Abstract
A Rh(III)-catalyzed protocol for the amidation of anilide and enamide C–H bonds with isocyanates has been developed. This method provides direct and efficient syntheses of N-acyl anthranilamides, enamine amides, and pyrimidin-4-one heterocycles.
Transition-metal catalyzed C–H bond functionalization reactions have emerged as effective strategies for streamlining chemical synthesis by avoiding tedious and costly substrate pre-activation steps. While the development of methods for the functionalization of C–H bonds with alkenes and alkynes has been extensively investigated,1 the identification of related procedures for additions across polar C–N π-bonds has seen considerably less progress.2 Given the ubiquity of amines in bioactive molecules and drugs, the installment of nitrogen-based functional groups into molecules through the direct addition of C–H bonds to unsaturated C–N multiple bonds represents a worthwhile pursuit with profound synthetic potential.
Recently, we showed that [Cp*RhCl2]2/AgSbF6 mixtures are capable of catalyzing the addition of 2-arylpyridines to N-Boc and N-sulfonyl imines via C–H functionalization to afford α-branched amine products.2a,3 Building on this result, we focused on expanding this reactivity to include the insertion of C–H bonds across isocyanates towards the synthesis of amides.4 Initially, we demonstrated the feasibility of this transformation by successfully employing the 2-pyridyl directing group (eq 1), but immediately refocused our efforts to the use of the N-acyl amino directing group present in anilides and enamides for the synthesis of N-acyl anthranilamides and enamine amides.
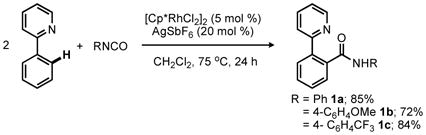 |
(1) |
The atom-economical synthesis of N-acyl anthranilamides from readily available anilides and isocyanates is of significant practical utility given that this structural motif is found in numerous drugs and drug candidates.5 Anthranilamides are typically prepared from the corresponding anthranilic acids; however, this approach is inherently restricted by the limited selection of commercially available anthranilic acids.6 N-Acyl enamine amides obtained from enamides and isocyanates are also useful intermediates because they can readily be reduced to β-amino amides, which are present in important drugs as well as β-peptides.7 Moreover, both N-acyl anthranilamides and enamine amides are poised to undergo cyclodehydration reactions to provide quinazolinone and pyrimidinone frameworks, which are also a common feature in approved drugs and drug candidates.8 Herein we report the first examples of the coupling of anilides and enamides with isocyanates to form amides. This unprecedented method enables the efficient preparation of N-acyl anthranilamides and enamine amides from readily available starting materials.
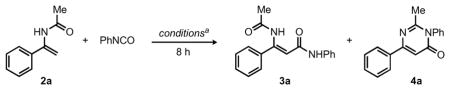
Our initial investigations focused on the identification of a suitable catalyst and reaction conditions for the selective coupling of phenyl isocyanate with the vinylic C–H bond in N-acetyl enamine 2a to afford the amidation product 3a.9,10 Although the use of 2.5 mol % of [Cp*RhCl2]2 proved unsuccessful in catalyzing this reaction (Table 1, entry 1), employing a mixture of 2.5 mol % of [Cp*RhCl2]2 and either 10 mol % of AgSbF6 or AgB(C6F5)4 in THF at 75 °C provided an excellent combined yield of amidation products.11 However, the ratio of the desired amidation product 3a to the cyclodehydrated pyrimidin-4-one 4a remained low (Table 1, entry 2 and 3). Notably, comparable catalyst activity was achieved through the use of the more practical Rh(III) precursor [Cp*Rh(MeCN)3](SbF6)2,12 which was used for all subsequent optimization (Table 1, entry 4). When conducted in the absence of the Rh(III) catalyst, preferential reaction between the amide functionality of the substrate and the isocyanate occurred rather than the desired C–C bond formation (Table 1, entry 5). In addition, as shown in entries 6 to 8, a variety of acids and bases, as well as Lewis acids, did not promote the desired reaction. Alternative solvents, such as CH2Cl2 and tBuOH, provided good yields of the amidation products 3a and 4a, but did not improve the product ratios (Table 1, entries 9 to 11). Variable substrate stoichiometries were investigated; the highest yields were observed for reactions employing 2 equiv of the enamide relative to phenyl isocyanate (Table 1, entry 12).13 The selective formation of either 3a or 4a was ultimately achieved by conducting the reaction at room temperature or 105 °C, respectively (Table 1, entries 13 and 14).
