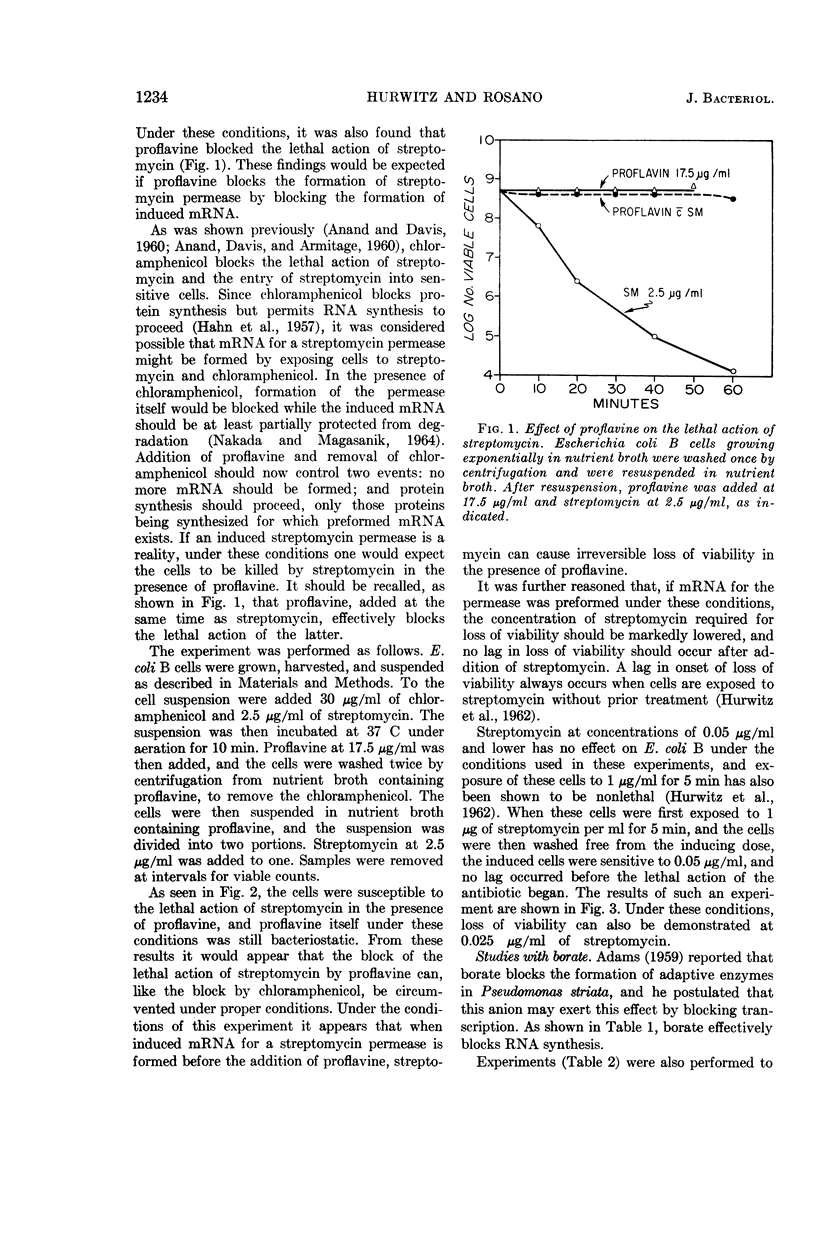
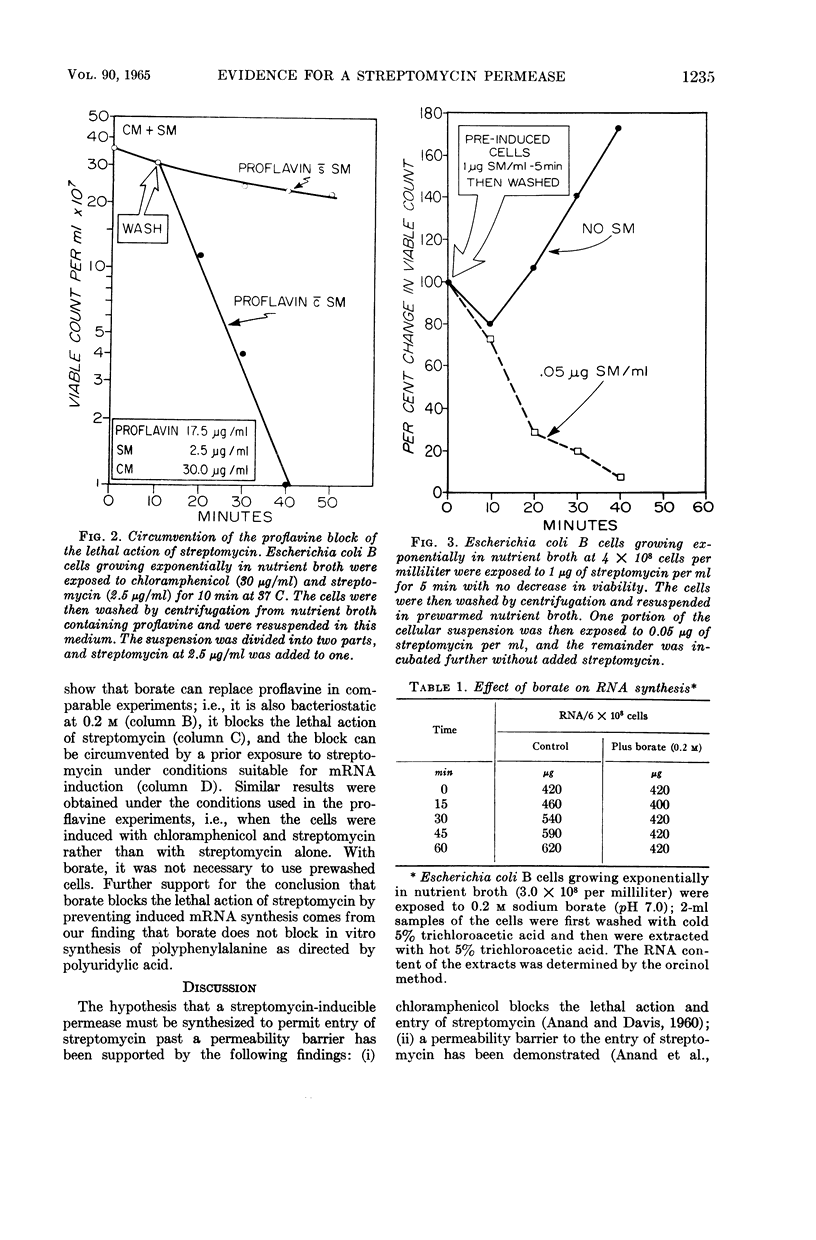
Abstract
Hurwitz, Charles (Veterans Administration Hospital, Albany, N.Y.), and Carmen L. Rosano. Evidence for a streptomycin permease. J. Bacteriol. 90:1233–1237. 1965.—The hypothesis that an induced streptomycin permease is required for entry of the antibiotic into cells is further supported by the finding that proflavine and borate, which inhibit transcription, also block the lethal action of streptomycin. Furthermore, if ribonucleic acid (RNA) synthesis is permitted to proceed in the presence of streptomycin and chloramphenicol, and chloramphenicol is then replaced with either proflavine or borate, these inhibitors of transcription no longer block the lethal action of streptomycin. This finding is interpreted to mean that, if induced messenger RNA for streptomycin-permease is formed before transcription is blocked, inhibitors of transcription no longer block the lethal action of streptomycin by preventing formation of the permease.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS E. Hydroxyproline metabolism. I. Conversion to alpha-ketoglutarate by extracts of Pseudomonas. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):2073–2084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANAND N., DAVIS B. D., ARMITAGE A. K. Uptake of streptomycin by Escherichia coli. Nature. 1960 Jan 2;185:23–24. doi: 10.1038/185023a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANAND N., DAVIS B. D. Damage by streptomycin to the cell membrane of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1960 Jan 2;185:22–23. doi: 10.1038/185022a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES J., GILBERT W., GORINI L. STREPTOMYCIN, SUPPRESSION, AND THE CODE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 May;51:883–890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.5.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLAKS J. G., COX E. C., WITTING M. L., WHITE J. R. Polypeptide synthesis with ribosomes from streptomycin-resistant and dependent E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 May 11;7:390–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90321-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORINI L., KATAJA E. STREPTOMYCIN-INDUCED OVERSUPPRESSION IN E. COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jun;51:995–1001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.6.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUNDERSEN W. B. NEW TYPE OF STREPTOMYCIN RESISTANCE RESULTING FROM ACTION OF THE EPISOMELIKE MUTATOR FACTOR IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Bacteriol. 1963 Sep;86:510–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.3.510-516.