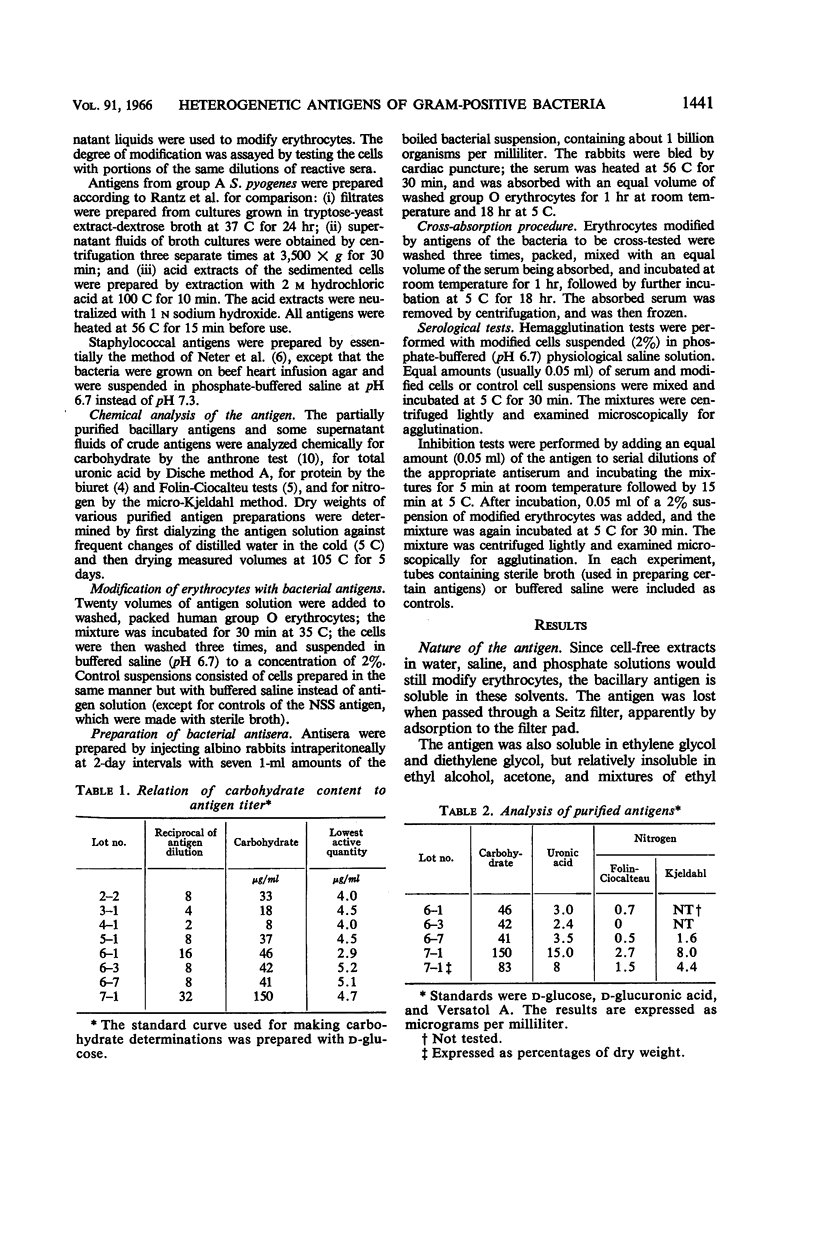
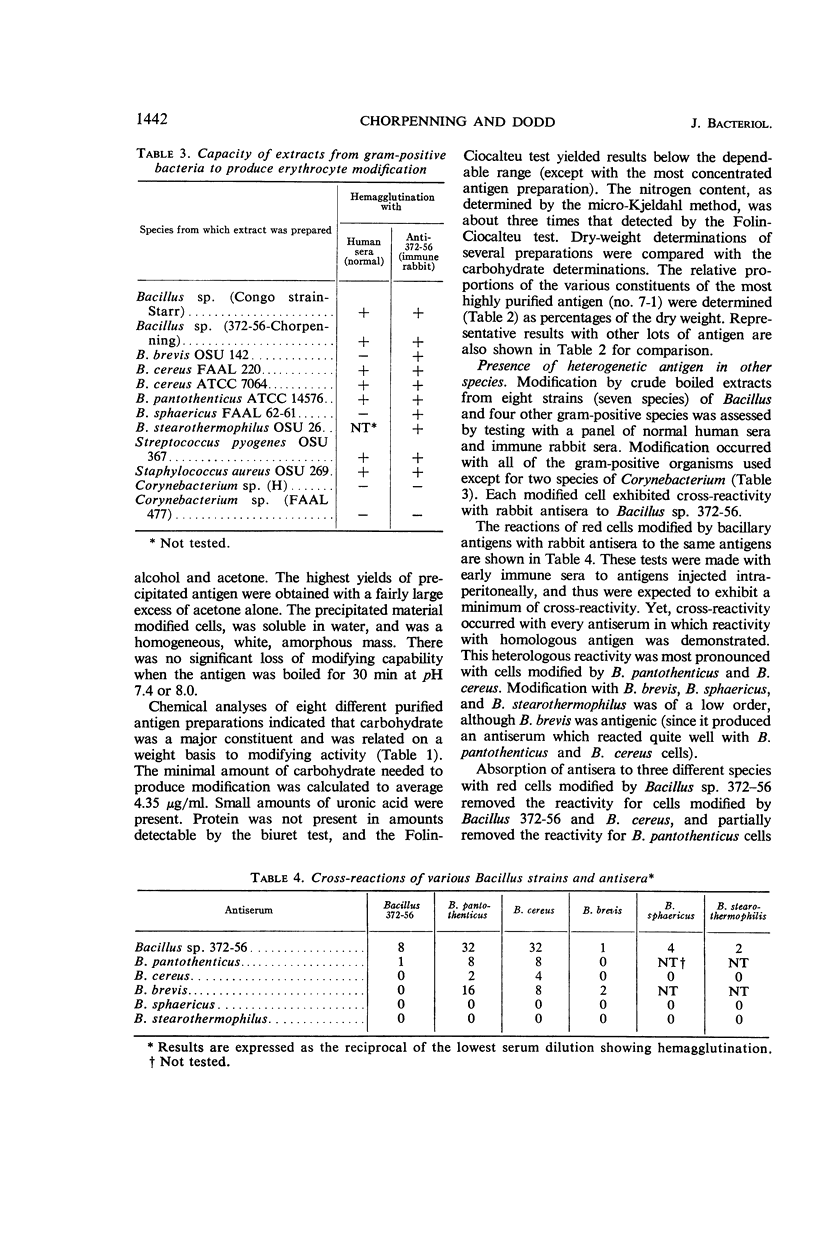
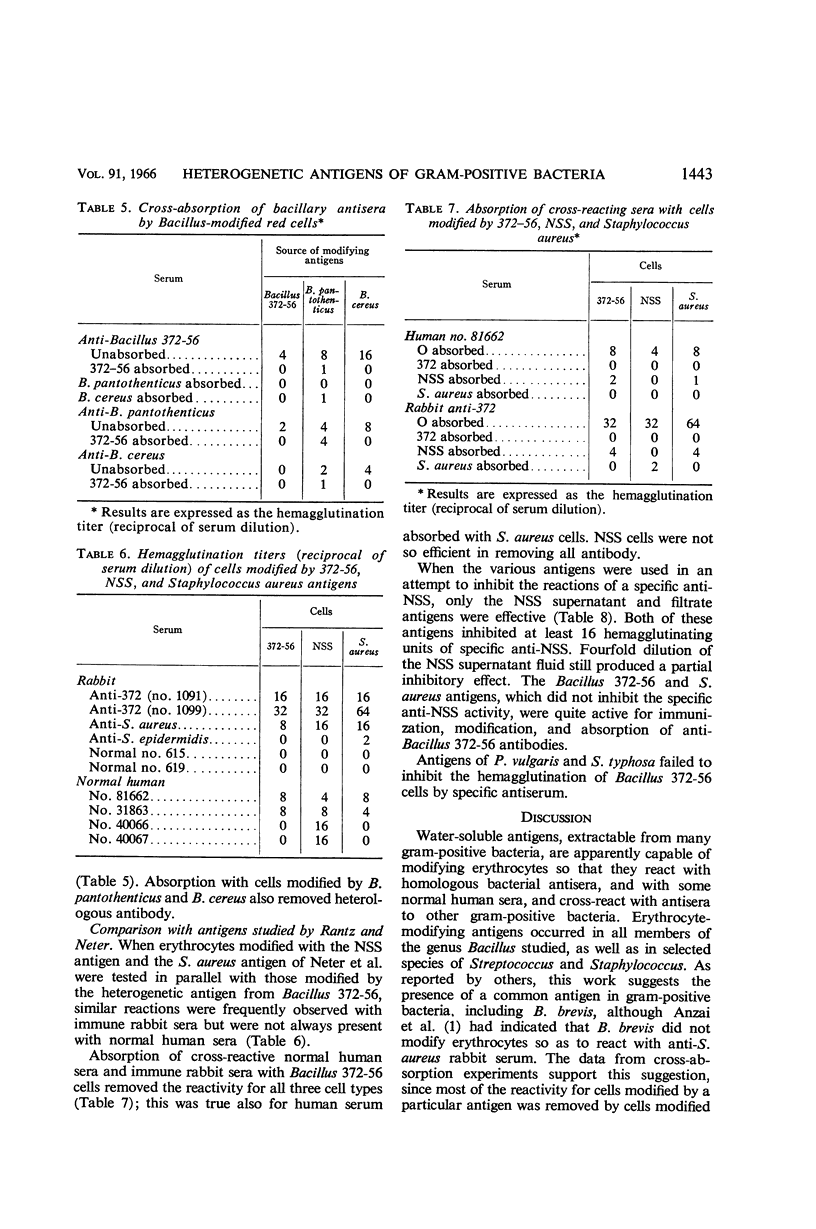
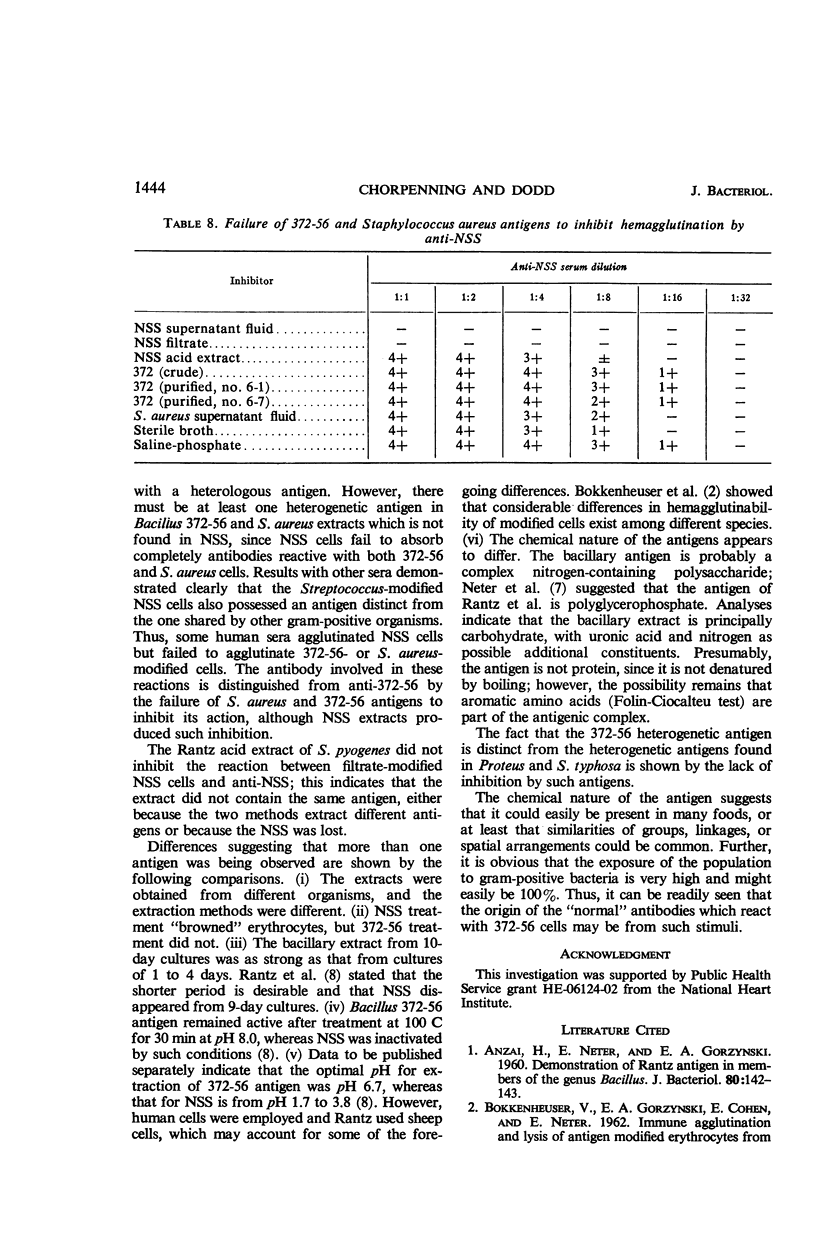
Abstract
Chorpenning, Frank W. (The Ohio State University, Columbus), and Matthew C. Dodd. Heterogenetic antigens of gram-positive bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 91:1440–1445. 1966.—Soluble antigens obtained by various methods from gram-positive bacteria were used to modify erythrocytes whose hemagglutinating reactions with immune rabbit sera and normal human sera were then studied. Antigens from all gram-positive organisms studied except corynbacteria altered red cells, causing them to react with specific bacterial antisera and with normal human sera; however, cross-absorption and inhibition tests indicated that at least three different specificites were involved. One of these antigens seemed to be similar