Abstract
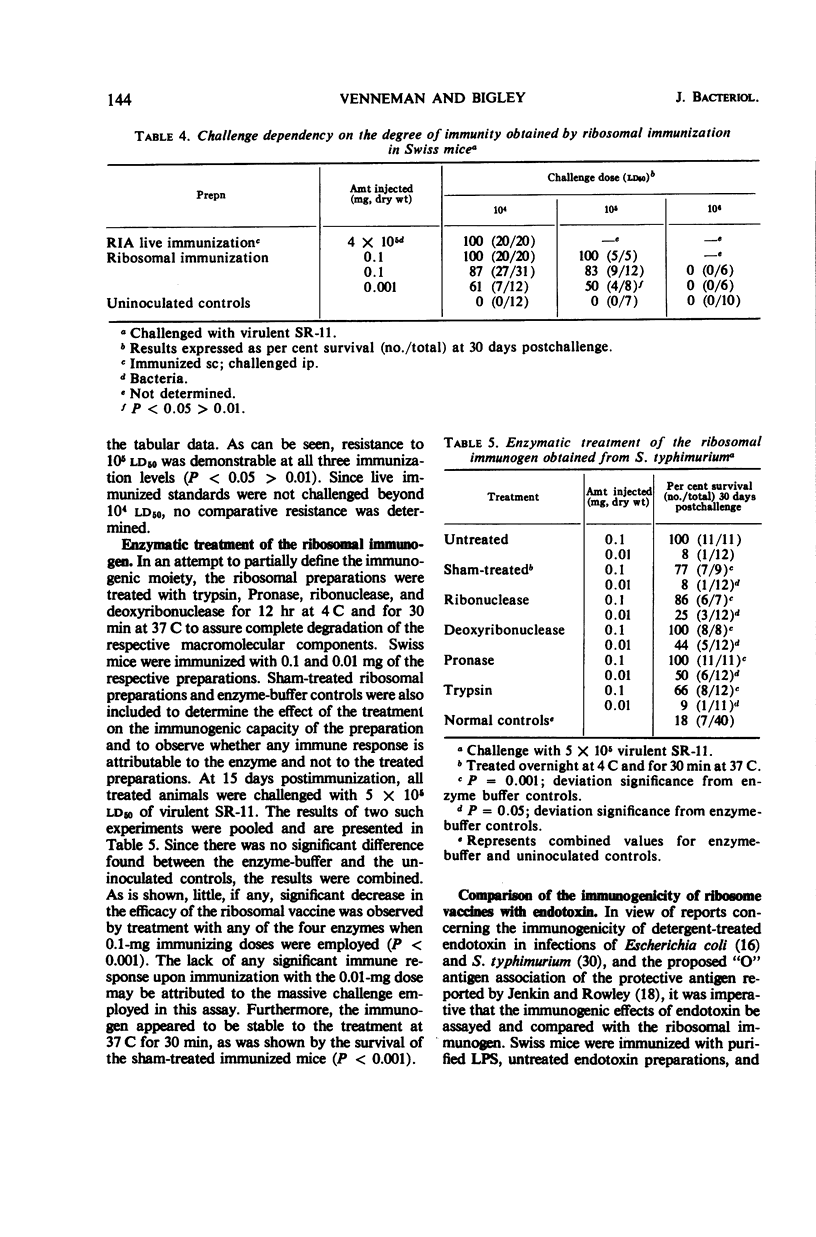
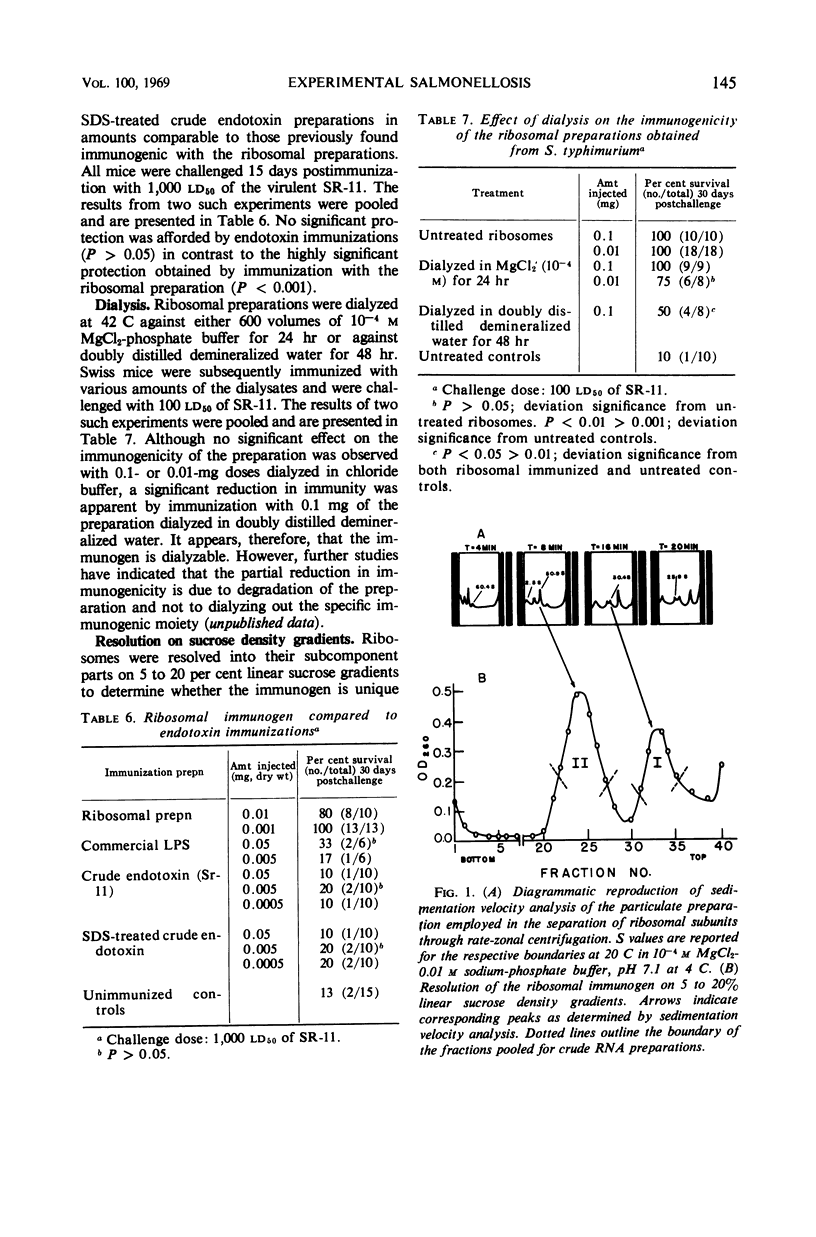
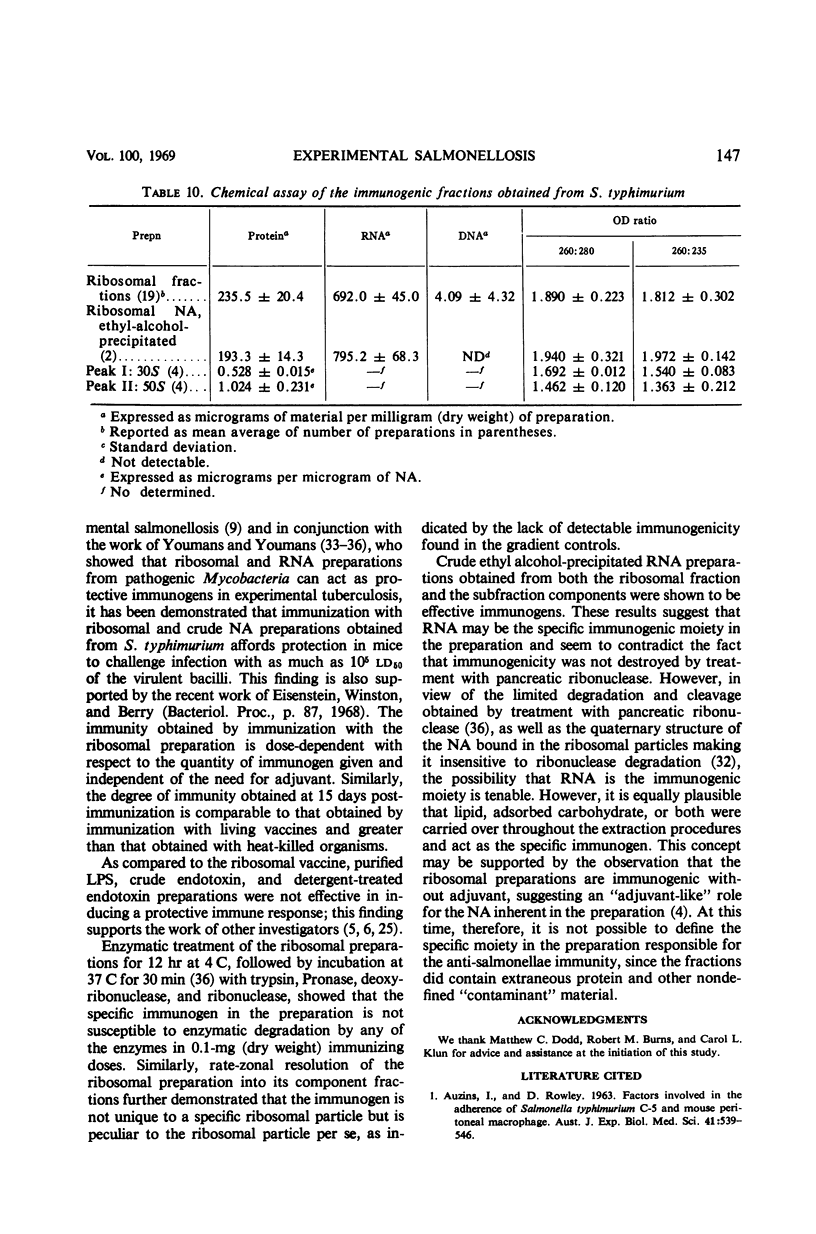
Ribosomal preparations obtained from Salmonella typhimurium by differential centrifugation and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) treatment of the bacillary lysate were found to be immunogenic in F1 hybrid (C3H/HeJ × DBA/2J) and albino Swiss mice, as determined by progressive host survival. The immunity obtained was independent of the need for adjuvant and dependent on the dosage of immunogen given. Immunizations with the ribosomal preparations induced an immune response comparable to that obtained by vaccination with living organisms and significantly greater than that obtained by immunization with heat-killed salmonellae, purified lipopolysaccharide, or crude and SDS-treated endotoxin preparations. No effect on the immunogenicity of the ribosomal fraction was observed by enzymatic treatment with trypsin, Pronase, deoxyribonuclease, and pancreatic ribonuclease. Linear sucrose density gradient resolution of the preparations showed that the immunogenicity of the ribosomal fraction was not unique to any one of its subcomponents. Ethyl alcohol-precipitated, crude ribonucleic acid preparations obtained from the ribosomal and sucrose density-resolved ribosomal preparations were found to induce an immune response comparable to that obtained by immunization with the entire ribosomal fraction. Dialysis in doubly distilled demineralized water slightly reduced the immunogenicity of the preparation; however, comparable dialysis in 10−4m MgCl2-phosphate buffer did not. Chemical assays of the preparations found to be immunogenic were performed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUZINS I., ROWLEY D. FACTORS INVOLVED IN THE ADHERENCE OF S. TYPHIMURIUM C5 AND MOUSE PERITONEAL MACROPHAGES. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1963 Oct;41:539–546. doi: 10.1038/icb.1963.