Abstract
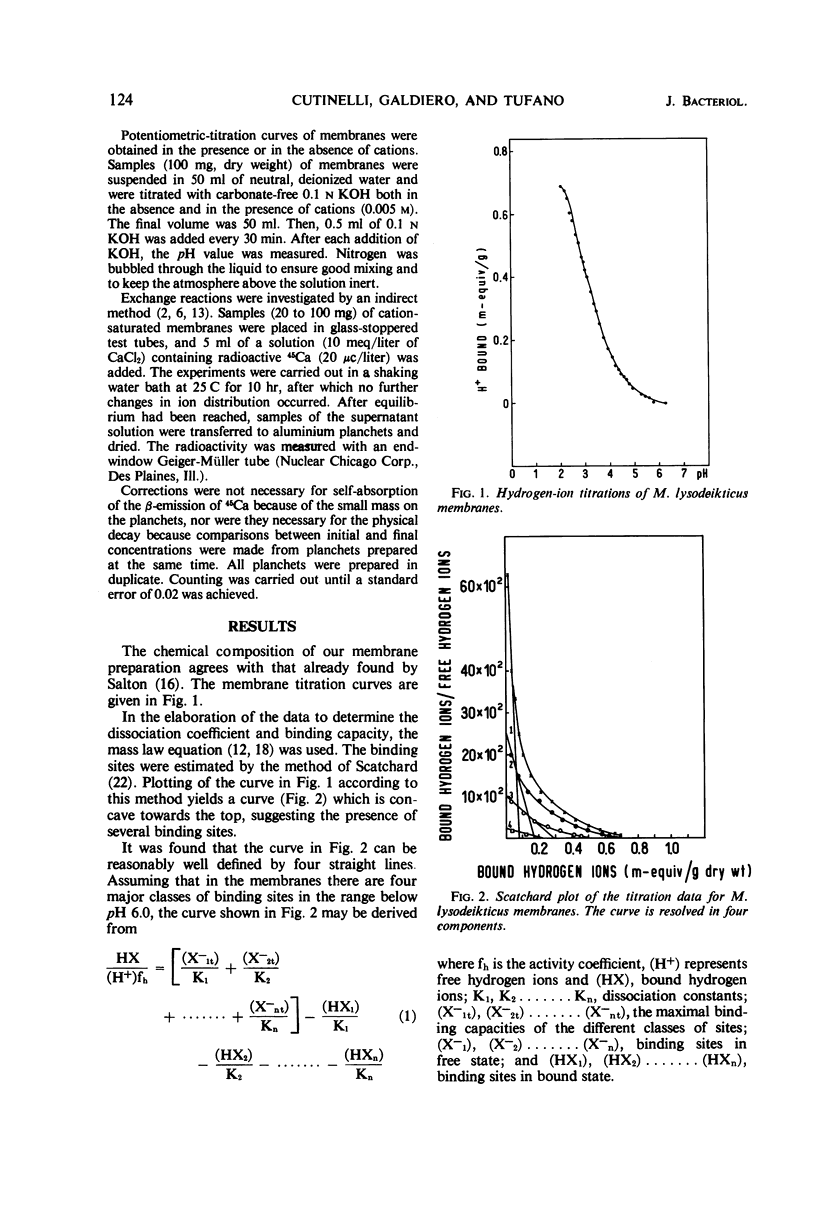
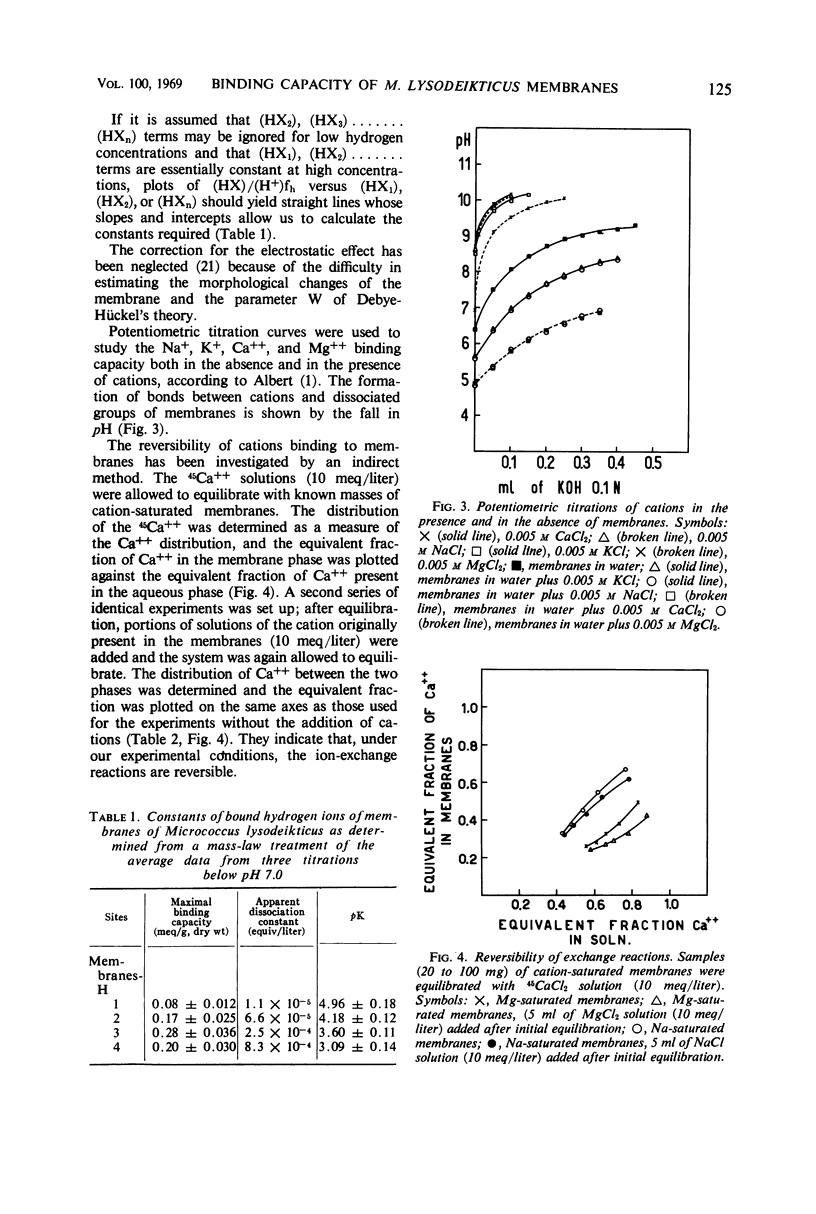
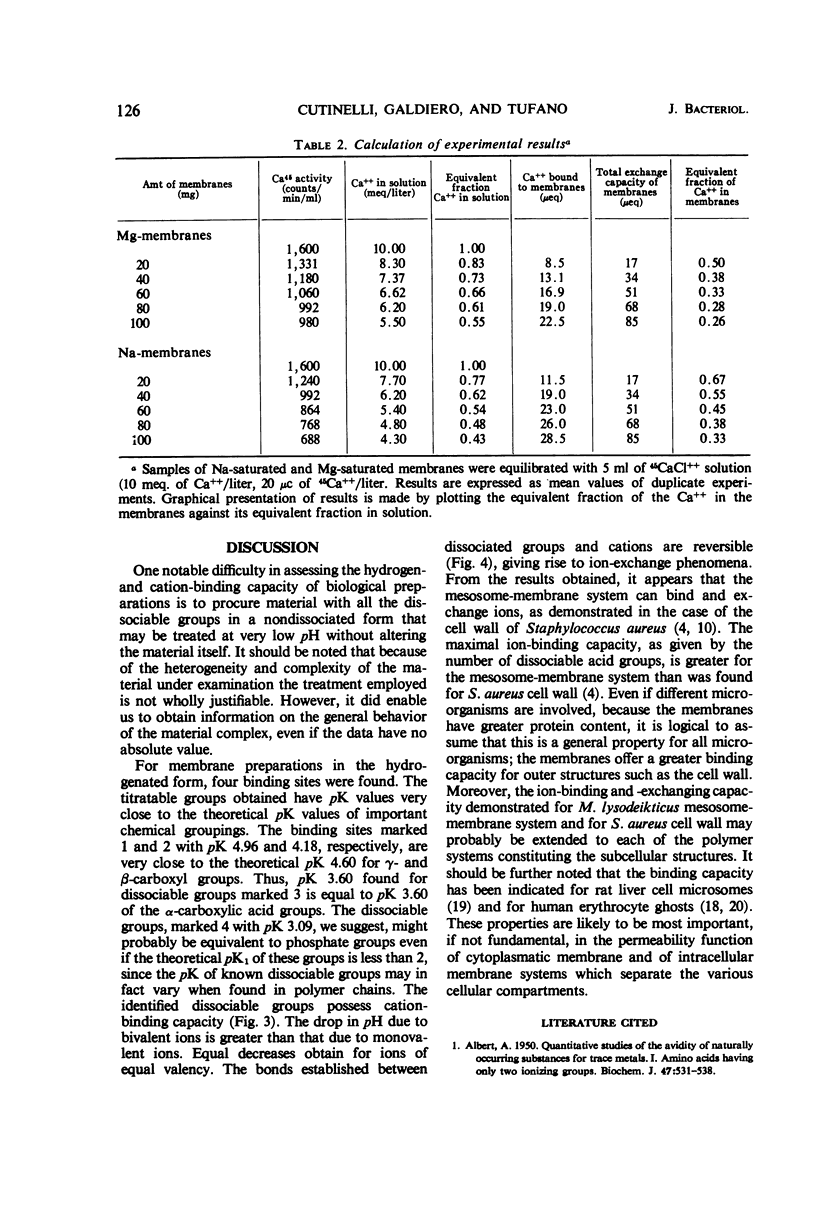
A study was made of H+, Na+, K+, Ca++, and Mg++ binding and ion-exchange properties of the plasma-mesosome membrane system isolated from Micrococcus lysodeikticus strain NCTC 2665. Titration curves were obtained on membranes prepared according to the method of M. R. J. Salton and further exposed to pH 4 for 4 hr (membranes-H). The dissociation coefficients and binding capacities were obtained by applying the mass law equation and the plot of G. Schatchard to the data. The membranes-H possess four kinds of dissociable groups with pK 4.96, 4.18, 3.60, and 3.09, respectively, and a total binding capacity of 0.65 meq/g (dry weight). Potentiometric titrations of cations in the presence and in the absence of membranes-H show that cations (Na+, K+, Ca++, and Mg++) are bound by the dissociated groups of the membrane. The fall in pH value for bivalent cations is greater than that for monovalent cations. Cations of the same valency produce equal diminutions on pH. Furthermore, ion-exchange tests carried out on membranes saturated with Mg++ or Na+ and suspended in a medium containing 45Ca show that the cations are reversibly bound.