Table 1.
Reaction Optimization
 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| entry | catalyst | solvent | temp | yieldb |
| 1 | [Cp*RhCl2]2 | THF | 75 | 0 |
| 2c | [Cp*RhCl2]2, AgSbF6 | THF | 75 | 93 (1:8) |
| 3c | [Cp*RhCl2]2, AgB(C6F5)4 | THF | 75 | 94 (1:3) |
| 4 | [Cp*Rh(MeCN)3](SbF6)2 | THF | 75 | 94 (1:3) |
| 5 | - | THF | 75 | 0 |
| 6d | AgSbF6 | THF | 75 | 0 |
| 7e | AcOH or TFA | THF | 75 | 0 |
| 8e | NEt3, K3PO4, or KO(tBu) | THF | 75 | 0 |
| 9 | [Cp*Rh(MeCN)3](SbF6)2 | CH2Cl2 | 75 | 85 (3:1) |
| 10 | [Cp*Rh(MeCN)3](SbF6)2 | tBuOH | 75 | 75 (1:8) |
| 11 | [Cp*Rh(MeCN)3](SbF6)2 | toluene | 75 | 30 (1:1) |
| 12f | [Cp*Rh(MeCN)3](SbF6)2 | THF | 75 | 78 (1:2) |
| 13 | [Cp*Rh(MeCN)3](SbF6)2 | THF | rt | 96 (15:1) |
| 14 | [Cp*Rh(MeCN)3](SbF6)2 | THF | 105 | 99 (1:50) |
Conditions: PhNCO:2a = 1:2, 0.05 mmol (0.1 mM) PhNCO scale, 5 mol % of Rh, 8 h.
Determined by 1H NMR relative to 2,6-dimethoxytoluene as an internal standard. Ratio of 3a:4a is indicated in parentheses.
Addition of 10 mol % of Ag salt.
20 mol % of AgSbF6 employed.
20 mol % of acid or base employed.
PhNCO:2a = 2:1.
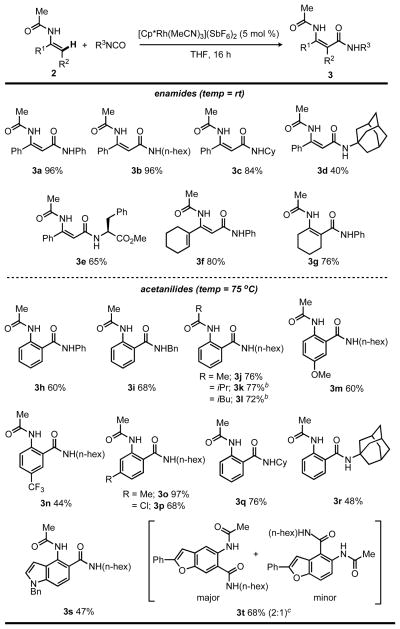
Having defined a highly effective catalyst system and reaction conditions for the selective amidation of N-acyl enamine 2a with phenyl isocyanate, we sought to further explore the reaction scope for other enamides and anilides with a broad range of isocyanates (Table 2). In addition to employing phenyl isocyanate, the amidation of 2a with primary and secondary alkyl isocyanate substrates provided amide products 3b and 3c in excellent yields (96 and 84%, respectively) when employing 5 mol % of Rh in THF at room temperature. Addition of the sterically-demanding tertiary 1-adamantyl isocyanate was also successful, albeit in a modest yield (3d; 40%). An isocyanate derived from the readily available amino acid phenylalanine was readily accommodated (3e; 65%), and served to highlight potential opportunities for the incorporation of chiral components in more complex synthesis. In addition to 2a, enamides derived from 1-acetyl-cyclohexene and cyclohexanone were readily converted to the amides 3f and 3g in good yields (80% and 76%, respectively).