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Mackaness G. B., Collins F. M. Mechanisms of acquired resistance in mouse typhoid. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):585–600. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun W., Firshein W. Biodynamic effects of oligonucleotides. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Jun;31(2):83–94. doi: 10.1128/br.31.2.83-94.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of specific immune mouse serum on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in mice preimmunized with living or ethyl alcohol-killed vaccines. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):676–683. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.676-683.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M. Effect of specific immune mouse serum on the growth of Salmonella enteritidis in nonvaccinated mice challenged by various routes. J Bacteriol. 1969 Feb;97(2):667–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.2.667-675.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Infection-immunity in experimental salmonellosis. J Exp Med. 1966 Oct 1;124(4):601–619. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.4.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Mackaness G. B. Delayed hypersensitivity and arthus reactivity in relation to host resistance in salmonella-infected mice. J Immunol. 1968 Nov;101(5):830–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. M., Milne M. Heat-labile antigens of Salmonella enteritidis. II. Mouse-protection studies. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):549–557. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.549-557.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURNESS G. Interaction between Salmonella typhimurium and phagocytic cells in cell culture. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):272–277. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOBSON D. Resistance to reinfection in experimental mouse typhoid. J Hyg (Lond) 1957 Sep;55(3):334–343. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400037244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKIN C. R., ROWLEY D. BASIS FOR IMMUNITY TO TYPHOID IN MICE AND THE QUESTION OF "CELLULAR IMMUNITY". Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Dec;27:391–404. doi: 10.1128/br.27.4.391-404.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENKIN C. R., ROWLEY D. PARTIAL PURIFICATION OF THE "PROTECTIVE" ANTIGEN OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM AND ITS DISTRIBUTION AMONGST VARIOUS STRAINS OF BACTERIA. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1965 Feb;43:65–78. doi: 10.1038/icb.1965.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. L. Immunogenicity of deoxycholate-disrupted endotoxins. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jan;97(1):13–15. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.1.13-15.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarini R. A., Santangelo E. Effect of chloramphenicol on the synthesis and stability of ribonucleic acid in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1212–1220. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1212-1220.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B., Blanden R. V. Cellular immunity. Prog Allergy. 1967;11:89–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Previte J. J. Immunogenicity of irradiated Salmonella typhimurium cells and endotoxin. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2165–2170. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2165-2170.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SATO I., TANAKA T., SAITO K., MITSUHASHI S. Inhibition of Salmonella enteritidis ingested in mononuclear phagocytes from liver and subcutaneous tissue of mice immunized with live vaccine. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1306–1312. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1306-1312.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarmina D. F., Milner K. C., Ribi E., Rudbach J. A. Modification of selected host-reactive properties of endotoxin by treatment with sodium deoxycholate. J Bacteriol. 1968 Nov;96(5):1611–1616. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.5.1611-1616.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Goldman D. S., Sachs I. B. Properties and fine structure of the ribosomes from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):122–129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS A. S., YOUMANS G. P. IMMUNOGENIC ACTIVITY OF A RIBOSOMAL FRACTION OBTAINED FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1291–1298. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1291-1298.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUMANS A. S., YOUMANS G. P. NATURE OF THE LABILE IMMUNOGENIC SUBSTANCE IN THE PARTICULATE FRACTION ISOLATED FROM MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1030–1037. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1030-1037.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Effect of trypsin and ribonuclease on the immunogenic activity of ribosomes and ribonucleic acid isolated from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2146–2154. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2146-2154.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youmans A. S., Youmans G. P. Preparation of highly immunogenic ribosomal fractions of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by use of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jun;91(6):2139–2145. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.6.2139-2145.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


