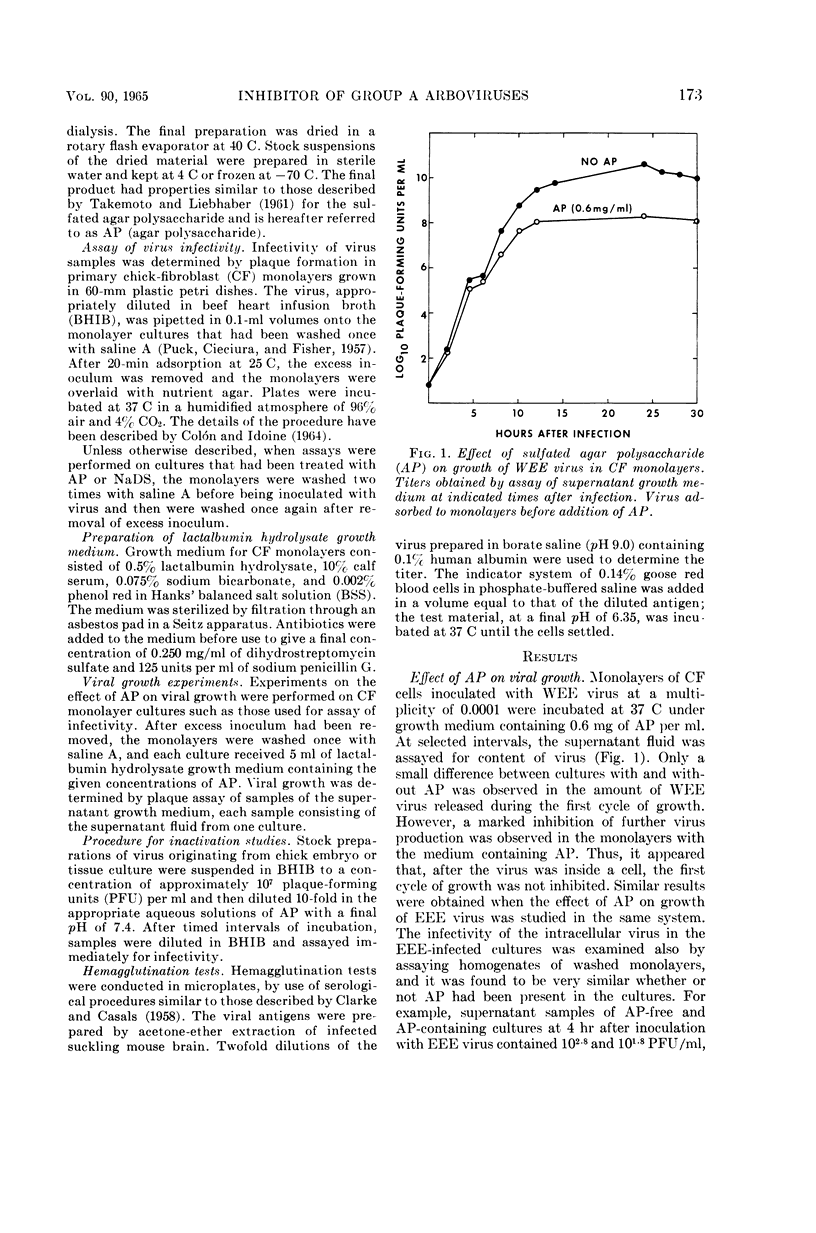
Abstract
Colón, Julio I. (Fort Detrick, Frederick, Md.), Jane B. Idoine, Orville M. Brand, and Richard D. Costlow. Mode of action of an inhibitor from agar on growth and hemagglutination of group A arboviruses. J. Bacteriol. 90:172–179. 1965.—A polysaccharide obtained from agar, and having properties similar to a previously described sulfated polysaccharide, was observed to inhibit growth and hemagglutination of some group A arboviruses. The evidence presented confirms that the inhibitory activity, in part, is the result of direct interaction between the agar polysaccharide (AP) and free virus particles. Additional evidence indicates that inhibition of viral growth also occurs as the result of interaction between AP and the chick-fibroblast cells used for propagation of the virus. The possibility was considered, therefore, that at least two different inhibitors could be present in AP—one that reacts directly with the virus particle and another that reacts with host cells. AP does not induce the production of interferon in the test system used.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHANOCK R. M., SABIN A. B. The hemagglutinin of St. Louis encephalitis virus. II. Physico-chemical properties and nature of its reaction with erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1953 Mar;70(3):286–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., SABIN A. B. The hemagglutinin of western equine encephalitis virus: recovery, properties and use for diagnosis. J Immunol. 1954 Nov;73(5):337–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLARKE D. H., CASALS J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;7(5):561–573. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1958.7.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLON J. I., IDOINE J. B. FACTORS AFFECTING PLAQUE FORMATION BY THE INFECTIOUS RIBONUCLEIC ACID OF THE EQUINE ENCEPHALITIS VIRUSES. J Infect Dis. 1964 Feb;114:61–68. doi: 10.1093/infdis/114.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARDY F. M. The growth of Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus in various tissue cultures. Am J Hyg. 1959 Jul;70(1):21–27. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEARN H. J., Jr Cross-protection between Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis and eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Jul;107:607–610. doi: 10.3181/00379727-107-26702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINSCHMIDT W. J., CLINE J. C., MURPHY E. B. INTERFERON PRODUCTION INDUCED BY STATOLON. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Sep;52:741–744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.3.741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBHABER H., TAKEMOTO K. K. Alteration plaque morphology of EMC virus with polycations. Virology. 1961 Aug;14:502–504. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90349-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBHABER H., TAKEMOTO K. K. THE BASIS FOR THE SIZE DIFFERENCES IN PLAQUES PRODUCED BY VARIANTS OF ENCEPHALOMYOCARDITIS (EMC) VIRUS. Virology. 1963 Aug;20:559–566. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAHMIAS A. J., KIBRICK S., BERNFELD P. EFFECT OF SYNTHETIC AND BIOLOGICAL POLYANIONS ON HERPES SIMPLEX VIRUS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Apr;115:993–996. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-29098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCK T. T., CIECIURA S. J., FISHER H. W. Clonal growth in vitro of human cells with fibroblastic morphology; comparison of growth and genetic characteristics of single epithelioid and fibroblast-like cells from a variety of human organs. J Exp Med. 1957 Jul 1;106(1):145–158. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.1.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULZE I. T., SCHLESINGER R. W. Inhibition of infectious and hemagglutinating properties of type 2 dengue virus by aqueous Agar extracts. Virology. 1963 Jan;19:49–57. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEMOTO K. K., LIEBHABER H. Virus-polysaccharide interactions. I. An agar polysaccharide determining plaque morphology of EMC virus. Virology. 1961 Aug;14:456–462. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90338-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEMOTO K. K., LIEBHABER H. Virus-polysaccharide interactions. II. Enhancement of plague formation and the detection of variants of poliovirus with dextran sulfate. Virology. 1962 Jul;17:499–501. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- USHIJIMA R. N., HILL D. W., DOLANA G. H., GEBHARDT L. P. Plaque mutants of WEE virus. Virology. 1962 Jun;17:356–357. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


