Abstract
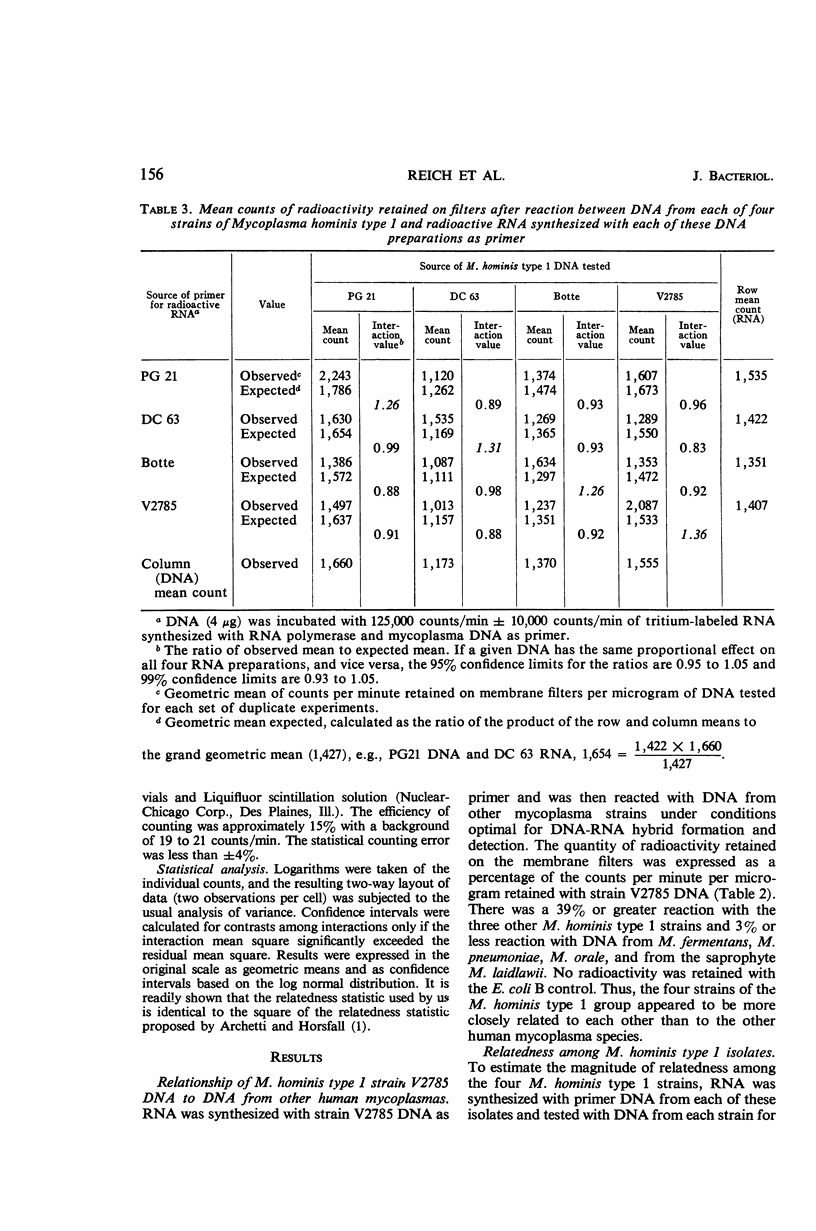
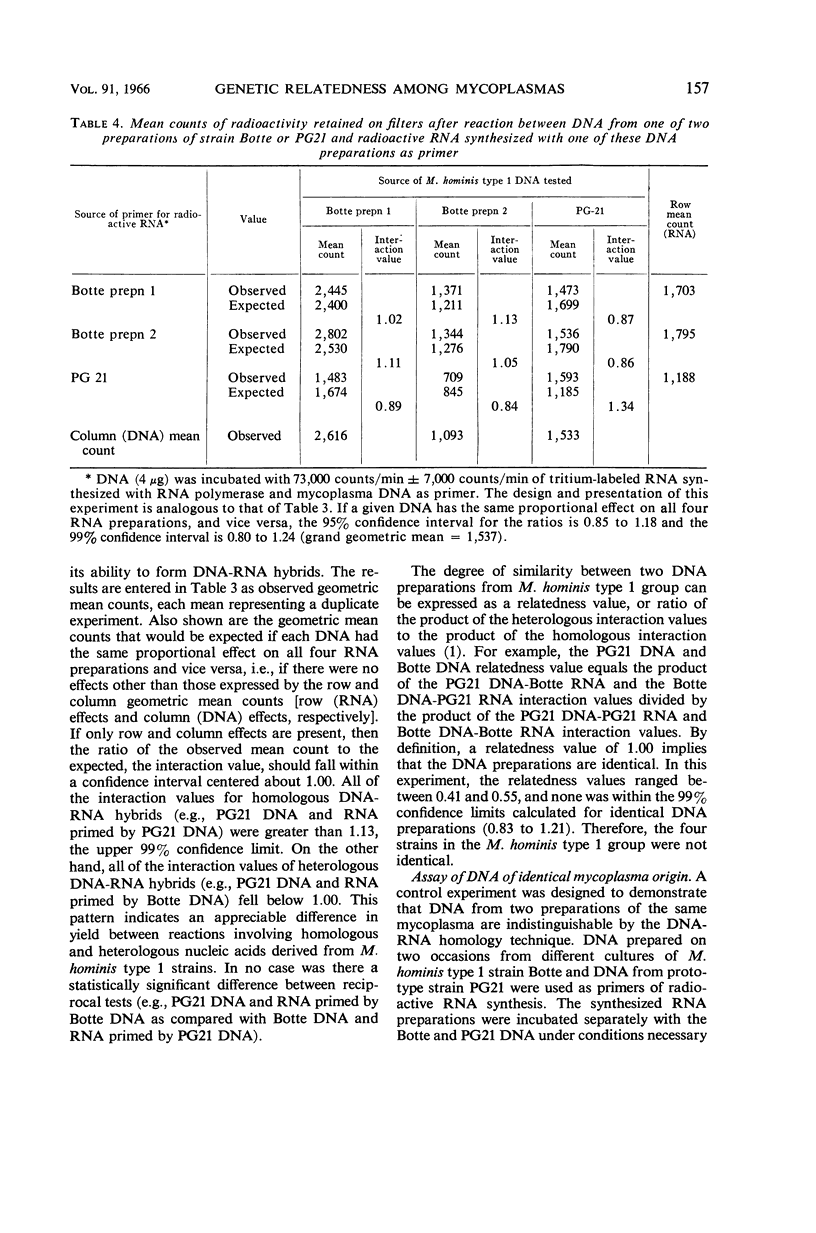
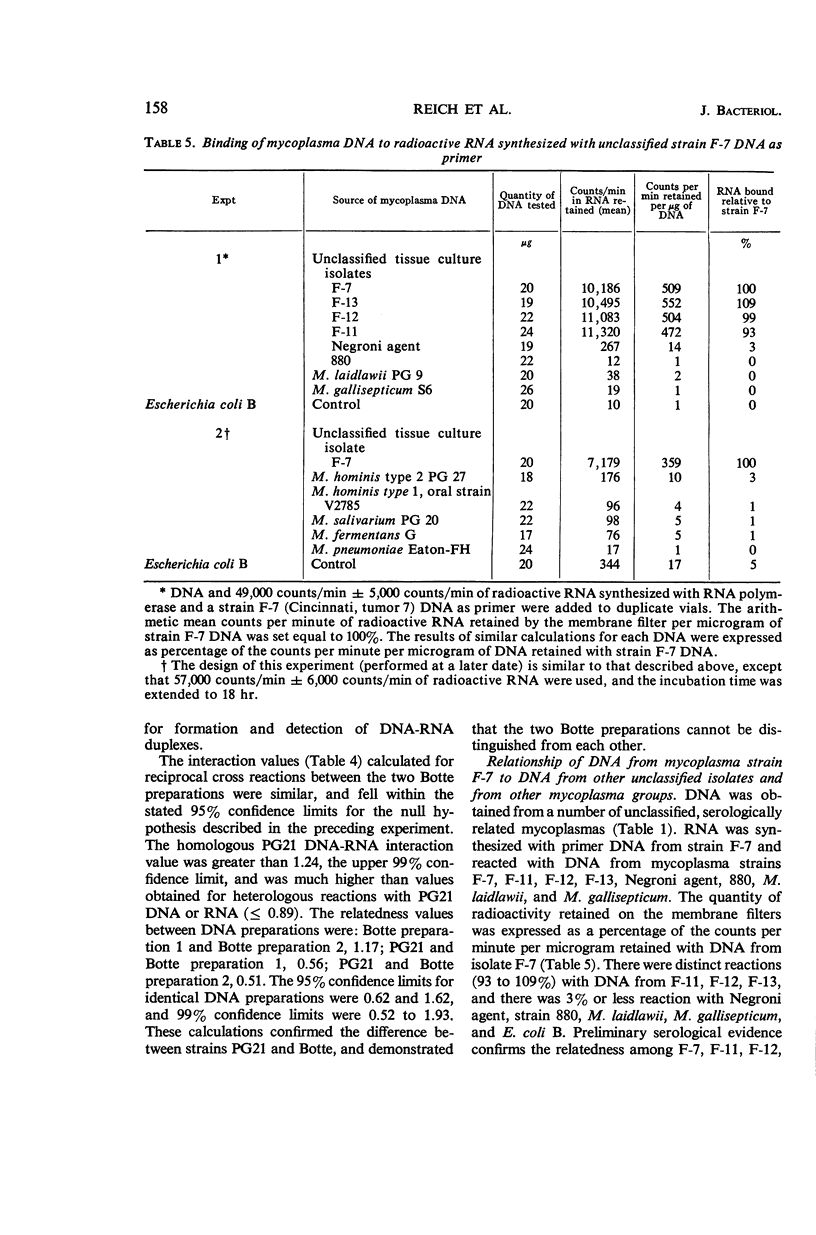
Reich, Paul R. (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Md.), Norman L. Somerson, James A. Rose, and Sherman M. Weissman. Genetic relatedness among mycoplasmas as determined by nucleic acid homology. J. Bacteriol. 91:153–160. 1966.—A sensitive membrane filter method to detect nucleic acid homology was used to determine genetic relatedness among mycoplasma isolates. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was isolated from mycoplasmas and used as a primer for synthesis of tritium-labeled, complementary ribonucleic acid (RNA) by the enzyme RNA polymerase. DNA from each mycoplasma isolate tested was reacted separately with complementary RNA synthesized with homologous or heterologous DNA as primer. The quantity of DNA-RNA hybrids formed was assayed by the nitrocellulose membrane filter method. The amount of radioactivity bound to the membrane filter was used to measure the degree of homology between the nucleic acids. The three mycoplasma isolates from human oral cavities (DC 63, V2785, Botteicher) and the prototype strain PG21 placed in the Mycoplasma hominis type 1 group by gel diffusion and complement-fixation testing were investigated with this technique. Analysis of the data confirmed their immunological grouping with the M. hominis type 1 and their distinction from other human mycoplasmas. In contrast to the data from immunological studies, none of the four isolates tested appeared to be identical to any other. Preliminary experiments with DNA from four other mycoplasma isolates from tissue cultures inoculated with human material revealed them to be closely related, and possibly identical. The advantages of this nucleic acid homology technique for the study of relatedness among mycoplasmas are described.