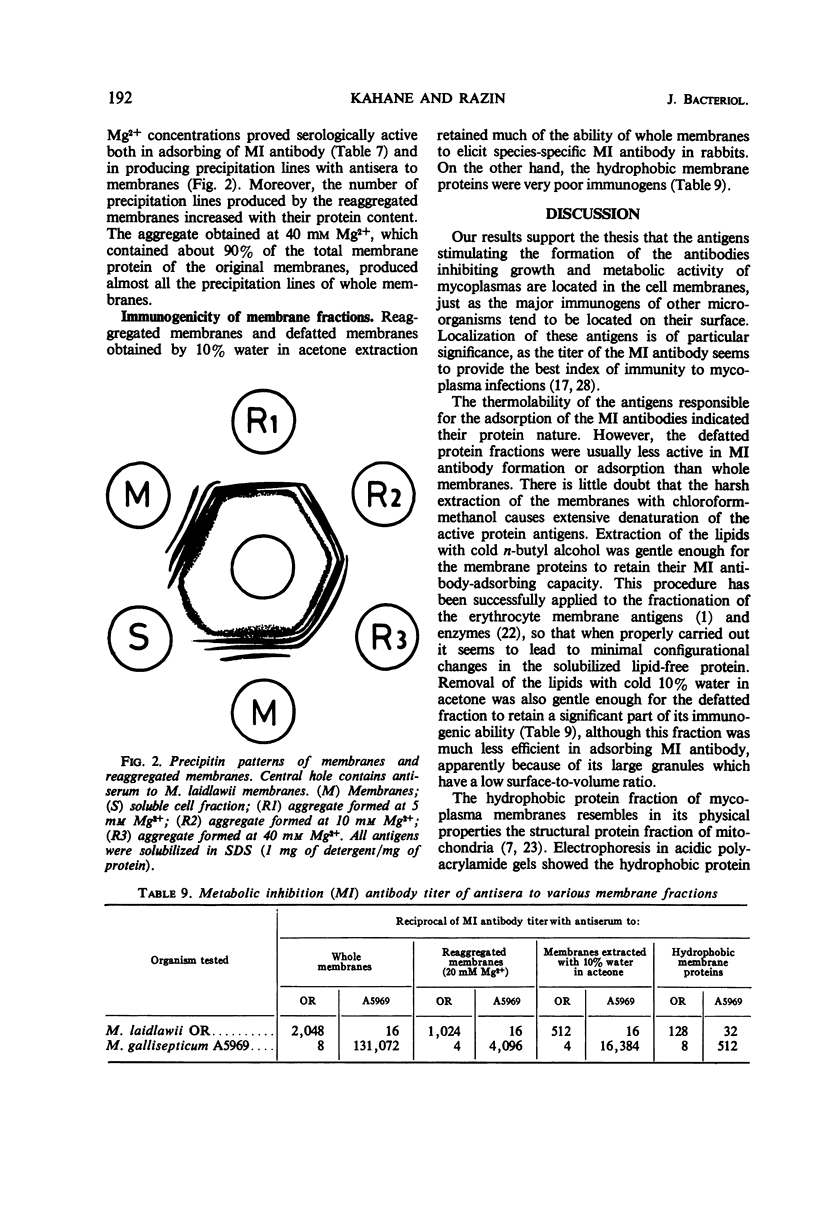
Abstract
The antigens responsible for the production of antibodies to Mycoplasma laidlawii and M. gallisepticum causing growth and metabolic inhibition of these organisms were localized in the cell membrane. Various membrane fractions were tested for serological activity. Membrane lipids were completely or almost completely inactive, whereas several preparations of defatted membrane proteins retained some serological activity, shown by their ability to stimulate metabolic inhibition antibody in rabbits and to adsorb metabolic inhibition antibody and form precipitation lines with an antiserum to the membrane. When the membranes were heated to 65 C for 1 hr, they virtually lost their ability to adsorb metabolic inhibition antibody, which suggests that the antigenic determinants are proteins. Serological activity was retained in reaggregated membranes obtained by dialysis against Mg2+ of membranes solubilized in sodium dodecyl sulfate. The amount of solubilized membrane protein and lipid incorporated into the reaggregated membranes could be regulated by varying the Mg2+ concentration. As the serological tests indicated that the various membrane antigens were selectively incorporated into the different reaggregated membranes, the use of controlled reaggregation of solubilized membranes is suggested as a new tool for the fractionation and antigenic analysis of membrane proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER H. E. A COMPARISON OF SOME CHARACTERISTICS OF MYCOPLASMA VAR. MYCOIDES AND MYCOPLASMA GALLISEPTICUM. Am J Vet Res. 1964 Jan;25:243–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adachi H., Furusawa M. Immunological analysis of the structural molecules of erythrocyte membrane in mice. I. Analysis of the aqueous phase molecules obtained by butanol fractionation of erythrocyte membrane. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Jun;50(3):490–496. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argaman M., Razin S. Antigenic properties of mycoplasma organisms and membranes. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Jan;55(1):45–58. doi: 10.1099/00221287-55-1-45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew L. E., Wheeler E., Nelson F. R. Heat-sensitive mycoplasma antigens. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jul;72(1):65–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckman B. L., Kenny G. E. Immunochemical analysis of serologically active lipids of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):1171–1180. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.1171-1180.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLYDE W. A., Jr MYCOPLASMA SPECIES IDENTIFICATION BASED UPON GROWTH INHIBITION BY SPECIFIC ANTISERA. J Immunol. 1964 Jun;92:958–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRIDDLE R. S., BOCK R. M., GREEN D. E., TISDALE H. Physical characteristics of proteins of the electron transfer system and interpretation of the structure of the mitochondrion. Biochemistry. 1962 Sep;1:827–842. doi: 10.1021/bi00911a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Fleischer B., Stoeckenius W. Fine structure of lipid-depleted mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jan;32(1):193–208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Razin S. Synthesis and turnover of membrane protein and lipid in Mycoplasma laidlawii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 3;183(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90131-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny G. E. Heat-lability and organic solvent-solubility of mycoplasma antigens. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):676–681. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton H. E., Roberts R. J. Production of anti-Mycoplasma (PPLO) antibodies in rabbits. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jun;125(2):538–543. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plackett P., Marmion B. P., Shaw E. J., Lemcke R. M. Immunochemical analysis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. 3. Separation and chemical identification of serologically active lipids. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1969 Apr;47(2):171–195. doi: 10.1038/icb.1969.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. D., Razin S., Pollack M. E., Cleverdon R. C. Fractionation of mycoplasma cells for enzyme localization. Life Sci. 1965 May;4(9):973–977. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90200-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell R. H., Wong D., Chanock R. M., Taylor-Robinson D., Canchola J., Valdesuso J. Significance of antibody to mycoplasma as measured by metabolic-inhibition techniques. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):664–675. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27712.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S. OSMOTIC LYSIS OF MYCOPLASMA. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Dec;33:471–475. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-3-471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S., Barash V. Solubilization of mycoplasma membranes by the nonionic detergent Triton X-100. FEBS Lett. 1969 May;3(3):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Structure and function in mycoplasma. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:317–356. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rega A. F., Weed R. I., Reed C. F., Berg G. G., Rothstein A. Changes in the properties of human erythrocyte membrane protein after solubilization by butanol extraction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 23;147(2):297–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(67)90408-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., McIntosh J. R. Erythrocyte membranes: effects on sonication. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 5;163(3):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S., Stein O., Razin S. Reassembly of Mycoplasma membranes disaggregated by detergents. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Apr;125(1):46–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90637-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salton M. R. Isolation and characterization of bacterial membranes. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Apr;29(6):764–781. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1967.tb02300.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobeslavský O., Prescott B., James W. D., Chanock R. M. Serological and immunogenic activities of different fractions of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1967 Jul 28;143(1):682–690. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1967.tb27714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson D., Purcell R. H., Wong D. C., Chanock R. M. A colour test for the measurement of antibody to certain mycoplasma species based upon the inhibition of acid production. J Hyg (Lond) 1966 Mar;64(1):91–104. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400040377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. H., Taylor-Robinson D. Antigenicity of Mycoplasma membranes. Nature. 1967 Aug 26;215(5104):973–974. doi: 10.1038/215973a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
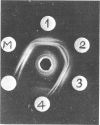
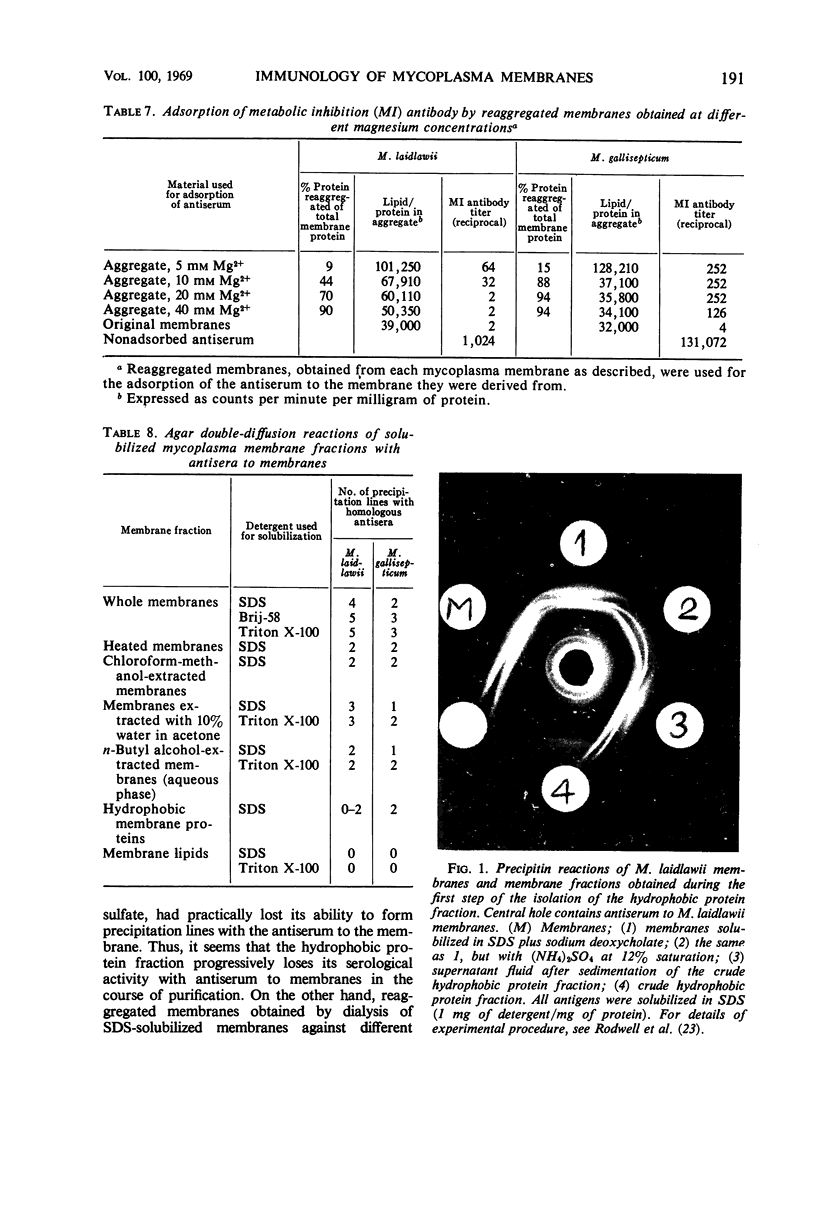
- Woodward D. O. Functional and organizational properties of Neurospora mitochondrial structural protein. Fed Proc. 1968 Sep-Oct;27(5):1167–1173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]