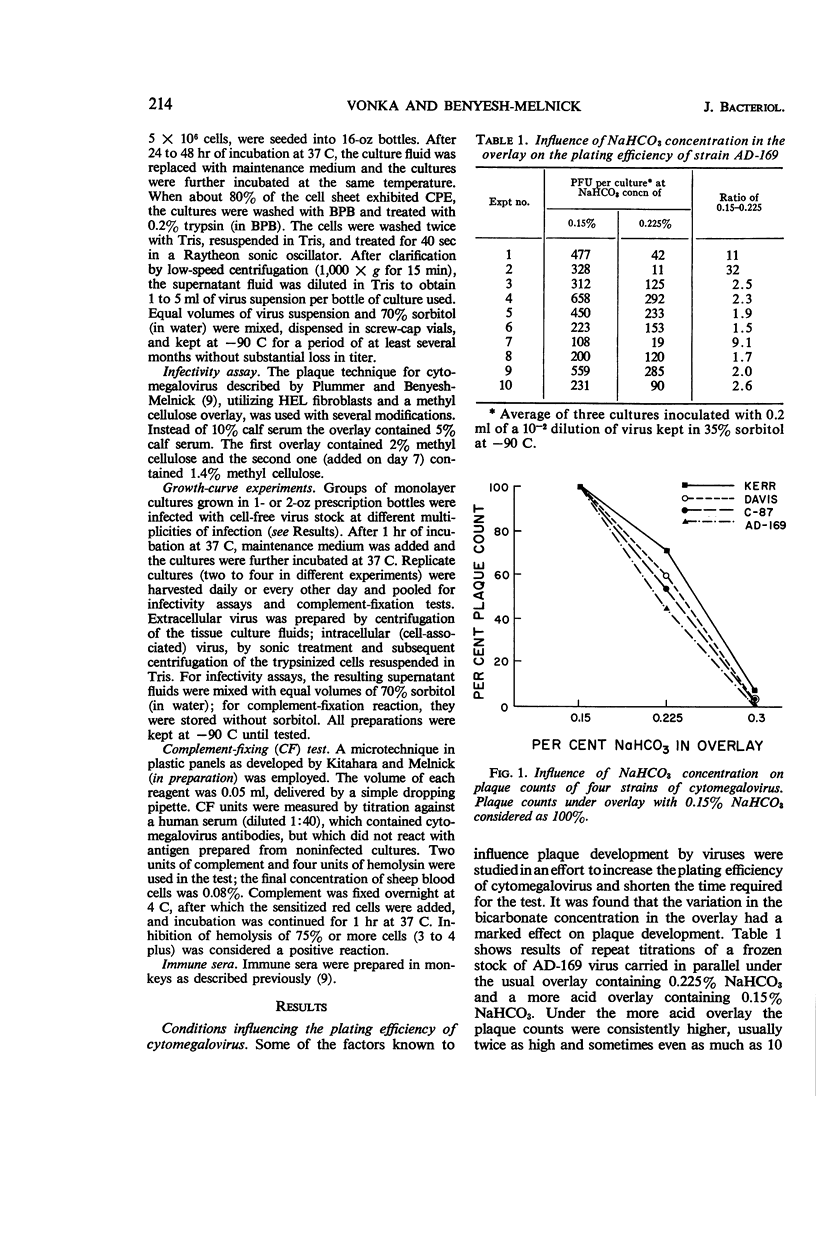
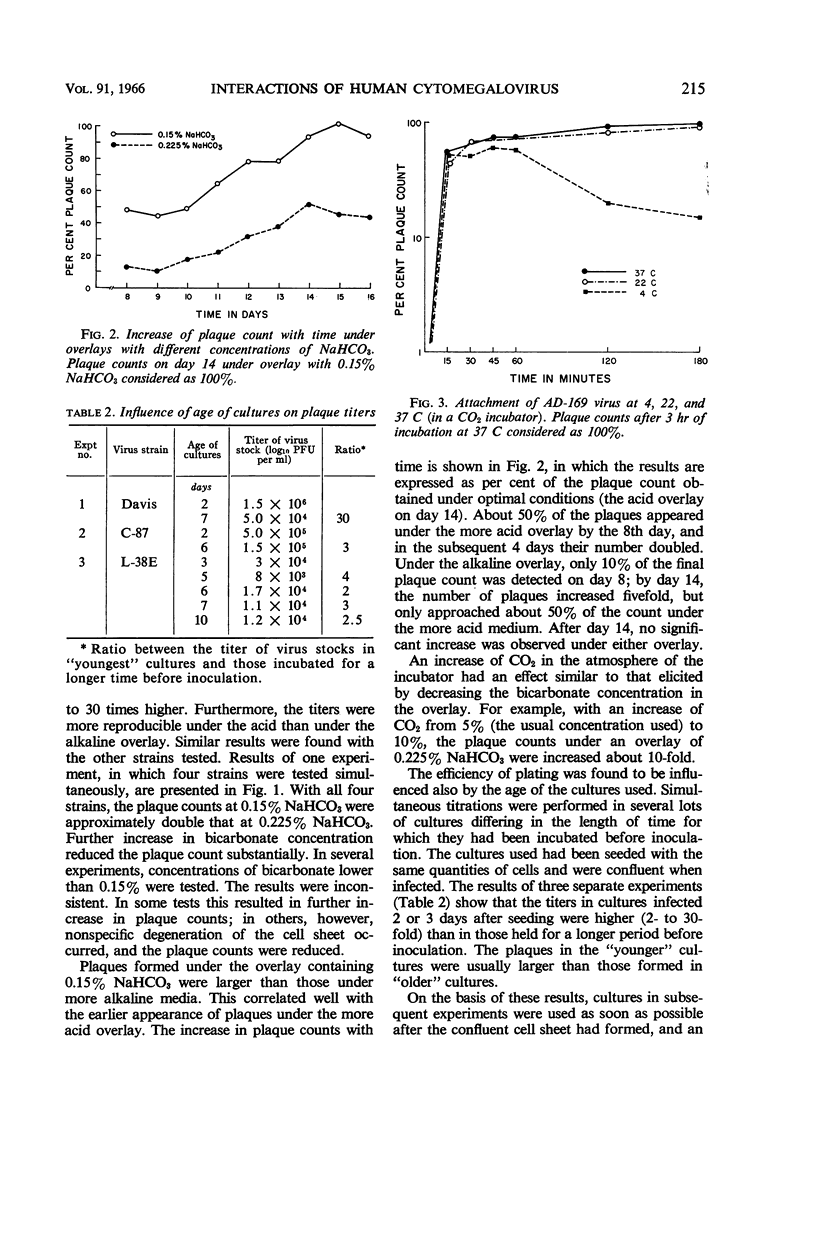
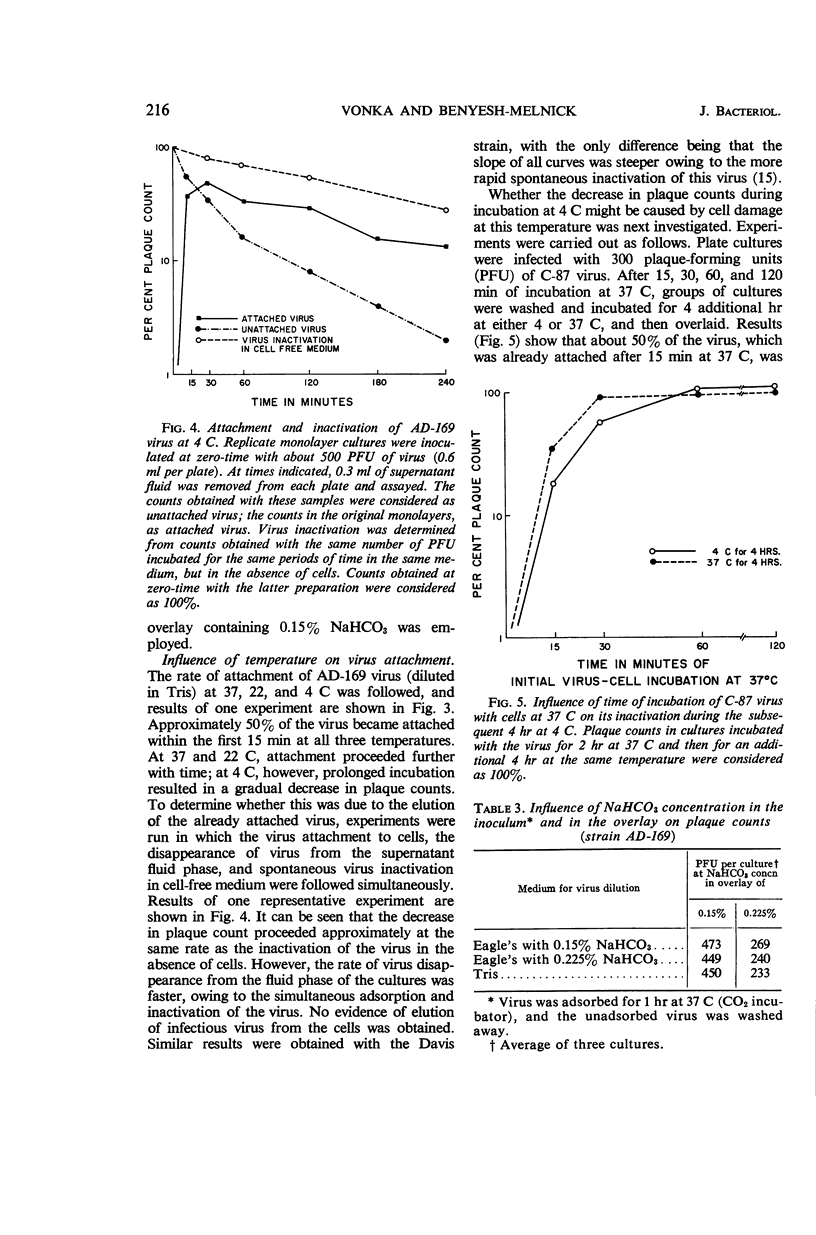
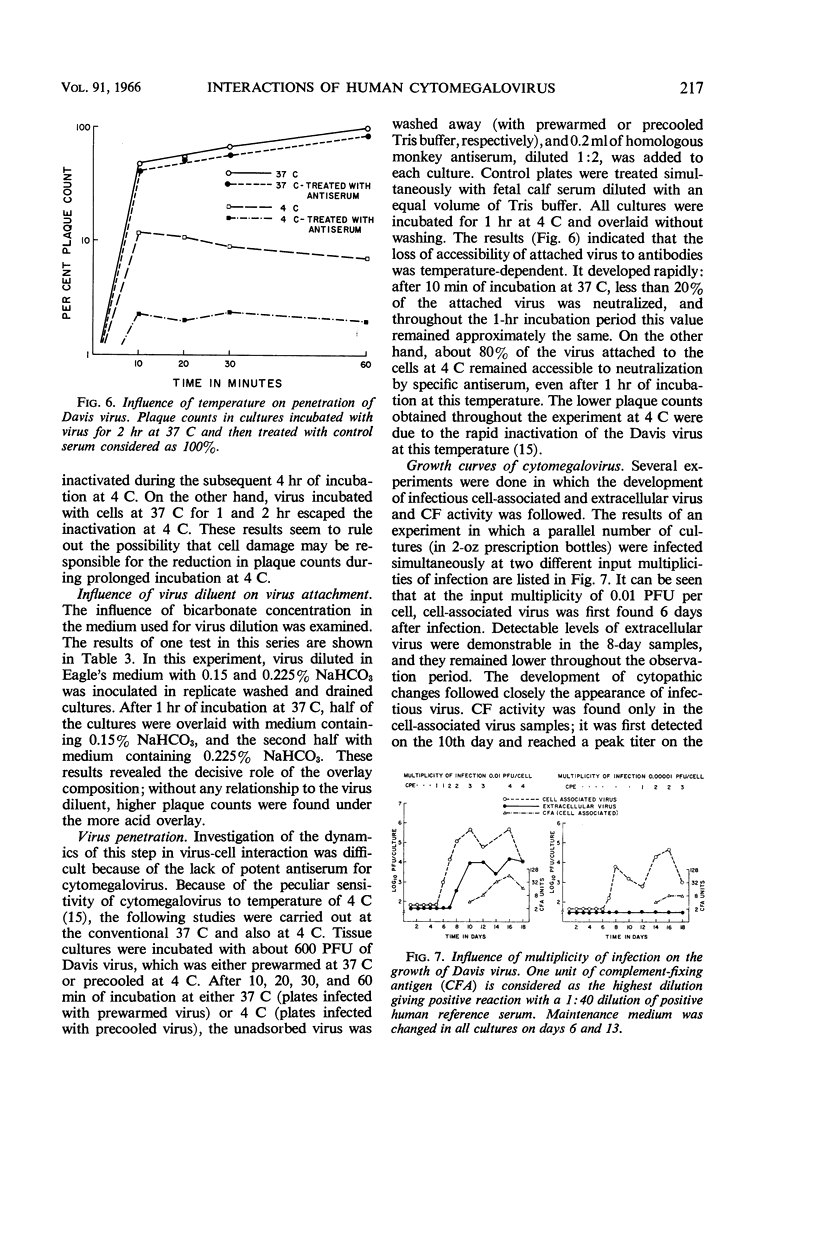
Abstract
Vonka, Vladimir (Baylor University College of Medicine, Houston, Tex.), and Matilda Benyesh-Melnick. Interactions of human cytomegalovirus with human fibroblasts. J. Bacteriol. 91:213–220. 1966.—Virus attachment of human cytomegalovirus to human embryo lung fibroblasts was found to be temperature-independent, from 4 to 37 C. Prolonged incubation at 4 C, however, resulted in inactivation of a high proportion of attached virus. Virus penetration seemed to be temperature-dependent, occurring at 37 C but not at 4 C. Detailed studies of the growth curve of the virus were made. Cell-associated virus preceded the appearance of virus in the fluid phase by 2 to 5 days. Complement-fixing antigen could be detected, but only when the cytopathic effect was advanced, and it was demonstrable only in the cell-associated fraction. Under methyl cellulose, decreasing the bicarbonate concentration in the overlay from 0.225 to 0.15% resulted in marked increase in plating efficiency with all strains tested. However, varying the concentration of bicarbonate from 0.3 to 0.15% in fluid medium did not influence the growth of virus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AGOL V. I., CHUMAKOVA M. Ia. An agar polysaccharide and d marker of poliovirus. Virology. 