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARCHETTI I., HORSFALL F. L., Jr Persistent antigenic variation of influenza A viruses after incomplete neutralization in ovo with heterologous immune serum. J Exp Med. 1950 Nov 1;92(5):441–462. doi: 10.1084/jem.92.5.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARMSTRONG D., HENLE G., SOMERSON N. L., HAYFLICK L. CYTOPATHOGENIC MYCOPLASMAS ASSOCIATED WITH TWO HUMAN TUMORS. I. ISOLATION AND BIOLOGICAL ASPECTS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Aug;90:418–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.2.418-424.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER M., LEACH R. H. A MYCOPLASMA WHICH INDUCES ACIDITY AND CYTOPATHIC EFFECT IN TISSUE CULTURE. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Feb;34:285–294. doi: 10.1099/00221287-34-2-285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMBERLIN M., BERG P. Deoxyribo ucleic acid-directed synthesis of ribonucleic acid by an enzyme from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:81–94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M., HAYFLICK L., BARILE M. F. Growth on artificial medium of an agent associated with atypical pneumonia and its identification as a PPLO. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Jan 15;48:41–49. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARD D. G., FREUNDT E. A. The classification and nomenclature of organisms of the pleuropneumonia group. J Gen Microbiol. 1956 Feb;14(1):197–207. doi: 10.1099/00221287-14-1-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEIDUSCHEK E. P., NAKAMOTO T., WEISS S. B. The enzymatic synthesis of RNA: complementary interaction with DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Sep 15;47:1405–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.9.1405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIRARDI A. J., HAYFLICK L., LEWIS A. M., SOMERSON N. L. RECOVERY OF MYCOPLASMAS IN THE STUDY OF HUMAN LEUKAEMIA AND OTHER MALIGNANCIES. Nature. 