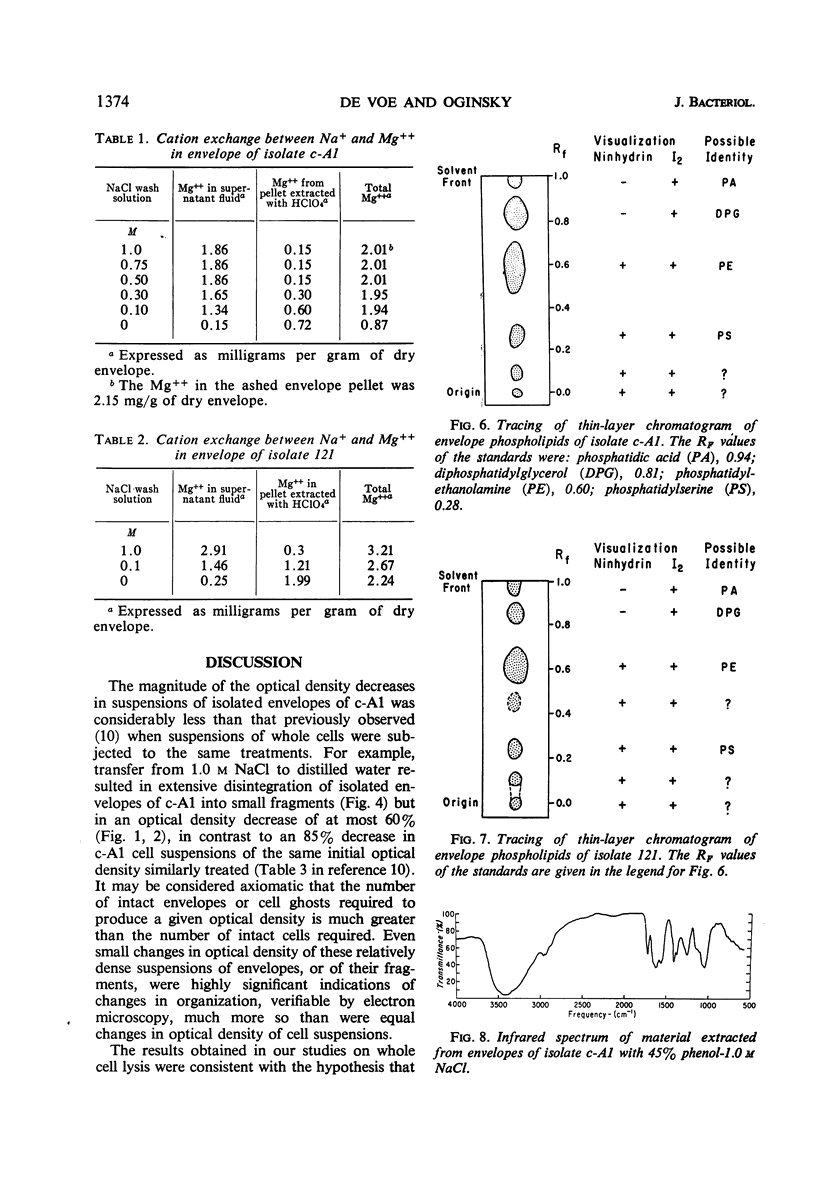
Envelopes of a marine isolate, c-A1, and of a terrestrial isolate, 121, were compared for their susceptibility to disintegration in distilled water after exposure to 0.05 m MgCl2 and to 0.1 and 1.0 m NaCl. After exposure to MgCl2 alone, both types of envelopes remained intact in distilled water. Envelopes of marine isolate c-A1, but not of the terrestrial isolate, fragmented in distilled water after exposure to 1.0 m NaCl. Partial reaggregation of the c-A1 envelope fragments occurred on addition of MgCl2. In cation-exchange experiments, bound Mg++ in the envelopes of both organisms was displaced by Na+. The envelopes of c-A1 were found to contain lipopolysaccharide, muramic acid, and a variety of phospholipids, of which the major component was phosphatidylethanolamine, accompanied by lesser amounts of phosphatidic acid, diphosphatidylglycerol, and phosphatidylserine. Analyses of envelope acid hydrolysates revealed a similar amino acid distribution in the marine and terrestrial isolates, but envelopes of c-A1 had less than half the total amino acid content of envelopes of 121 per envelope dry weight. Possible relationships between cations and biochemical components of the envelopes are considered in terms of differences in behavior of the two organisms in low ionic environments.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMSON D., BLECHER M. QUANTITATIVE TWO-DIMENSIONAL THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF NATURALLY OCCURRING PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Oct;5:628–631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbell M. A., Eagon R. G. The role of multivalent cations in the organization and structure of bacterial cell walls. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Mar 22;22(6):664–671. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERST M., BRINI M., JOSSANG P. T., KREMBEL J., MINCK R. ETUDE PAR SPECTROGRAPHIE INFRA-ROUGE DE L'ANTIG'ENE SOMATIQUE DE PROTEUS P 18. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Feb;106:249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D., SHOREY C. D. Preliminary observations on the cell envelopes of two species of Halobacterium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 7;59:258–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90731-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D., TURNER H. P. MEMBRANE STABILITY AND SALT TOLERANCE IN GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Nature. 1963 Jul 20;199:301–302. doi: 10.1038/199301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckmire F. L., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XIV. On the mechanism of lysis of a marine bacterium. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Aug;11(4):677–691. doi: 10.1139/m65-091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Forsberg C., Matula T. I., Buckmire F. L., MacLeod R. A. Nutrition and metabolism of marine bacteria. XVI. Formation of protoplasts, spheroplasts, and related forms from a gram-negative marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1764–1777. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1764-1777.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Voe I. W., Oginsky E. L. Antagonistic effect of monovalent cations in maintenance of cellular integrity of a marine bacterium. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jun;98(3):1355–1367. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.3.1355-1367.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner R. J. Colorimetric determination of magnesium in plasma or serum by means of titan yellow. Biochem J. 1946;40(5-6):828–831. doi: 10.1042/bj0400828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORNUNG M. PAPER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF PNEUMOCOCCAL CELL-WALL HYDROLYSATES CONTAINING GLUCOSAMINE, GALACTOSAMINE, MURAMIC ACID, AND PEPTIDES. J Bacteriol. 1963 Dec;86:1345–1346. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.6.1345-1346.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. L. Hydrolysis of proteins. Adv Protein Chem. 1965;20:37–107. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60388-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUSHNER D. J., BAYLEY S. T., BORING J., KATES M., GIBBONS N. E. MORPHOLOGICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF CELL ENVELOPES OF THE EXTREME HALOPHILE, HALOBACTERIUM CUTIRUBRUM. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Jun;10:483–497. doi: 10.1139/m64-058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACLEOD R. A. THE QUESTION OF THE EXISTENCE OF SPECIFIC MARINE BACTERIA. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Mar;29:9–24. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY R. G., STEED P., ELSON H. E. THE LOCATION OF THE MUCOPEPTIDE IN SECTIONS OF THE CELL WALL OF ESCHERICHIA COLI AND OTHER GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA. Can J Microbiol. 1965 Jun;11:547–560. doi: 10.1139/m65-072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. T., Elson L. A. A colorimetric method for the determination of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylchrondrosamine. Biochem J. 1934;28(3):988–995. doi: 10.1042/bj0280988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERKINS H. R., ROGERS H. J. The products of the partial acid hydrolysis of the mucopeptide from cell walls of Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochem J. 1959 Aug;72:647–654. doi: 10.1042/bj0720647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soo-Hoo T. S., Brown A. D. A basis of the specific sodium requirement for morphological integrity of Halobacterium halobium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 1;135(1):164–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(67)90020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Strange R. E. Variation in content and distribution of magnesium, and its influence on survival, in Aerobacter aerogenes grown in a chemostat. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Aug;44(2):273–279. doi: 10.1099/00221287-44-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





