Abstract
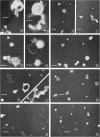
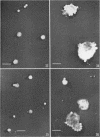
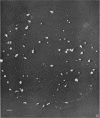
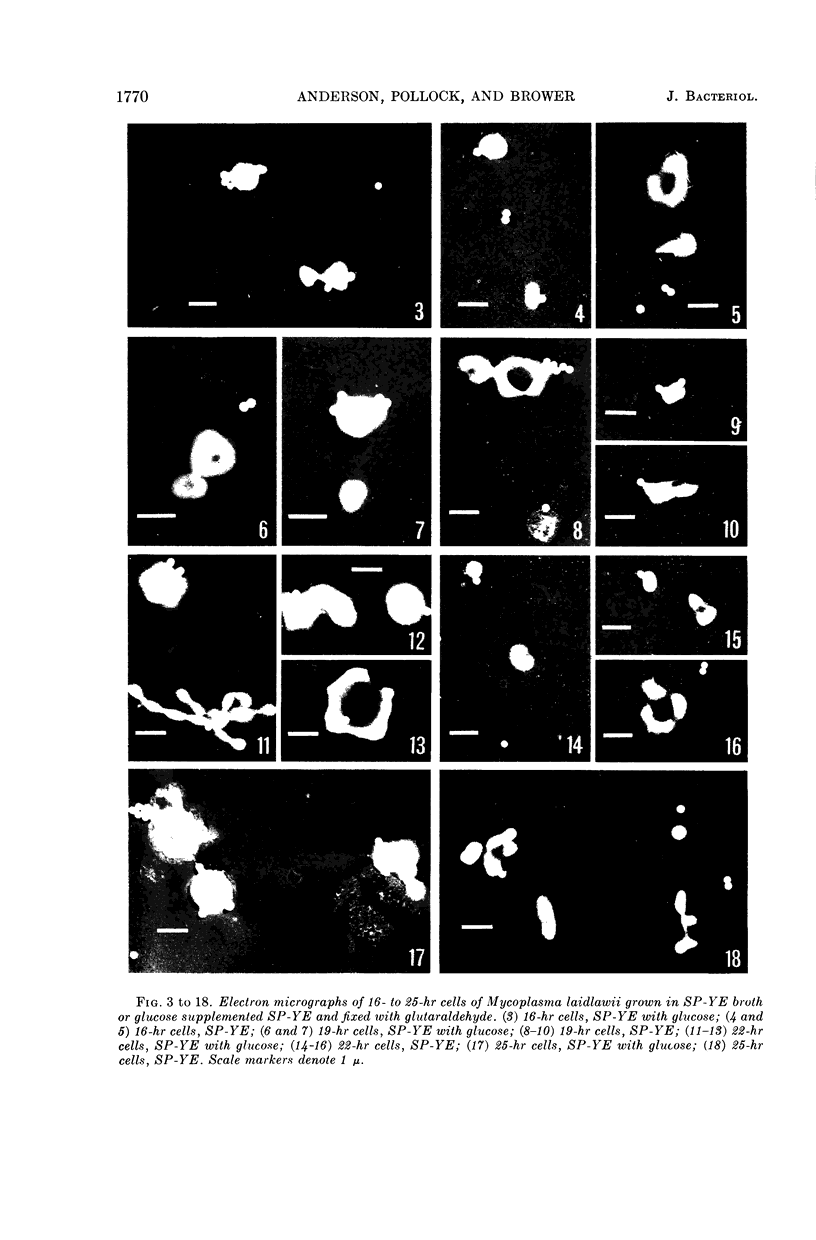
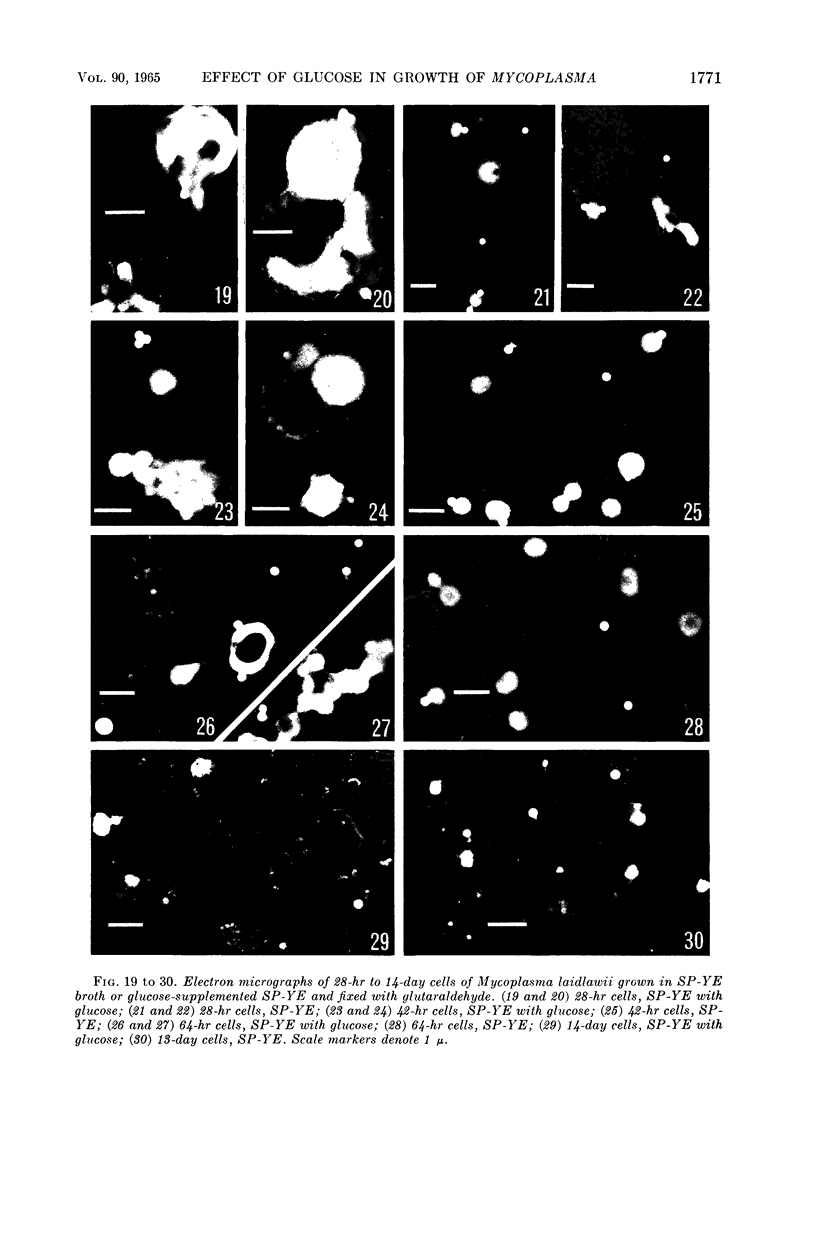
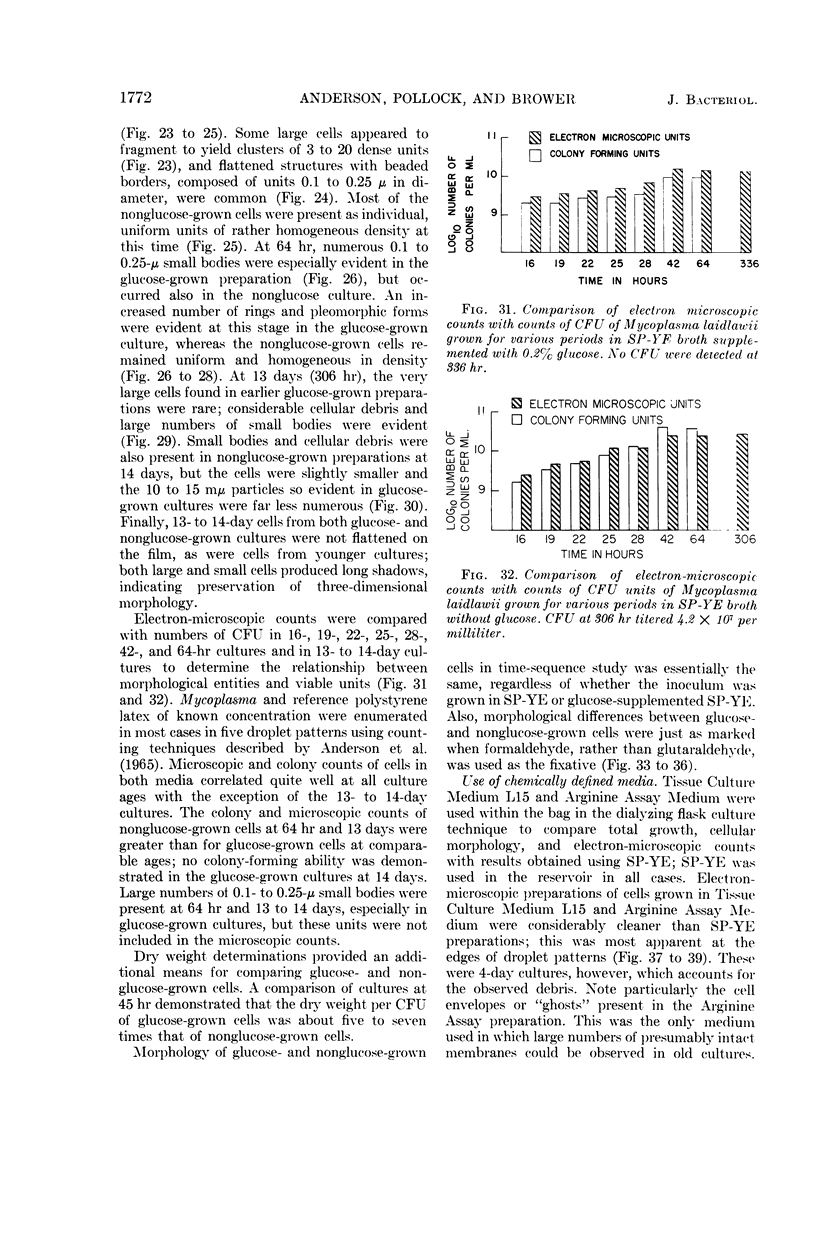
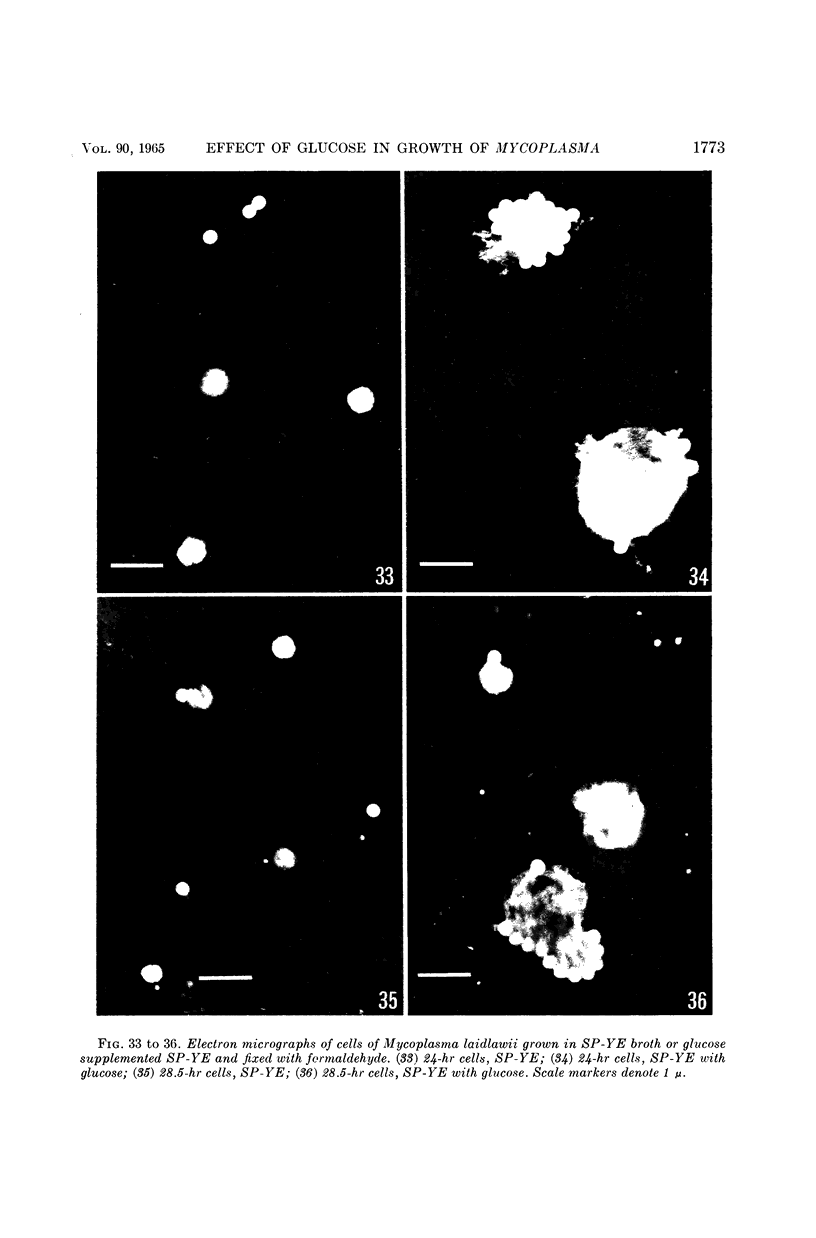
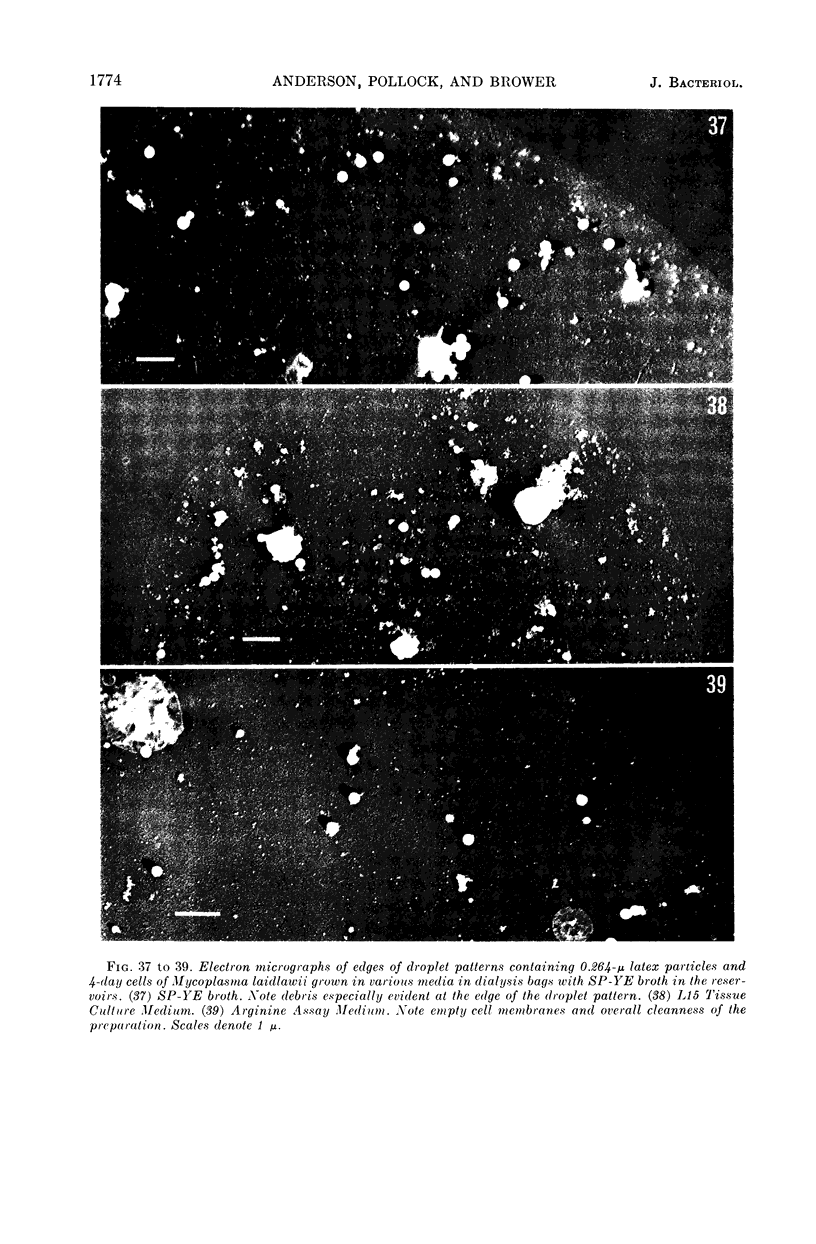
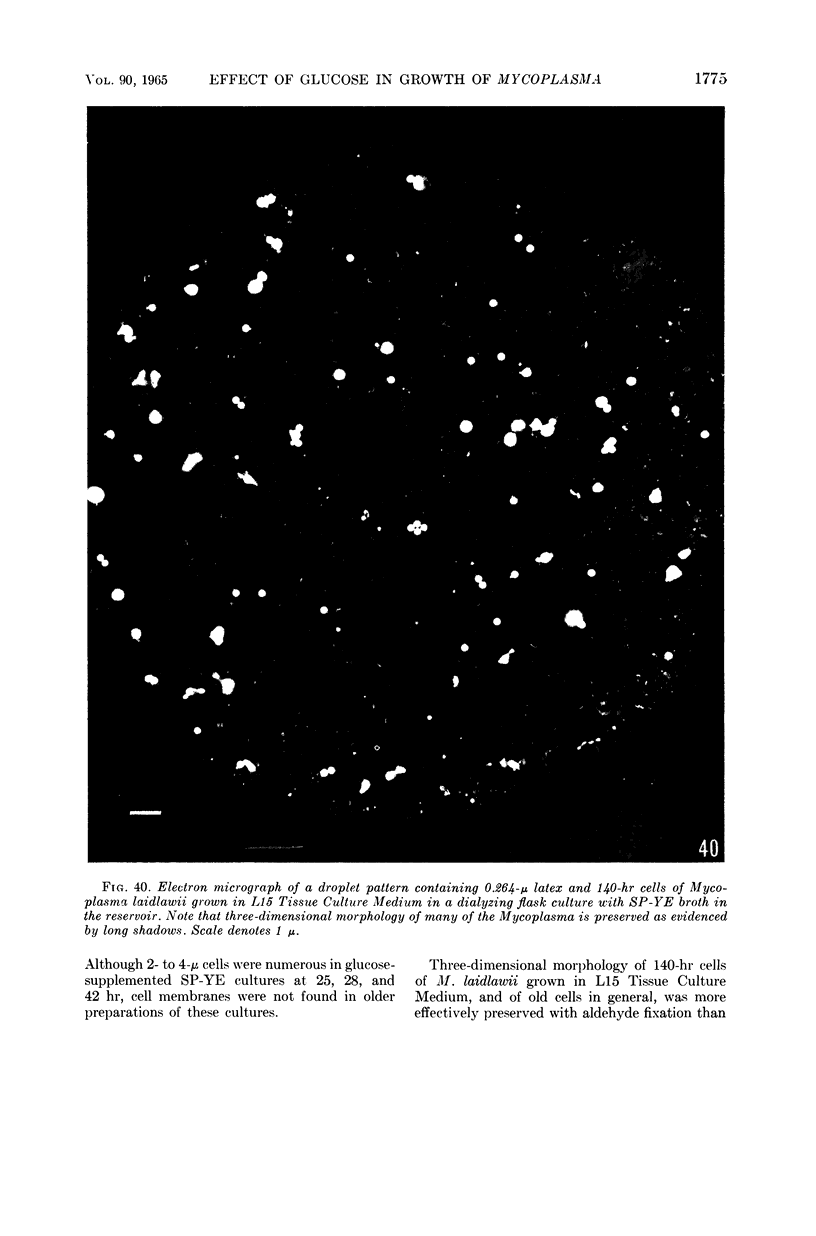
Anderson, D. L. (University of Minnesota, Minneapolis), M. E. Pollock, and L. F. Brower. Morphology of Mycoplasma laidlawii type A. II. Effect of glucose on growth and cellular morphology. J. Bacteriol. 