Table 2.
Substrate Scopea
|
Conditions: R3NCO:2 = 1:2, 0.25 mmol (0.25 mM) R3NCO scale, 5 mol % of Rh, 16 h; yields represent isolated material.
Reaction conducted at 120 °C for 24 h. 1H NMR yield relative to 2,6-dimethoxytoluene.
Reaction conducted at 120 °C.
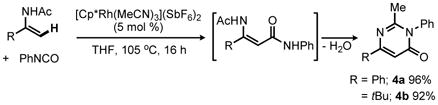
Literature methods are available for the efficient cyclodehydration of N-acyl anthranilamides and enamine amides to quinazolinone and pyrimidinones, respectively.14 However, we postulated that by conducting the Rh(III)-catalyzed reaction at high temperature, both the isocyanate coupling and cyclization might be accomplished in a single step. Indeed, heating enamides 2a (R = Ph) and 2b (R = tBu) with phenyl isocyanate at 105 °C in the presence of 5 mol % of [Cp*Rh(MeCN)3](SbF6)2 directly provided the corresponding pyrimidin-4-ones 4a and 4b in excellent yields (eq 2).15 When monitored by 1H NMR, the initial enamine amide products (3) are formed along with the heterocycles (4) at early conversion. Notably, heating the isolated amide 3a in the absence of [Cp*Rh(MeCN)3](SbF6)2 resulted in negligible conversion to 4a suggesting that cyclodehydration of 3a to 4a is facilitated by the rhodium catalyst rather than being solely thermally-induced.16
 |
(2) |
The substrate scope was extended further to include anilides to provide direct access to anthranilamide derivatives from readily available anilines and isocyanates (Table 2). Although the reaction did not proceed at room temperature, good yields were obtained at 75 °C (3h–3t). Consistent with the substrate scope for enamides (3a–3g), primary, secondary, and tertiary alkyl isocyanates all readily coupled with acetanilide (3i–3t). Significantly, alternative more bulky anilide acyl groups, such as iPr and iBu, provided good yields of anthranilamides 3k and 3l (77% and 72%, respectively). Electron-rich or electron-poor acetanilides featuring meta- or para-substitution provided the desired anthranilamide products with good to excellent yields (3m–3p; 44–97%). Moreover, meta-substituted acetanilides exclusively provided the less substituted anthranilamide products (3o and 3p). N-acylamino substituted nitrogen and oxygen heterocycles were also evaluated and provided anthranilimides that incorporate indole (3s) and benzofuran (3t) functionality, with two regioisomeric products obtained for the substituted benzofuran substrate (3t).
The product regiochemistry observed for the isocyanate additions to aromatic substrates is most consistent with a Rh-mediated C–H cleavage step directed by a Lewis basic group instead of a more traditional electrophilic aromatic substitution mechanism. Specifically, ortho-functionalization rather than meta-substitution is observed for 2-phenylpyridine, and exclusive ortho-substitution, as opposed to ortho-/para-product mixtures, is observed for anilides.
To provide preliminary insight into the reaction mechanism for the Rh(III)-catalyzed addition of isocyanates to acetanilides, deuterium kinetic isotope effects (DKIE) were also investigated. When a competition reaction was conducted with an equimolar ratio of deuterio- and protio-acetanilide, a ≥2-fold product ratio favoring the protio-derived product was observed at early conversion (eq 3).13 However, when acetanilide-d5 was subjected to the standard reaction conditions modest deuterium exchange was observed at the ortho-positions of both the unreacted anilide (21% H) and the product N-acyl anthranilamide (18% H) (eq 4), thus complicating the interpretation of the data presented in eq 3. The DKIE was therefore also evaluated for the reaction of phenyl isocyanate with N-cyclohexenyl acetamide 2b and the analogous deuterated enamide 2b-d3. Indeed, a comparison of the initial rates of enamine amide product formation at early conversions revealed a DKIE of 2.2 (eq 5).13 Importantly, no background H/D exchange was observed for unreacted 2b-d3 under these reaction conditions. Although elucidation of the rate law for the reaction is necessary to interpret this result properly, a primary isotope effect is consistent with rate-limiting C-H bond activation rather than direct π-bond addition to the isocyanate electrophile.17 We plan to carry out a more thorough kinetic examination of the reaction to confirm this inference.