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAHN F. E., SCHAECHTER M., CEGLOWSKI W. S., HOPPS H. E., CIAK J. Interrelations between nucleic acid and protein biosynthesis. I. Synthesis and fate of bacterial nucleic acids during exposure to, and recovery from the action of chloramphenicol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Dec;26(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90092-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ C., ROSANO C. L. Accumulation of label from C14-streptomycin by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1193–1201. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1193-1201.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ C., ROSANO C. L. Chloramphenicol-sensitive and -insensitive phases of the lethal action of streptomycin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Jun 17;41:162–163. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90387-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ C., ROSANO C. L. Chloramphenicol-sensitive and-insensitive phases of the lethal action of streptomycin. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1202–1209. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1202-1209.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ C., ROSANO C. L., LANDAU J. V. Kinetics of loss of vibility of Escherichia coli exposed to streptomycin. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1210–1216. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1210-1216.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKADA D., MAGASANIK B. THE ROLES OF INDUCER AND CATABOLITE REPRESSOR IN THE SYNTHESIS OF BETA-GALACTOSIDASE BY ESCHERICHIA COLI. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jan;8:105–127. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80153-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENKRANZ H. S. BASIS OF STREPTOMYCIN RESISTANCE IN ESCHERICHIA COLI WITH A "MULTIPLE DRUG RESISTANCE" EPISOME. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 17;80:342–345. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGER R. GENES OUTSIDE THE CHROMOSOMES. Sci Am. 1965 Jan;212:70–79. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0165-70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPEYER J. F., LENGYEL P., BASILIO C. Ribosomal localization of streptomycin sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Apr 15;48:684–686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.4.684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T., WATANABE M. Transduction of streptomycin resistance in Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1959 Aug;21:16–29. doi: 10.1099/00221287-21-1-16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOESE C., NAONO S., SOFFER R., GROS F. Studies on the breakdown of messenger RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Jun 20;11:435–440. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