90:1768–1777. 1965.—Cells of Mycoplasma laidlawii A grown in soy peptone-yeast extract (SP-YE) broth reached higher maximal titers than cells grown in SP-YE supplemented with 0.2% glucose, and remained viable longer than glucose-grown cells. Moreover, addition of glucose to SP-YE markedly affected the morphological developmental sequence of the organism. The diameter of glucose-grown cells at 28 to 40 hr was often two to four times that of cells grown without glucose; these large glucose-grown cells deteriorated progressively, and presumably liberated 0.1- to 0.25-μ small bodies. In contrast, pleomorphic 22- to 28-hr cells grown in SP-YE without glucose gave rise to uniform bodies 0.5 to 1.0 μ in diameter; limited numbers of 0.1- to 0.25-μ small bodies were also liberated in nonglucose cultures after 45 to 64 hr. Electron-microscopic counts of 16- to 64-hr cultures agreed well with counts of colony-forming units (CFU) when organisms larger than 0.25 μ were included in the microscopic counts. Small bodies, 0.1 to 0.25 μ in diameter, apparently did not contribute substantially to numbers of CFU. Droplet patterns of cells grown in Arginine Assay Medium and L15 Tissue Culture Medium were cleaner than patterns of cells grown in SP-YE.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. L., Pollock M. E., Brower L. F. Morphology of Mycoplasma laidlawii type A. I. Comparison of electron microscopic counts with colony-forming units. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1764–1767. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1764-1767.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDLER G., KANDLER O., HUBER O. Untersuchungen über die Morphologie und die Vermehrung der pleuropneumonieähnlichen Organismen und der L-Phase der Bakterien. II. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen. Arch Mikrobiol. 1954;21(2):202–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KANDLER G., KANDLER O. Untersuchungen über die Morphologie und die Vermehrung der pleuropneumonie-ähnlichen Organismen und der L-Phase der Bakterien. I. Licht mikroskopische Untersuchungen. Arch Mikrobiol. 1954;21(2):178–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLIENEBERGER-NOBEL E. A study of organisms of the pleuropneumonia group by electron microscopy. J Gen Microbiol. 1955 Feb;12(1):95–99. doi: 10.1099/00221287-12-1-95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOROWITZ H. J., TOURTELLOTTE M. E. The smallest living cells. Sci Am. 1962 Mar;206:117–126. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0362-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock M. E. Use of dialyzing culture technique for high yield of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1965 Dec;90(6):1682–1685. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.6.1682-1685.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]