to Rantz's streptococcal NSS, which is shared with Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus spp., and is therefore heterogenetic. Another was found in streptococci but was apparently not present in S. aureus and Bacillus spp. A third antigen, also heterogenetic, appeared to be shared by several species of Bacillus and by S. aureus, but not by streptococci or any gram-negative bacteria. The third antigen was heat-stable at pH 8.0, and appeared to be essentially polysaccharide in nature. Normal human sera varied in their content of antibodies which reacted with erythrocytes modified by extracts from gram-positive bacteria. Whereas some sera reacted very broadly with red cells modified by extracts of practically any gram-positive organism, other sera agglutinated only cells which had been modified by streptococcal antigen.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anzai H., Neter E., Gorzynski E. A. DEMONSTRATION OF RANTZ ANTIGEN IN MEMBERS OF THE GENUS BACILLUS. J Bacteriol. 1960 Jul;80(1):142–143. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.1.142-143.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chorpenning F. W., Dodd M. C. Polyagglutinable erythrocytes associated with bacteriogenic transfusion reactions. Vox Sang. 1965 Jul-Aug;10(4):460–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1965.tb04359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., GORZYNSKI E. A., DRISLANE A. M., HARRIS A. H., RAJNOVICH E. Detection of staphylococcal antibodies in human gamma globulin and serum by hemagglutination tests. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jul;101(3):484–487. doi: 10.3181/00379727-101-24990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., RAJNOVICH E., GORZYNSKI E. A. Study of staphylococcal antibodies of the Rantz type: placental transfer and titers in sera of children of various ages. Pediatrics. 1960 Jan;25:21–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANTZ L. A., RANDALL E., ZUCKERMAN A. Hemolysis and hemagglutination by normal and immune serums of erythrocytes treated with a nonspecies specific bacterial substance. J Infect Dis. 1956 Mar-Apr;98(2):211–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/98.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANTZ L. A., ZUCKERMAN A., RANDALL E. Hemolysis of red blood cells treated by bacterial filtrates in the presence of serum and complement. J Lab Clin Med. 1952 Mar;39(3):443–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STIENECKER C. D., RHEINS M. S. A micro-modification of the anthrone test for serum samples of limited quantity. Am J Med Technol. 1959 Nov-Dec;25:377–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


