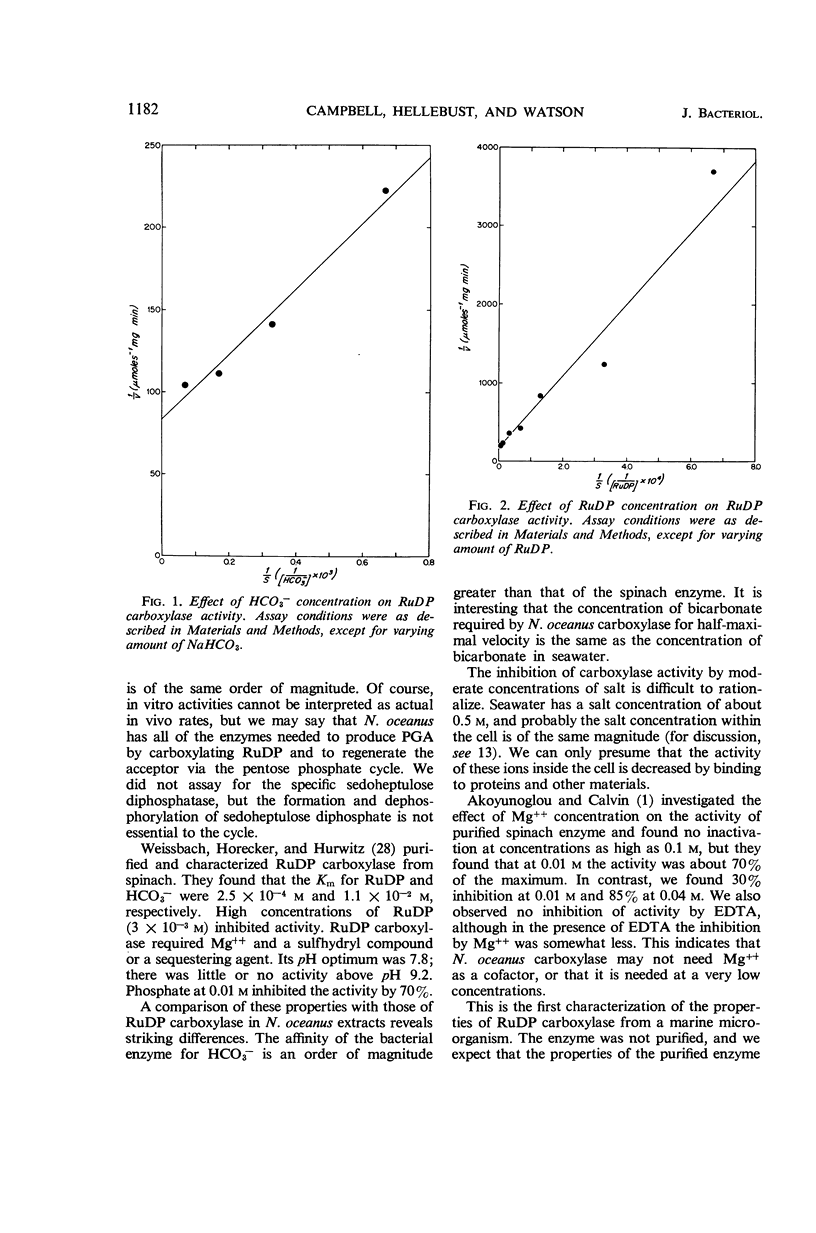
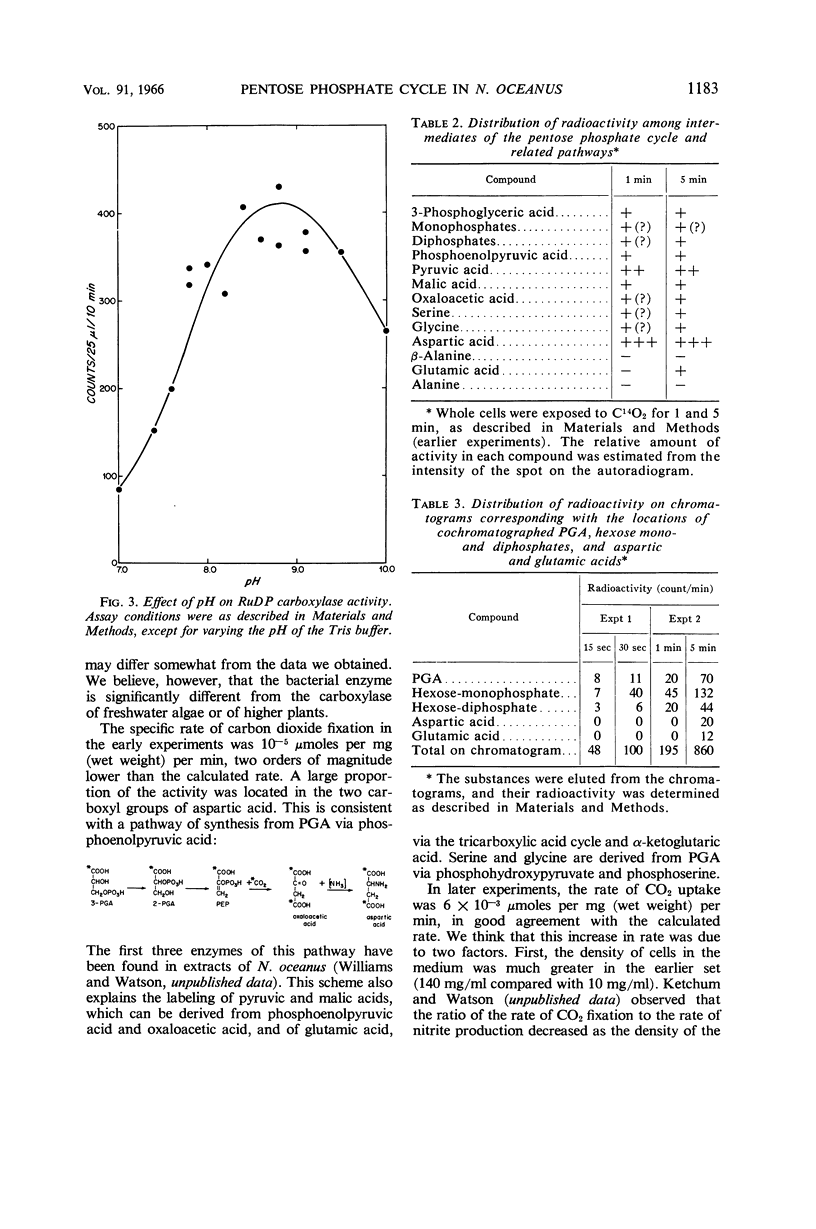
Abstract
Campbell, Ann E. (Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, Mass.), Johan A. Hellebust, and Stanley W. Watson. Reductive pentose phosphate cycle in Nitrosocystis oceanus. J. Bacteriol. 91:1178–1185. 1966.—Assays in cell-free extracts of Nitrosocystis oceanus, a marine chemoautotrophic bacterium, have demonstrated the presence of all of the enzymes of the reductive pentose phosphate cycle, with activities high enough to account for the normal growth rate of the cells. Studies on ribulosediphosphate carboxylase activity in these extracts showed that it is inhibited by MgCl2 (30% at 0.01 m), MnCl2 (70% at 0.01 m), NaCl and KCl (100% at 0.5 m, 63% at 0.2 m), and by sulfate (35% at 0.01 m); phosphate, glutathione, and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid had no effect. The bacterial enzyme differs from the spinach enzyme with respect to its affinity for bicarbonate and its pH optimum. Whole cells were incubated with C14O2, and the acid-soluble fraction was analyzed by paper chromatography and autoradiography. Phosphoglyceric acid and the sugar phosphates were the earliest labeled compounds; several amino acids and organic acids were also labeled. It is concluded that N. oceanus incorporates CO2 primarily via the reductive pentose phosphate cycle.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AKOYUNOGLOU G., CALVIN M. MECHANISM OF THE CARBOXYDISMUTASE REACTION. II. CARBOXYLATION OF THE ENZYME. Biochem Z. 1963;338:20–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AUBERT J. P., MILHAUD G., MILLET J. L'assimilation de l'anhydride carbonique par les bactéries chimioautotrophes. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1957 Apr;92(4):515–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- AXELROD B., JANG R. Purification and properties of phosphoribo-isomerase from alfalfa. J Biol Chem. 1954 Aug;209(2):847–855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANDURSKI R. S., AXELROD B. The chromatographic identification of some biologically important phosphate esters. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):405–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGMANN F. H., TOWNE J. C., BURRIS R. H. Assimilation of carbon dioxide by hydrogen bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jan;230(1):13–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORECKER B. L., HURWITZ J., WEISSBACH A. The enzymatic synthesis and properties of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):785–794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURWITZ J., WEISSBACH A., HORECKER B. L., SMYRNIOTIS P. Z. Spinach phosphoribulokinase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):769–783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOLAS D. J., RAO P. S. THE INCORPORATION OF LABELLED CO2 INTO CELLS AND EXTRACTS OF NITROSOMONAS EUROPAEA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Feb 10;82:394–397. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(64)90311-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E., SCHROEDER E. A. The reductive pentose phosphate cycle. II. Specific C-1 phosphatases for fructose 1,6-diphosphate and sedoheptulose 1,7-diphosphate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Apr;74(2):326–344. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E. The reductive pentose phosphate cycle. I. Phosphoribulokinase and ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Jul;69:300–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANTER M., VISHNIAC W. CO2 incorporation by extracts of Thiobacillus thioparus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1955 Sep;18(1):157–158. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(55)90033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUZUKI I., WERKMAN C. H. Chemoautotrophic carbon dioxide fixation by extracts of Thiobacillus thiooxidans. II. Formation of phosphoglyceric acid. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Sep;77(1):112–123. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABACHNICK M., SRERE P. A., COOPER J., RACKER E. The oxidative pentose phosphate cycle. III. The interconversion of ribose 5-phosphate, ribulose 5-phosphate and xylulose 5-phosphate. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Apr;74(2):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VISHNIAC W., SANTER M. The thiobacilli. Bacteriol Rev. 1957 Sep;21(3):195–213. doi: 10.1128/br.21.3.195-213.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HORECKER B. L., HURWITZ J. The enzymatic formation of phosphoglyceric acid from ribulose diphosphate and carbon dioxide. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):795–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