1965 Jan 9;205:188–189. doi: 10.1038/205188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HYER B. H., MCCARTHY B. J., BOLTON E. T. A MOLECULAR APPROACH IN THE SYSTEMATICS OF HIGHER ORGANISMS. DNA INTERACTIONS PROVIDE A BASIS FOR DETECTING COMMON POLYNUCLEOTIDE SEQUENCES AMONG DIVERSE ORGANISMS. Science. 1964 May 22;144(3621):959–967. doi: 10.1126/science.144.3621.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEMCKE R. M. THE SEROLOGICAL DIFFERENTIATION OF MYCOPLASMA STRAINS (PLEURO-PNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS) FROM VARIOUS SOURCES. J Hyg (Lond) 1964 Jun;62:199–219. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400039930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU C. Studies on primary atypical pneumonia. I. Localization, isolation, and cultivation of a virus in chick embryos. J Exp Med. 1957 Oct 1;106(4):455–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.106.4.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCARTHY B. J., BOLTON E. T. An approach to the measurement of genetic relatedness among organisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jul;50:156–164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUFSON M. A., LUDWIG W. M., PURCELL R. H., CATE T. R., TAYLOR-ROBINSON D., CHANOCK R. M. EXUDATIVE PHARYNGITIS FOLLOWING EXPERIMENTAL MYCOPLASMA HOMINIS: TYPE 1 INFECTION. JAMA. 1965 Jun 28;192:1146–1152. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080260034010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmur J., Lane D. STRAND SEPARATION AND SPECIFIC RECOMBINATION IN DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACIDS: BIOLOGICAL STUDIES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Apr;46(4):453–461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.4.