Abstract
Saunders, Grady F. (University of Illinois, Urbana), and L. Leon Campbell. Ribonucleic acid and ribosomes of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J. Bacteriol. 91:332–339. 1966.—The ability of some thermophilic bacteria to grow at temperatures as high as 76 C emphasizes the remarkable thermal stability of their crucial macromolecules. An investigation of the ribonucleic acid (RNA) and ribosomes of Bacillus stearothermophilus was conducted. Washed log-phase cells were disrupted either by sonic treatment or by alumina grinding in 10−2m MgCl2–10−2m tris-(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane buffer, pH 7.4 (TM buffer). Ultracentrifugal analysis revealed peaks at 72.5S, 101S, and 135S, with the 101S peak being the most prominent. By lowering the Mg++ concentration to 10−3m, the ribosome preparation was dissociated to give 40S, 31S, and 54S peaks. These in turn were reassociated in the presence of 10−2m Mg++ to give the larger 73S and 135S particles. When heated in TM buffer, Escherichia coli ribosomes began a gradual dissociation at 58 C, and at 70 C underwent a large hyperchromic shift with a Tm at 72.8 C. In contrast, B. stearothermophilus ribosomes did not show a hyperchromic shift below 70 C; they had a Tm of 77.9 C. The thermal denaturation curves of the 4S, 16S, and 23S RNA from both organisms were virtually identical. The gross amino acid composition of B. stearothermophilus ribosomes showed no marked differences from that reported for E. coli ribosomes. These data suggest that the unusual thermal stability of B. stearothermophilus ribosomes may reflect either an unusual packing arrangement of the protein to the RNA or differences in the primary structure of the ribosomal proteins.
Full text
PDF


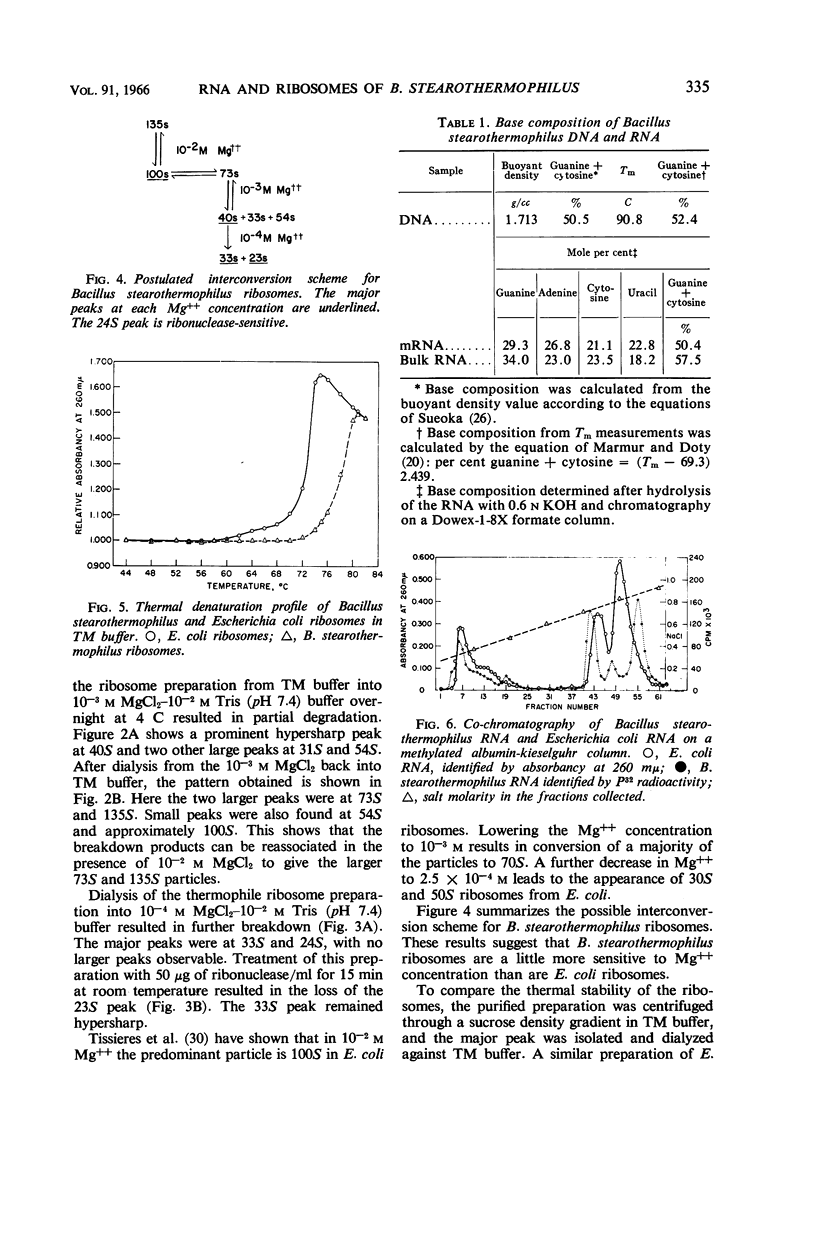


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALLEN M. B. The thermophilic aerobic sporeforming bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1953 Jun;17(2):125–173. doi: 10.1128/br.17.2.125-173.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ARCA M., CALVORI C., FRONTALI L., TECCE G. THE ENZYMIC SYNTHESIS OF AMINOACYL DERIVATIVES OF SOLUBLE RIBONUCLEIC ACID FROM BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 22;87:440–448. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(64)90116-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL L. L., CLEVELAND P. D. Thermostable alpha-amylase of Bacillus stearothermophilus. IV. Amino-terminal and carboxyl-terminal amino acid analysis. J Biol Chem. 1961 Nov;236:2966–2969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL L. L., MANNING G. B. Thermostable alpha-amylase of Bacillus stearothermophilus. III. Amino acid composition. J Biol Chem. 1961 Nov;236:2962–2965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