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERT A. Quantitative studies of the avidity of naturally occurring substances for trace metals; amino-acids having only two ionizing groups. Biochem J. 1950 Nov-Dec;47(5):531–538. doi: 10.1042/bj0470531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D. HYDROGEN ION TITRATIONS OF INTACT AND DISSOLVED LIPOPROTEIN MEMBRANES. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:491–508. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80272-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutinelli C., Galdiero F. Ion-binding properties of the cell wall of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):2022–2023. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.2022-2023.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNSTONE J. R. Ion-exchange reactions between cartilage and various cations. Biochem J. 1960 Oct;77:164–170. doi: 10.1042/bj0770164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galdiero F., Lembo M., Tufano M. A. Affinity of various cations for Staphylococcus aureus cell-wall. Experientia. 1968 Jan 15;24(1):34–36. doi: 10.1007/BF02136776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh B. K., Carroll K. K. Isolation, composition, and structure of membrane of Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Feb;95(2):688–699. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.2.688-699.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANUI H., CARVALHO A. P., PACE N. Relationship of hydrogen ion binding to sodium and potassium binding by rat liver cell microsomes and human erythrocyte ghosts. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1962 Jun;59:241–250. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030590303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANUI H., PACE N. Sodium and potassium binding by human erythrocyte ghosts. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1962 Jun;59:251–257. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030590304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANUI H., PACE N. Sodium and potassium binding by rat liver cell microsomes. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Jul 20;42(6):1325–1345. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.6.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton M. R., Freer J. H. Composition of the membranes isolated from several Gram-positive bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 18;107(3):531–538. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton M. R., Netschey A. Physical chemistry of isolated bacterial membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Oct 18;107(3):539–545. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90198-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBULL C. Characterization of the protoplasmic constituents of bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1953 Dec;66(6):696–702. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.6.696-702.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