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICOL C. S., EDWARD D. G. Role of organisms of the pleuropneumonia group in human genital infections. Br J Vener Dis. 1953 Sep;29(3):141–150. doi: 10.1136/sti.29.3.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NYGAARD A. P., HALL B. D. A method for the detection of RNA-DNA complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1963 Jul 18;12:98–104. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(63)90242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUITER M., WENTHOLT H. M. Isolation of a pleuropneumonia-like organism (G-strain) in a case of fusospirillary vulvovaginitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1953;33(1-2):123–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR-ROBINSON D., CANCHOLA J., FOX H., CHANOCK R. M. A NEWLY IDENTIFIED ORAL MYCOPLASMA (M. ORALE) AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO OTHER HUMAN MYCOPLASMAS. Am J Hyg. 1964 Jul;80:135–148. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR-ROBINSON D., SOMERSON N. L., TURNER H. C., CHANOCK R. M. SEROLOGICAL RELATIONSHIPS AMONG HUMAN MYCOPLASMAS AS SHOWN BY COMPLEMENT-FIXATION AND GEL DIFFUSION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1261–1273. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1261-1273.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAMOTO R., ADLER H. E. Characterization of pleuropneumonia-like organisms of avian origin. II. Cultural, biochemical, morphological and further serological studies. J Infect Dis. 1958 May-Jun;102(3):243–250. doi: 10.1093/infdis/102.3.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