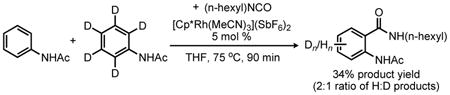 |
(3) |
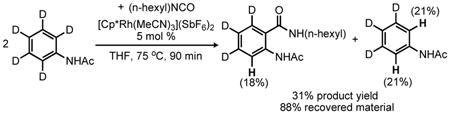 |
(4) |
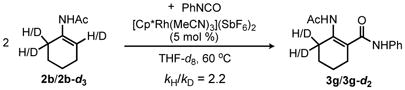 |
(5) |
In summary, we have identified [Cp*Rh(MeCN)3](SbF6)2 as an effective catalyst for the addition of anilide and enamide C–H bonds across a broad range of isocyanates to afford valuable N-acyl anthranilamides and enamine amides. Studies are on-going to better understand the reaction mechanism as well as to apply the method to natural product and drug synthesis.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NIH grant GM069559 (to J.A.E.) and by the Director, Office of Energy Research, Office of Basic Energy Science, Chemical Sciences Division, U.S. Department of Energy under contract DE-AC02-05CH11231 (to R.G.B.). K.D.H. is grateful to the National Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) for a post-doctoral fellowship.
Footnotes
Supporting Information. Full experimental details and characterization data. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.For recent reviews on C–H functionalization employing alkenes and alkynes, see: Satoh T, Miura M. Chem Eur J. 2010;16:11212–11222. doi: 10.1002/chem.201001363.Colby DA, Bergman RG, Ellman JA. Chem Rev. 2010;110:624–655. doi: 10.1021/cr900005n.Karimi B, Behzadnia H, El-hamifar D, Akhavan PF, Esfahani FK, Zamani A. Synthesis. 2010:1399–1427.Wang X, Zhou L, Lu W. Curr Org Chem. 2010;14:289–307.Chen X, Engle KM, Wang D–H, Yu J–Q. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2009;48:5094–5115. doi: 10.1002/anie.200806273.
- 2.For reports on C–H additions to C–N multiple bonds, see: Tsai AS, Tauchert ME, Bergman RG, Ellman JA. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:1248–1250. doi: 10.1021/ja109562x.Li Y, Li B–J, Wang W–H, Huang W–P, Zhang X–S, Chen K, Shi Z–J. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2011;50:2115–2119. doi: 10.1002/anie.201007464.Kuninobu Y, Kikuchi K, Tokunaga Y, Nishina Y, Takai K. Tetrahedron. 2008;64:5974–5981.Kuninobu Y, Tokunaga Y, Kawata A, Takai K. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:202–209. doi: 10.1021/ja054216i.Zhou C, Larock RC. J Org Chem. 2006;71:3551–3558. doi: 10.1021/jo060220g.Zhou C, Larock RC. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:2302–2303. doi: 10.1021/ja038687l.Fukumoto Y, Sawada K, Hagihara M, Chatani N, Murai S. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2002;41:2779–2781. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20020802)41:15<2779::AID-ANIE2779>3.0.CO;2-J.Hong P, Yamazaki H, Sonogashira K, Hagihara N. Chem Lett. 1978:535–538.
- 3.For leading references concerning the Rh(III)-catalyzed addition of C–H bonds to alkenes and alkynes, see: Umeda N, Hirano K, Satoh T, Shibata N, Sato H, Miura M. J Org Chem. 2011;76:13–24. doi: 10.1021/jo1021184.Patureau FW, Besset T, Glorius F. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2011;50:1064–1067. doi: 10.1002/anie.201006222.Patureau FW, Glorius F. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:9982–9983. doi: 10.1021/ja103834b.Hyster TK, Rovis T. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:10565–10569. doi: 10.1021/ja103776u.Chen J, Song G, Pan C–L, Li X. Org Lett. 2010;12:5426–5429. doi: 10.1021/ol1022596.Wang F, Song G, Li X. Org Lett. 2010;12:5430–5433. doi: 10.1021/ol102241f.Stuart DR, Bertrand-Laperle M, Burgess KMN, Fagnou K. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:16474–16475. doi: 10.1021/ja806955s.Li L, Brennessel WW, Jones WD. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:12414–12419. doi: 10.1021/ja802415h.Ueura K, Satoh T, Miura M. Org Lett. 2007;9:1407–1409. doi: 10.1021/ol070406h.
