Abstract
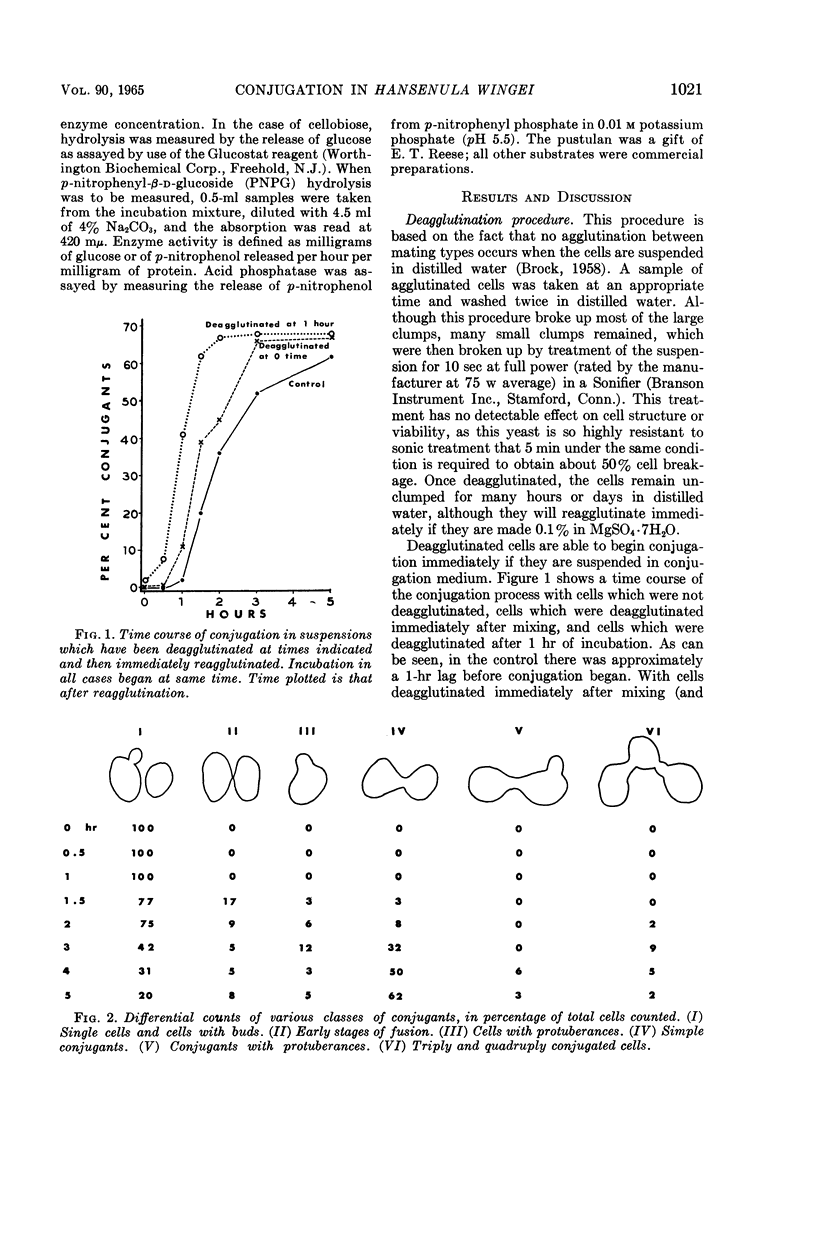
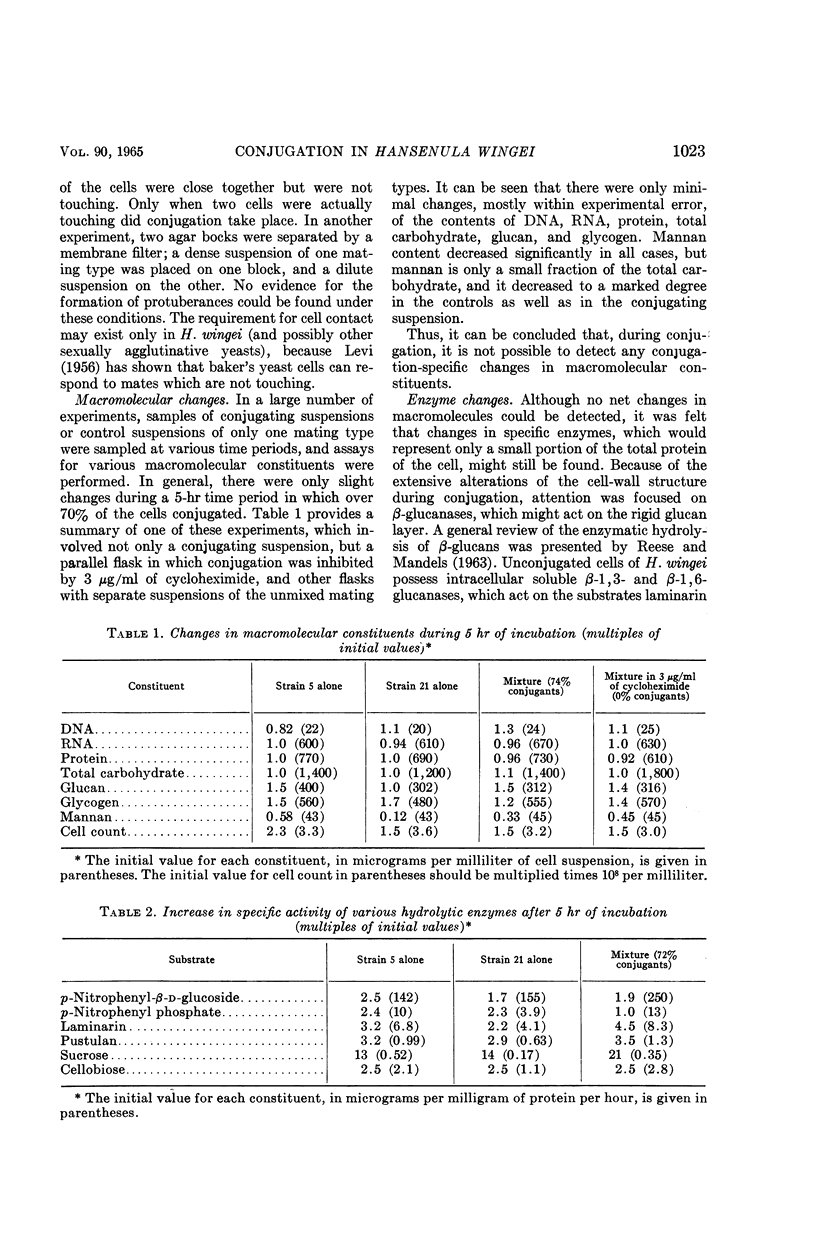
Brock, Thomas D. (Indiana University, Bloomington). Biochemical and cellular changes occurring during conjugation in Hansenula wingei. J. Bacteriol. 90:1019–1025. 1954.—A technique has been devised for deagglutinating mixed populations of conjugating cells so as to be able to visualize microscopically early stages of the conjugation process. A cell can form a conjugation tube only when in contact with a cell of opposite mating type, but may do so even if the mate is unresponsive or ultraviolet-inactivated. Cell fusion occurs, however, only when both cells are able to form conjugation tubes in a region of contact. Fusion begins almost as soon as the two cells begin to form protuberances, and long before any dissolution of cell-wall material between the cells occurs. A cell which has conjugated in one region of its cell wall is still able to conjugate with another cell in another region, so that triply and quadruply conjugated cells are occasionally formed. There is no significant net increase in deoxyribonucleic acid, ribonucleic acid, protein, or carbohydrate which might be related to the conjugation process, because any minor changes that occur in these components are also detected when cells of only one mating type are incubated or when the conjugation process is inhibited with the antibiotic cycloheximide. Changes in activity of β-1,3-glucanase (with laminarin as substrate) and β-1,6-glucanase (with pustulan as substrate) have been measured during the conjugation process, in addition to changes in the activity of several control enzymes which would not be expected to be related to the conjugation process. Significant increases in invertase (sucrase), laminarinase, and pustulanase were detected, and minimal increases occurred in β-glucosidase and acid phosphatase. However, these same increases were also observed in controls involving only one mating type; thus, these increases are probably not related to the conjugation process, but may be a result of other processes which probably occur during incubation in the conjugation medium.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROCK T. D. Biochemical basis of mating in yeast. Science. 1959 Apr 10;129(3354):960–961. doi: 10.1126/science.129.3354.960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D. Mating reaction in the yeast Hansenula wingei; preliminary observations and quantitation. J Bacteriol. 1958 Jun;75(6):697–701. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.6.697-701.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D. Physiology of the conjugation process in the yeast Hansenula wingei. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 Nov;26:487–497. doi: 10.1099/00221287-26-3-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D. Beta-glucanase of yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 May 18;19(5):623–629. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONTI S. F., BROCK T. D. ELECTRON MICROSCOPY OF CELL FUSION IN CONJUGATING HANSENULA WINGEI. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:524–533. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.524-533.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR N. W. INACTIVATION OF SEXUAL AGGLUTINATION IN HANSENULA WINGEI AND SACCHAROMYCES KLUYVERI BY DISULFIDE-CLEAVING AGENTS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:929–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.929-936.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., HARRISON J. S. Studies on yeast metabolism. I. Fractionation and microdetermination of cell carbohydrates. Biochem J. 1952 Jan;50(3):298–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0500298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



