Abstract
Some strains of Staphylococcus aureus grew as compact colonies in Brain Heart Infusion–serum-soft agar but as diffuse colonies in a modified Staphylococcus 110–serum-soft agar. These strains were designated “pseudocompact.” Strains showing compact-type colonial morphology in both media were designated “compact,” whereas strains showing diffuse-type growth in both media were designated “diffuse.” It was observed that the most recently isolated strains of S. aureus were of the pseudocompact type, whereas most stock culture strains tested were of the compact type. Using cultures recently isolated from clinical material, it was shown that pseudocompact strains convert to compact-type growth after prolonged incubation. Interconversion of compact, diffuse, and pseudocompact growth forms could be induced in vitro by appropriate cultural conditions, and conversion of growth type was also observed in vivo. Femoral abscesses produced in mice by four different compact-type strains showed conversion to diffuse or pseudocompact-type growth during the course of the infection.
Full text
PDF

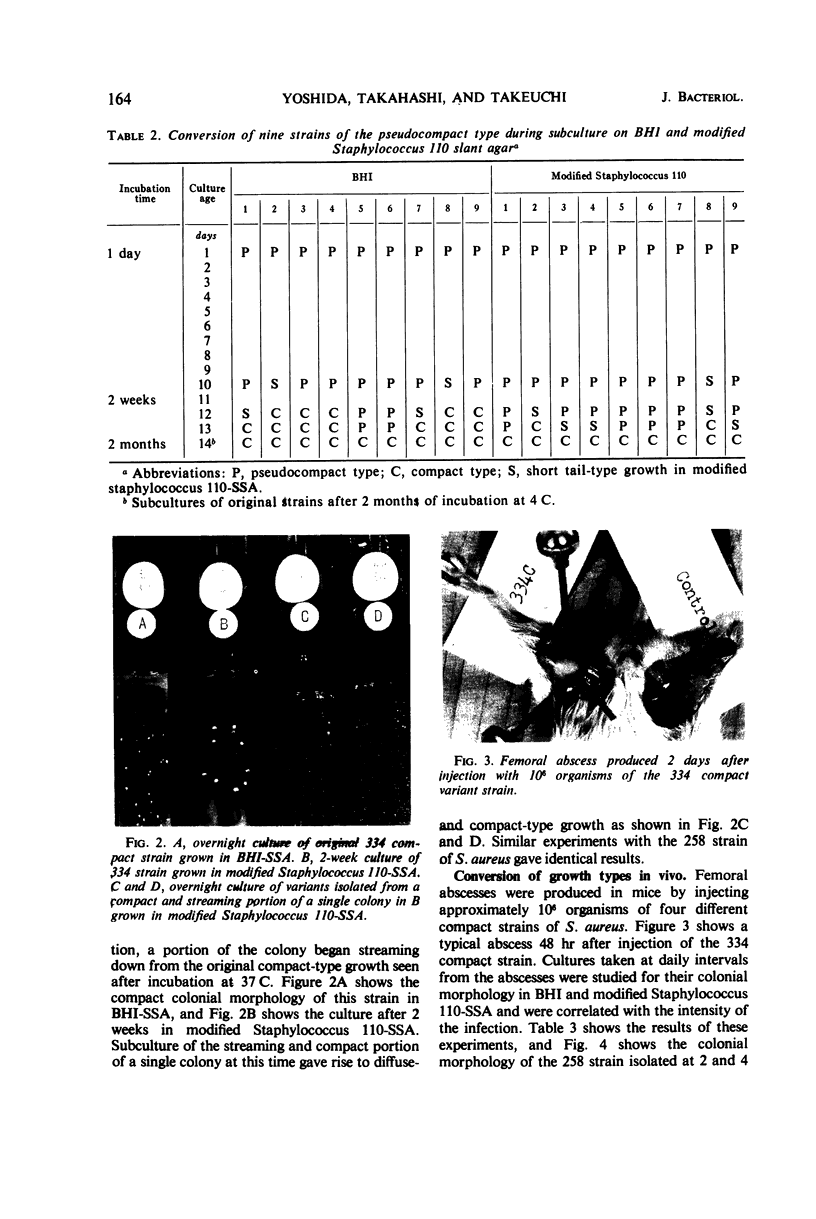
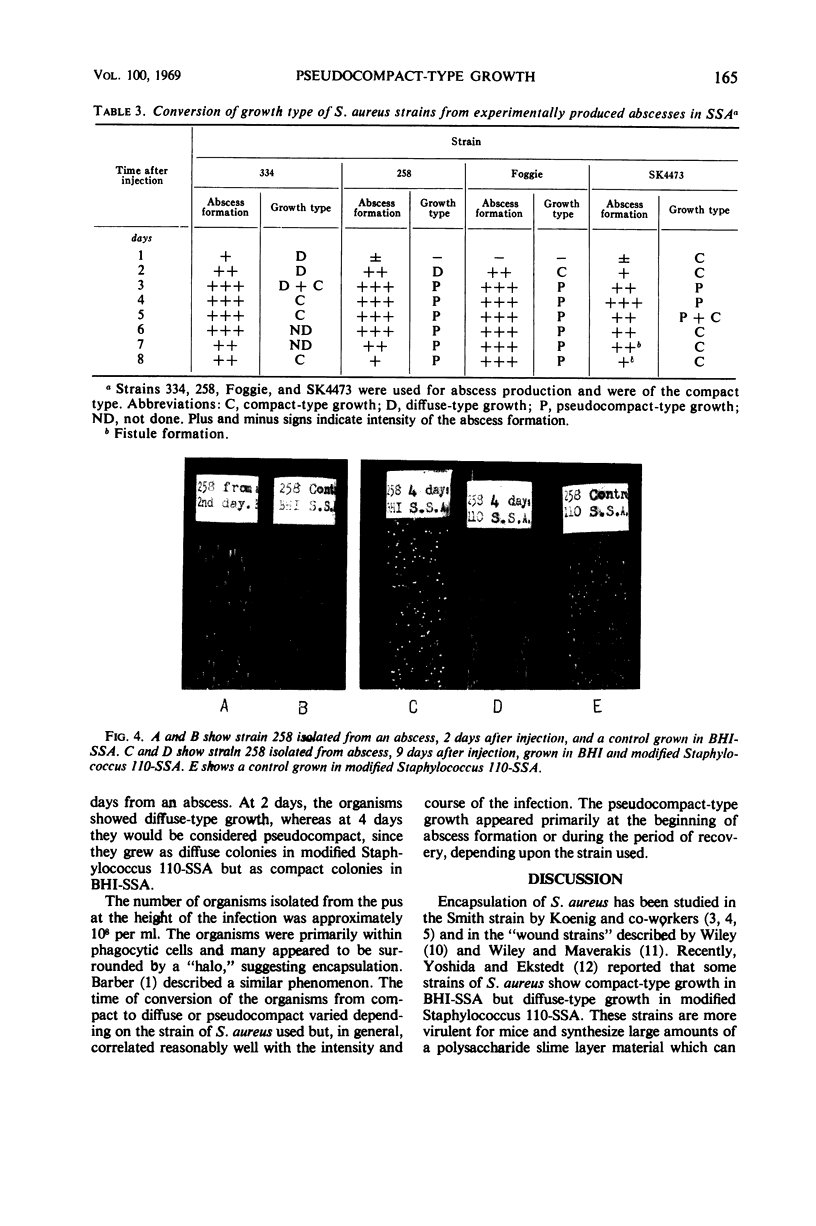
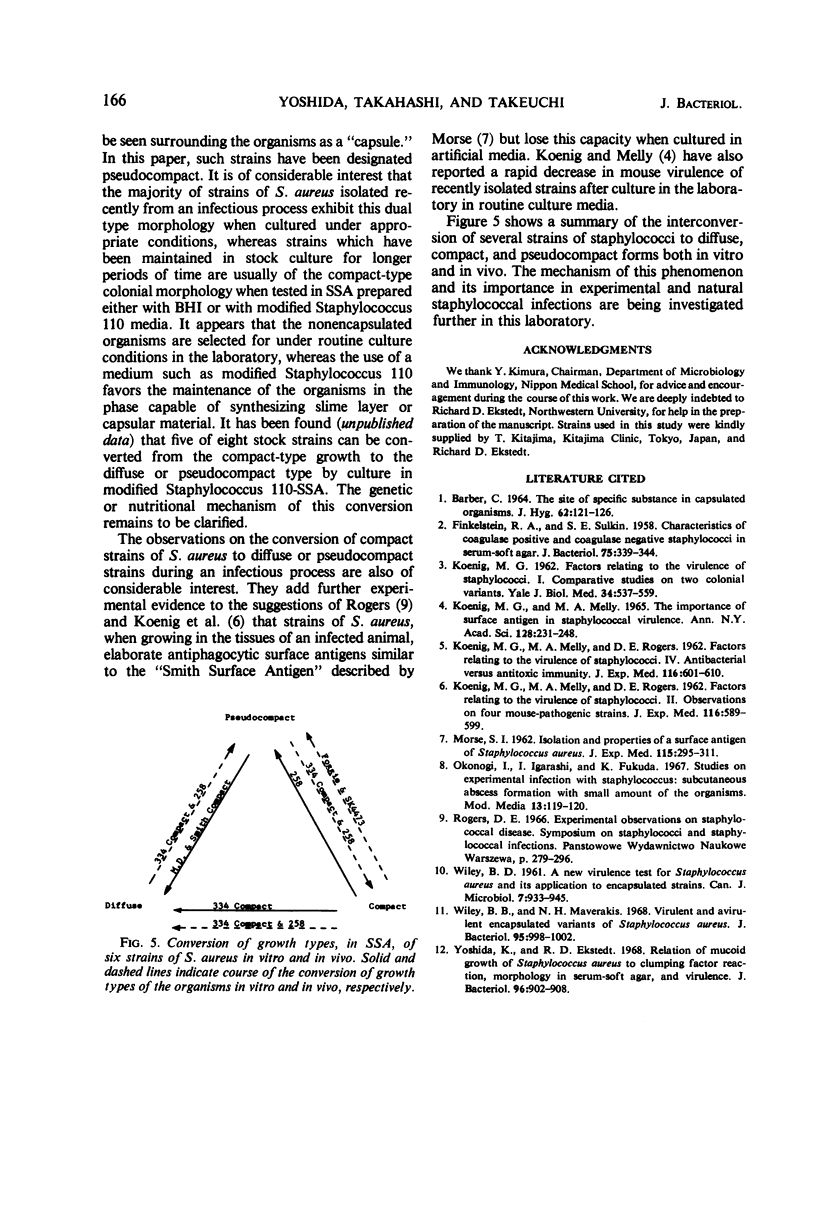
