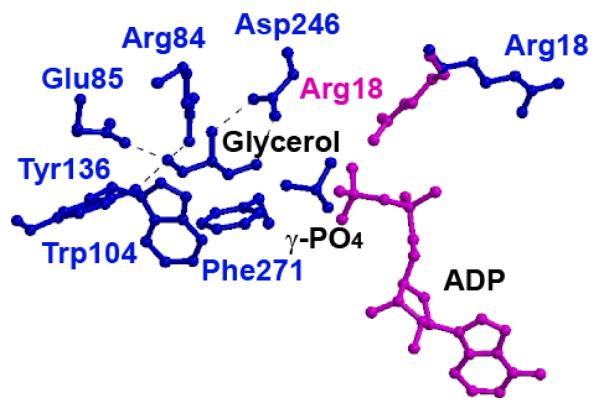
Figure 2. Glycerol Binding Site in His232Arg and His232Glu GlpK Mutants.
The glycerol binding site from the His232Arg GlpK enzyme, with ADP modeled in according to the E. coli structure (PDB accession number 1GLB; 14). In the His232Glu GlpK structure (blue), Arg18 points away from the glycerol, whereas in the His232Arg GlpK (pink), Arg18 points toward the substrate, glycerol. In this conformation, Arg18 bridges between the γ,β-phosphate group of ATP and glycerol, enhancing G3P formation, as detailed in the text. Binding of glycerol is predominantly mediated through residues Trp104 and Phe271, which provide large hydrophobic surfaces to align the glycerol substrate. Hydrogen bond distances between glycerol hydroxyl oxygens to active site residues converge within 0.2 Å in all the structures; these include Arg84 (2.7 - 2.8 Å), Glu85 (2.5 - 2.7 Å), Tyr136 (2.6 - 2.8 Å), and Asp246 (2.5 - 2.7 Å).