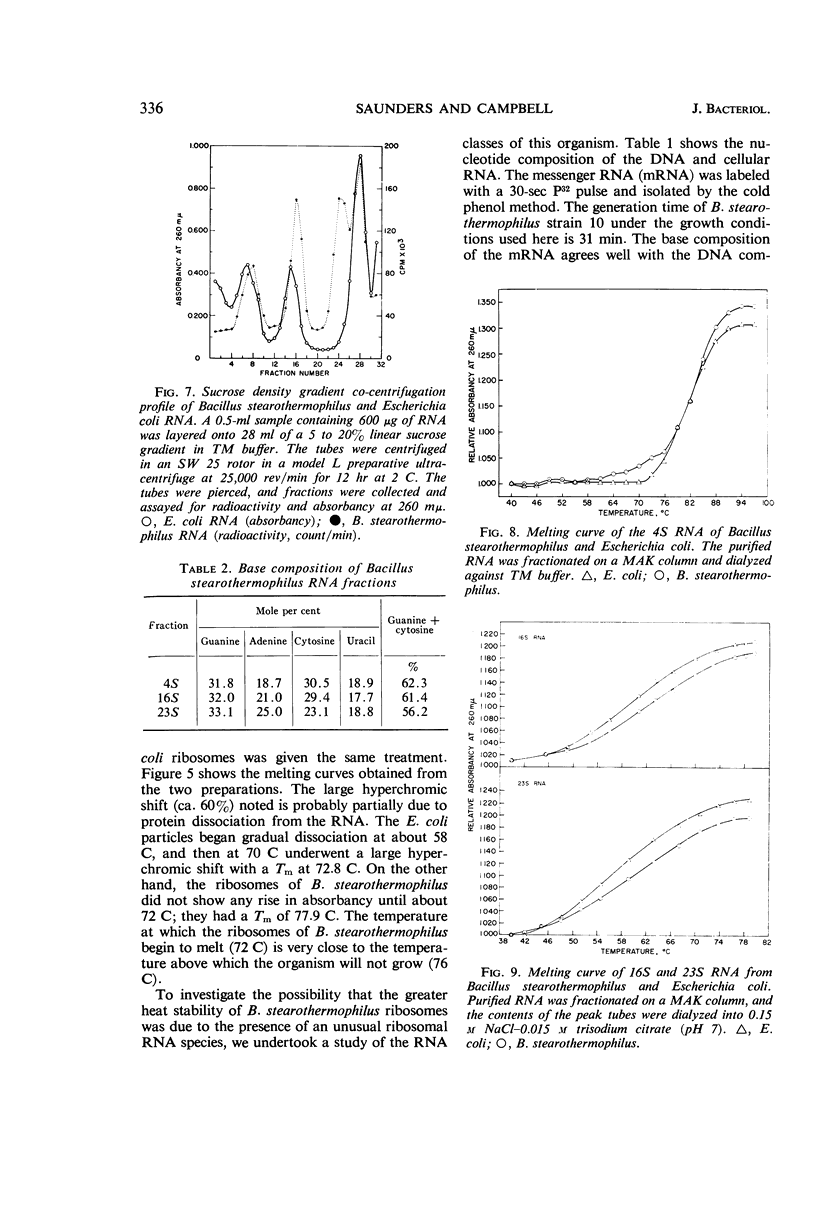
- DOWNEY R. J., GEORGI C. E., MILITZER W. E. Electron transport particles from Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1962 May;83:1140–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.5.1140-1146.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDMAN S. M., WEINSTEIN I. B. LACK OF FIDELITY IN THE TRANSLATION OF SYNTHETIC POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:988–996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIACOMONI D., SPIEGELMAN S. Origin and biologic individuality of the genetic dictionary. Science. 1962 Dec 21;138(3547):1328–1331. doi: 10.1126/science.138.3547.1328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIERER A., SCHRAMM G. Infectivity of ribonucleic acid from tobacco mosaic virus. Nature. 1956 Apr 14;177(4511):702–703. doi: 10.1038/177702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaughran E. R. THE THERMOPHILIC MICROORGANISMS. Bacteriol Rev. 1947 Sep;11(3):189–225. doi: 10.1128/br.11.3.189-225.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYASHI M., SPIEGELMAN S. The selective synthesis of informational RNA in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1961 Oct 15;47:1564–1580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.47.10.1564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOFFLER H. Protoplasmic differences between mesophiles and thermophiles. Bacteriol Rev. 1957 Dec;21(4):227–240. doi: 10.1128/br.21.4.227-240.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANDELL J. D., HERSHEY A. D. A fractionating column for analysis of nucleic acids. Anal Biochem. 1960 Jun;1:66–77. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(60)90020-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANNING G. B., CAMPBELL L. L., FOSTER R. J. Thermostable alpha-amylase of Bacillus stearothermophilus. II. Physical properties and molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1961 Nov;236:2958–2961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANNING G. B., CAMPBELL L. L. Thermostable alpha-amylase of Bacillus stearothermophilus. I. Crystallization and some general properties. J Biol Chem. 1961 Nov;236:2952–2957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its thermal denaturation temperature. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:109–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80066-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARMUR J. Thermal denaturation of deoxyribosenucleic acid isolated from a thermophile. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Feb 26;38:342–343. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHEMEIER P. F., MORITA R. Y. INFLUENCE OF SUBSTRATE-COFACTOR RATIOS ON PARTIALLY PURIFIED INORGANIC PYROPHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY AT ELEVATED TEMPERATURES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1661–1666. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1661-1666.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORITA R. Y., HAIGHT R. D. Malic dehydrogenase activity at 101 C under hydrostatic pressure. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jun;83:1341–1346. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.6.1341-1346.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORITA R. Y., MATHEMEIER P. F. TEMPERATURE-HYDROSTATIC PRESSURE STUDIES ON PARTIALLY PURIFIED INORGANIC PYROPHOSPHATASE ACTIVITY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1667–1671. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1667-1671.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPAHR P. F. Amino acid composition of ribosomes from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1962 May;4:395–406. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAEHELIN T., BRINTON C. C., WETTSTEIN F. O., NOLL H. STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF E. COLI ERGOSOMES. Nature. 1963 Aug 31;199:865–870. doi: 10.1038/199865a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUEOKA N., CHENG T. Y. Fractionation of nucleic acids with the methylated albumin column. J Mol Biol. 1962 Mar;4:161–172. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON P. J., THOMPSON T. L. Some characteristics of a purified heat-stable aldolase. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:694–700. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.694-700.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELKER N. E., CAMPBELL L. L. INDUCTION AND PROPERTIES OF A TEMPERATURE BACTERIOPHAGE FROM BACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:175–184. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.175-184.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]