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARBER C. THE SITE OF SPECIFIC SUBSTANCES IN CAPSULATED ORGANISMS. J Hyg (Lond) 1964 Mar;62:121–126. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400039826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKELSTEIN R. A., SULKIN S. E. Characteristics of coagulase positive and coagulase negative staphylococci in serum-soft agar. J Bacteriol. 1958 Mar;75(3):339–344. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.3.339-344.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG M. G. Factors relating to the virulence of staphylococci. I. Comparative studies on two colonial variants. Yale J Biol Med. 1962 Jun;34:537–559. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG M. G., MELLY M. A., ROGERS D. E. Factors relating to the virulence of Staphylococci. II. Observations on four mouse-pathogenic strains. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:589–599. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOENIG M. G., MELLY M. A., ROGERS D. E. Factors relating to the virulence of Staphylococci. III. Antibacterial versus antioxic immunity. J Exp Med. 1962 Nov 1;116:601–610. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.5.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M. G., Melly M. A. The importance of surface antigens in staphylococcal virulence. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Jul 23;128(1):231–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb11641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE S. I. Isolation and properties of a surface antigen of Staphylococcus aureus. J Exp Med. 1962 Feb 1;115:295–311. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILEY B. B. A new virulence test for Staphylococcus aureus and its application to encapsulated strains. Can J Microbiol. 1961 Dec;7:933–943. doi: 10.1139/m61-118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley B. B., Maverakis N. H. Virulent and avirulent encapsulated variants of Staphyococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):998–1002. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.998-1002.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Ekstedt R. D. Relation of mucoid growth of Staphylococcus aureus to clumping factor reaction, morphology in serum-soft agar, and virulence. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):902–908. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.902-908.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]