- 4.Related transformations have been reported for the Re-catalyzed imine directed addition of isocyanates to electron-rich heterocycles: see reference 2c.
- 5.Typing the name of these drug and drug candidates into Pub-chem provides the compound structure, bioactivity, full list of literature, and access to ongoing clinical trials, applications, and usage: betrixaban (CID 10275777) and tariquidar (CID 148201).
- 6.For a recent report of the synthesis of N-acyl anthranilic acids by the Pd-catalyzed carboxylation of anilide C–H bonds with CO, see: Giri R, Lam JK, Yu J–Q. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:686–693. doi: 10.1021/ja9077705.
- 7.(a) Juaristi E, Soloshonok V, editors. Enantioselective Synthesis of β-Amino Acids. 2. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; Hoboken: 2005. [Google Scholar]; (b) Weber AE, Thornberry N. Annu Rep Med Chem. 2007;42:95–109. [Google Scholar]; (c) Cheng RP, Gellman SH, DeGrado WF. Chem Rev. 2001;101:3219–3232. doi: 10.1021/cr000045i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Typing the name of these drugs into Pubchem provides the compound structure, bioactivityand access to ongoing clinical trials and applications: Tarceva (CID 176870) and Iressa (CID 123631).
- 9.Enamides used in this study were readily prepared from the corresponding ketones: Guan Z–H, Zhang Z–Y, Ren Z–H, Wang Y–Y, Zhang X. J Org Chem. 2011;76:339–341. doi: 10.1021/jo1022348.Tang W, Capacci A, Sarvestani M, Wei X, Yee NK, Senanayake CH. J Org Chem. 2009;74:9528–9530. doi: 10.1021/jo902259u.
- 10.For recent examples of Rh(III)-catalyzed functionalization of vinylic C–H bonds of N-acetyl enamides with alkynes and alkenes, see: Huestis MP, Chan L, Stuart DR, Fagnou K. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2011;50:1338–1341. doi: 10.1002/anie.201006381.Stuart DR, Alsabeh P, Kuhn M, Fagnou K. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:18326–18339. doi: 10.1021/ja1082624.Rakshit S, Patureau FW, Glorius F. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:9585–9587. doi: 10.1021/ja104305s.
- 11.For examples of halide abstraction reagents used in conjunction with [Cp*RhCl2]2, see: (a) reference 2a. (b) reference 3c. (c) reference 10b,c. Schipper DJ, Hutchinson M, Fagnou K. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:6910–6911. doi: 10.1021/ja103080d.
- 12.White C, Thompson SJ, Maitlis PM. J Chem Soc, Dalton Trans. 1977:1654–1661. [Google Scholar]
- 13.See Supporting Information.
- 14.Kshirsagar UA, Mhaske SB, Argade NP. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007;48:3243–3246.For a review, see: Connolly DJ, Cusack D, O’Sullivan TP, Guiry PJ. Tetrahedron. 2005;61:10153–10202.Mazurkiewicz R. Monatsh Chem. 1989;120:973.
- 15.Cyclization occurs more slowly for the less acidic N-hexyl or N-cyclohexyl amides obtained from alkyl isocyanates.
- 16.The cyclodehydration of isolated 3a to 4a was achieved in an 80% 1H NMR yield (relative to 2,6-dimethoxytoluene) when treated with 5 mol % [Cp*Rh(MeCN)3](SbF6)2 in THF at 105 °C for 16 h.
- 17.Kinetic isotope studies for Rh(III)-catalyzed C–H/alkyne couplings have been shown to be consistent with rate-limiting C–H bond activation steps, see: Guimond N, Gorelsky SI, Fagnou K. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:6449–6457. doi: 10.1021/ja201143v.(b) reference 3a. (c) reference 10b.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


