Abstract
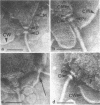
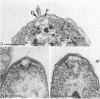
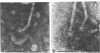
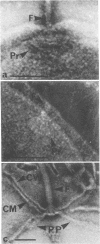
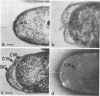
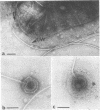
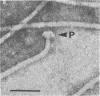
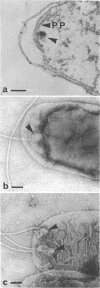
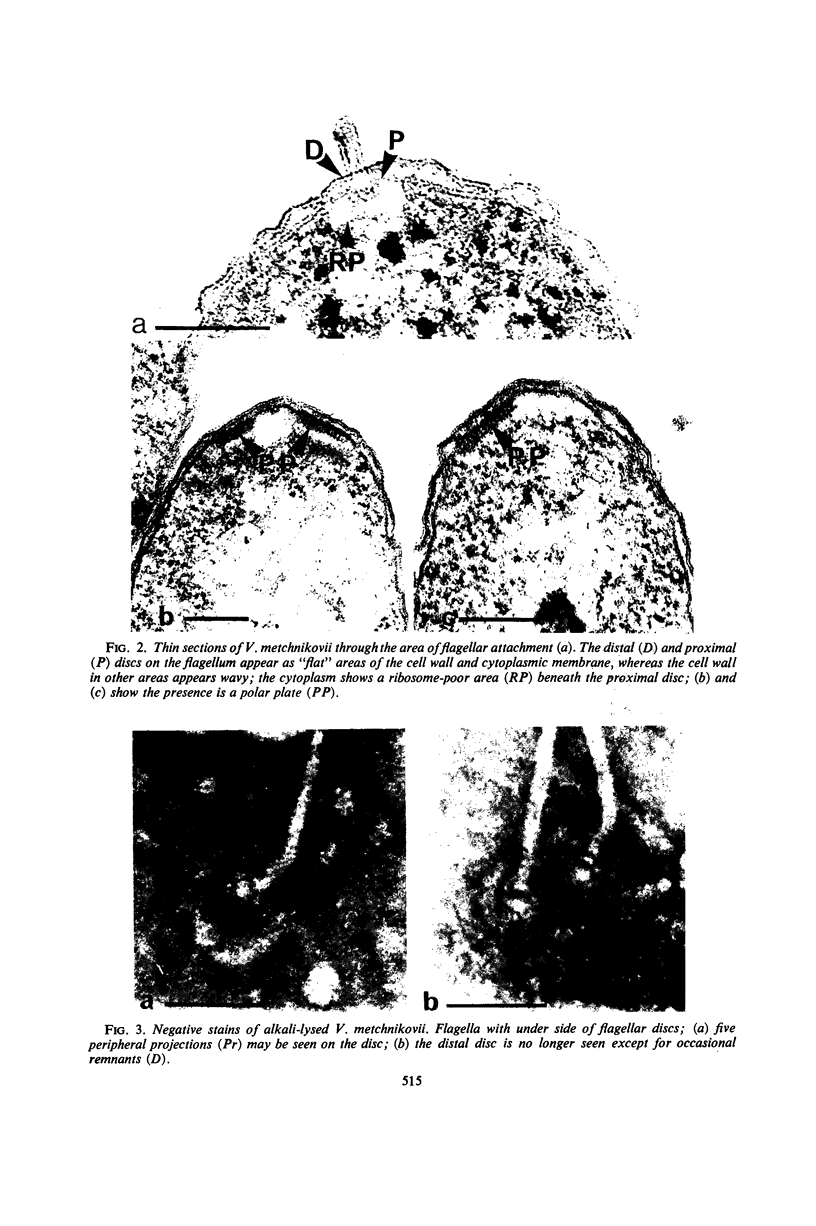
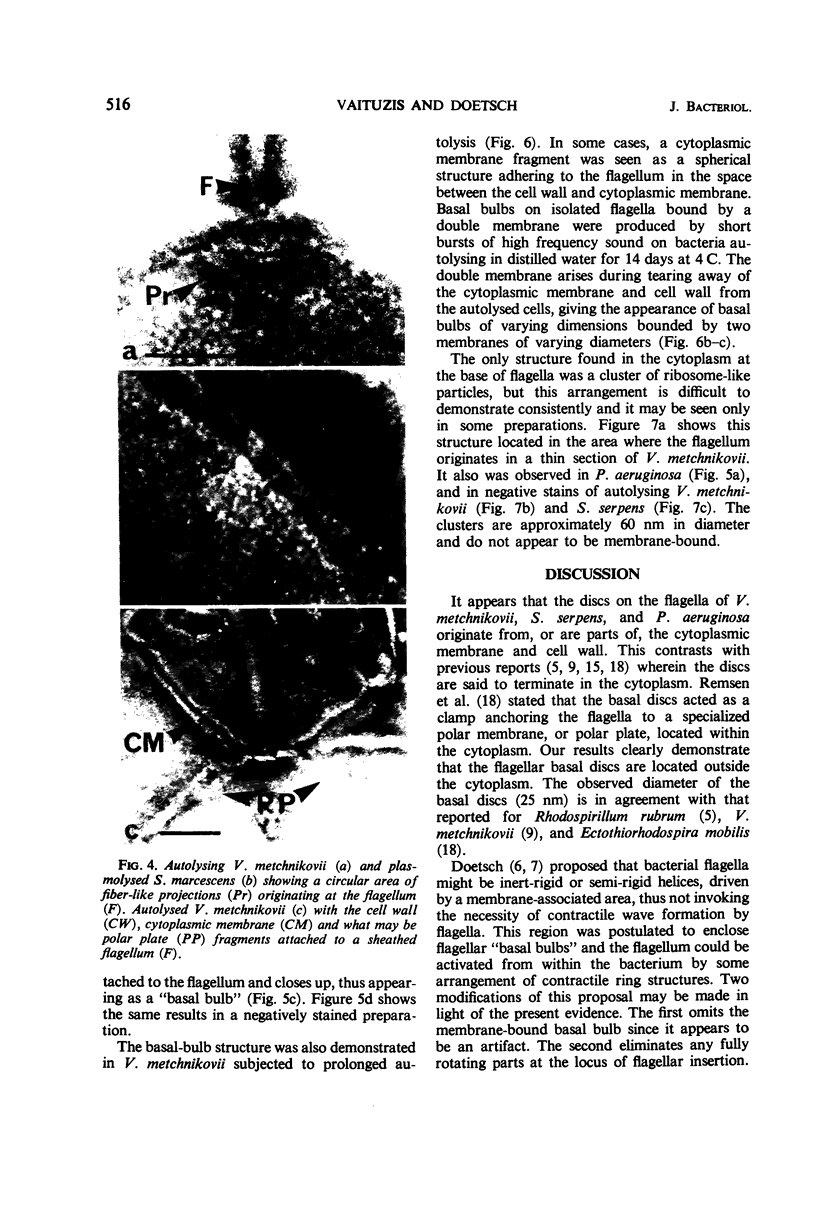
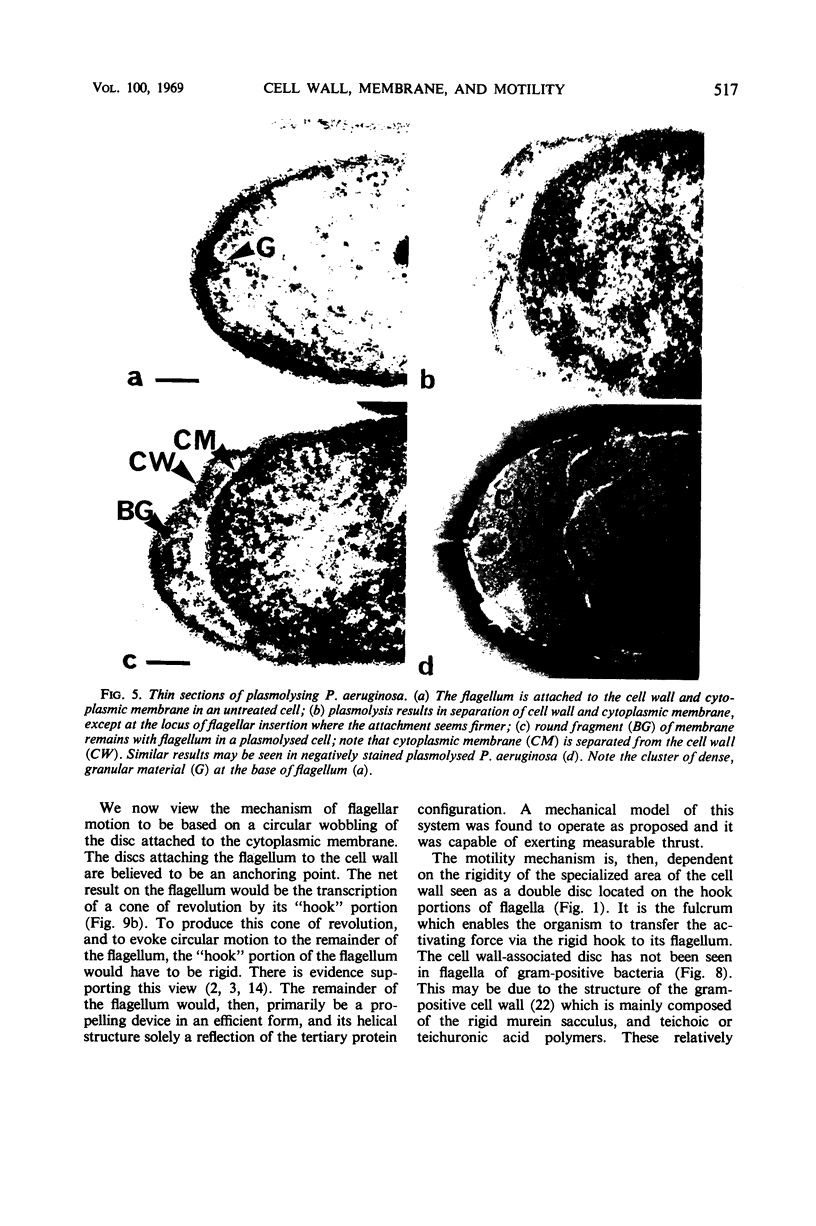
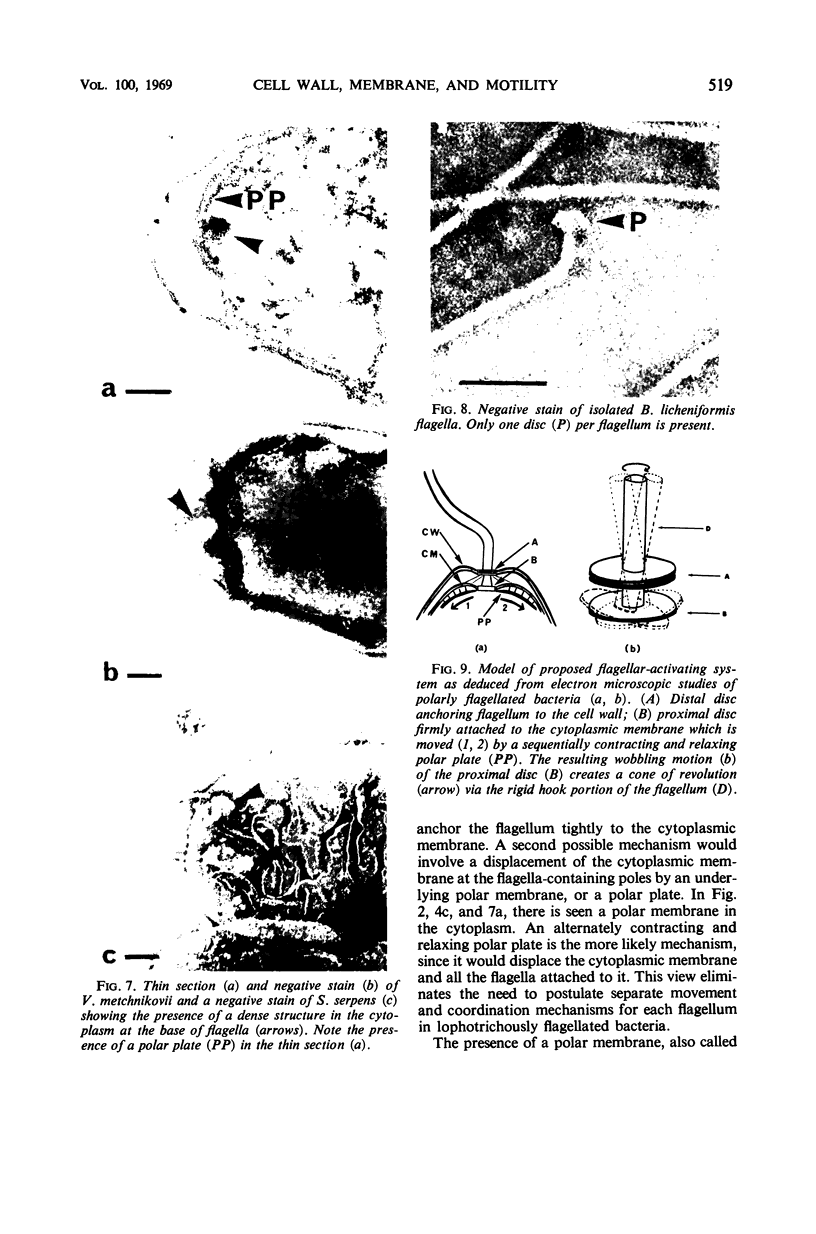
High-resolution electron microscopy of polarly flagellated bacteria revealed that their flagella originate at a circular, differentiated portion of the cytoplasmic membrane approximately 25 nm in diameter. The flagella also have discs attaching them to the cell wall. These attachment discs are extremely resistant to lytic damage and are firmly bound to the flagella. The cytoplasm beneath the flagellum contains a granulated basal body about 60 nm in diameter, and a specialized polar membrane. The existence of membrane-bound basal bodies is shown to be an artifact arising from adherence of cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane fragments to flagella in lysed preparations. Based on structures observed, a mechanism to explain bacterial flagellar movement is proposed. Flagella are considered to be anchored to the cell wall and activated by displacement of underlying cytoplasmic membrane to which they are also firmly attached. An explanation for the membrane displacement is given.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAM D. ELECTRON MICROSCOPE OBSERVATIONS ON INTACT CELLS, PROTOPLASTS, AND THE CYTOPLASMIC MEMBRANE OF BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:855–873. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.855-873.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abram D., Koffler H., Vatter A. E. Basal structure and attachment of flagella in cells of Proteus vulgaris. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1337–1354. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1337-1354.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abram D., Vatter A. E., Koffler H. Attachment and structural features of flagella of certain bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2045–2068. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2045-2068.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRENNER S., HORNE R. W. A negative staining method for high resolution electron microscopy of viruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:103–110. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90237-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Bazire G., London J. Basal organelles of bacterial flagella. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):458–465. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.458-465.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetsch R. N., Hageage G. J. Motility in procaryotic organisms: problems, points of view, and perspectives. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1968 Aug;43(3):317–362. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1968.tb00963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetsch R. N. Some speculations accounting for the movement of bacterial flagella. J Theor Biol. 1966 Aug;11(3):411–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(66)90101-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLAUERT A. M., KERRIDGE D., HORNE R. W. THE FINE STRUCTURE AND MODE OF ATTACHMENT OF THE SHEATHED FLAGELLUM OF VIBRIO METCHNIKOVII. J Cell Biol. 1963 Aug;18:327–336. doi: 10.1083/jcb.18.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRACE J. B. Some observations on the flagella and blepharoplasts of Spirillum and Vibrio spp. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Apr;10(2):325–327. doi: 10.1099/00221287-10-2-325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeniger J. F., Van Iterson W., Van Zanten E. N. Basal bodies of bacterial flagella in Proteus mirabilis. II. Electron microscopy of negatively stained material. J Cell Biol. 1966 Dec;31(3):603–618. doi: 10.1083/jcb.31.3.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeler R. F., Ritchie A. E., Bryner J. H., Elmore J. The preparation and characterization of cell walls and the preparation of flagella of Vibrio fetus. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jun;43(3):439–454. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-3-439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederberg J. BACTERIAL PROTOPLASTS INDUCED BY PENICILLIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1956 Sep;42(9):574–577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.42.9.574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy J. Structure of the proximal ends of bacterial flagella. J Mol Biol. 1965 Nov;14(1):297–299. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80251-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEASE P. Some observations upon the development and mode of attachment of the flagella in Vibrio and Spirillum species. Exp Cell Res. 1956 Feb;10(1):234–237. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(56)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTER A., KELLENBERGER E., BIRCHANDERSEN A., MAALOE O. Etude au microscope électronique de plasmas contenant de l'acide désoxyribonucliéique. I. Les nucléoides des bactéries en croissance active. Z Naturforsch B. 1958 Sep;13B(9):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remsen C. C., Watson S. W., Waterbury J. B., Trüper H. G. Fine structure of Ectothiorhodospira mobilis Pelsh. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2374–2392. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2374-2392.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie A. E., Keeler R. F., Bryner J. H. Anatomical features of Vibrio fetus: Electron microscopic survey. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 Jun;43(3):427–438. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-3-427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetze P. L., Doetsch R. N. Reversible "paralysis" of the flagella of certain gram-negative bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Aug;13(8):1114–1115. doi: 10.1139/m67-149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAWARA J. Electron-microscopic study on the flagella of Vibrio comma. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jan;73(1):89–90. doi: 10.1128/jb.73.1.89-90.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawara J. The root of flagella of Vibrio cholerae. Jpn J Microbiol. 1965 Mar;9(1):49–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1965.tb00274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VAITUZIS Z., DOETSCH R. N. FLAGELLA OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM SPHEROPLASTS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1586–1593. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1586-1593.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaituzis Z., Doetsch R. N. Flagella of Escherichia coli spheroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1966 May;91(5):2103–2104. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.5.2103-2104.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBULL C. The isolation of protoplasts from Bacillus megaterium by controlled treatment with lysozyme. J Bacteriol. 1953 Dec;66(6):688–695. doi: 10.1128/jb.66.6.688-695.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]