1962 May;17:221–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER P., MELNICK J. L., MAYOR H. D. A MORPHOLOGIC COMPARISON BETWEEN THE DEVELOPMENTAL STAGES OF HERPES ZOSTER AND HUMAN CYTOMEGALOVIRUS. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Feb;76:11–23. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENYESH-MELNICK M., DESSY S. I., FERNBACH D. J. CYTOMEGALOVIRURIA IN CHILDREN WITH ACUTE LEUKEMIA AND IN OTHER CHILDREN. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Nov;117:624–630. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENYESH-MELNICK M., ROSENBERG H. S., WATSON B. VIRUSES IN CELL CULTURES OF KIDNEYS OF CHILDREN WITH CONGENITAL HEART MALFORMATIONS AND OTHER DISEASES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Nov;117:452–459. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAIG J. M., MACAULEY J. C., WELLER T. H., WIRTH P. Isolation of intranuclear inclusion producing agents from infants with illnesses resembling cytomegalic inclusion disease. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Jan;94(1):4–12. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-22841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODHEART C. R., JAROSS L. B. Human cytomegalovirus. Assay by counting infected cells. Virology. 1963 Apr;19:532–535. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSIUNG G. D., MELNICK J. L. Effect of sodium bicarbonate concentration on plaque formation of virulent and attenuated polioviruses. J Immunol. 1958 Apr;80(4):282–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGAVRAN M. H., SMITH M. G. ULTRASTRUCTURAL, CYTOCHEMICAL, AND MICROCHEMICAL OBSERVATIONS ON CYTOMEGALOVIRUS (SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS) INFECTION OF HUMAN CELLS IN TISSUE CULTURE. Exp Mol Pathol. 1965 Feb;76:1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(65)90019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLUMMER G., BENYESH-MELNICK M. A PLAQUE REDUCTION NEUTRALIZATION TEST FOR HUMAN CYTOMEGALOVIRUS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Oct;117:145–150. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPP F., RASMUSSEN L. E., BENYESH-MELNICK M. THE IMMUNOFLUORESCENT FOCUS TECHNIQUE IN STUDYING THE REPLICATION OF CYTOMEGALOVIRUS. J Immunol. 1963 Nov;91:709–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWE W. P., HARTLEY J. W., WATERMAN S., TURNER H. C., HUEBNER R. J. Cytopathogenic agent resembling human salivary gland virus recovered from tissue cultures of human adenoids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jun;92(2):418–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUEBNER B. H., HIRANO T., SLUSSER R. J., MEDEARIS D. N., Jr HUMAN CYTOMEGALOVIRUS INFECTION. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC AND HISTOCHEMICAL CHANGES IN CULTURES OF HUMAN FIBROBLASTS. Am J Pathol. 1965 Mar;46:477–496. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEMOTO K. K., LIEBHABER H. Virus-polysaccharide interactions. II. Enhancement of plague formation and the detection of variants of poliovirus with dextran sulfate. Virology. 1962 Jul;17:499–501. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M., DULBECCO R., WENNER H. A. Mutants of poliomyelitis viruses with reduced efficiency of plating in acid medium and reduced neuropathogenicity. Virology. 1957 Aug;4(1):141–155. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90050-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonka V., Benyeshmelnick M. Thermoinactivation of human cytomegalovirus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):221–226. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.221-226.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLER T. H., HANSHAW J. B. Virologic and clinical observations on cytomegalic inclusion disease. N Engl J Med. 1962 Jun 14;266:1233–1244. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196206142662401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



