Abstract
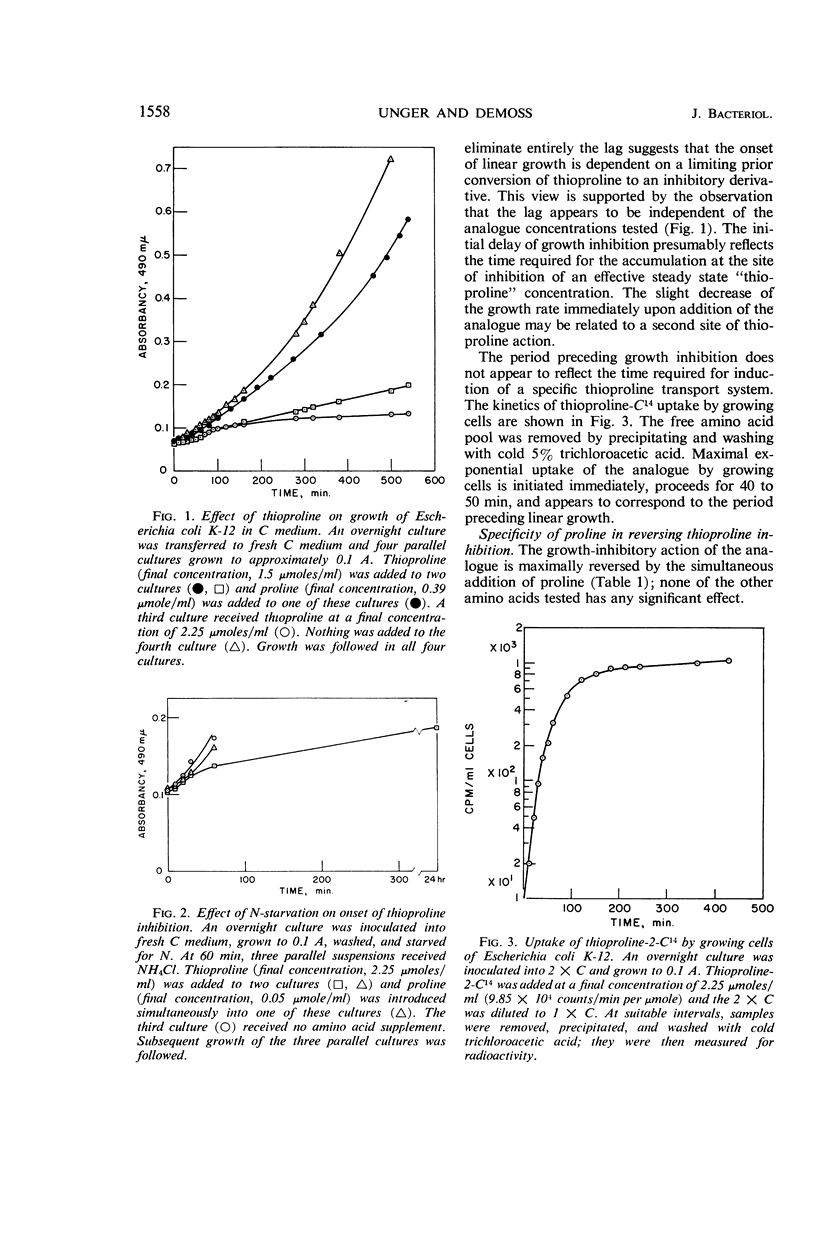
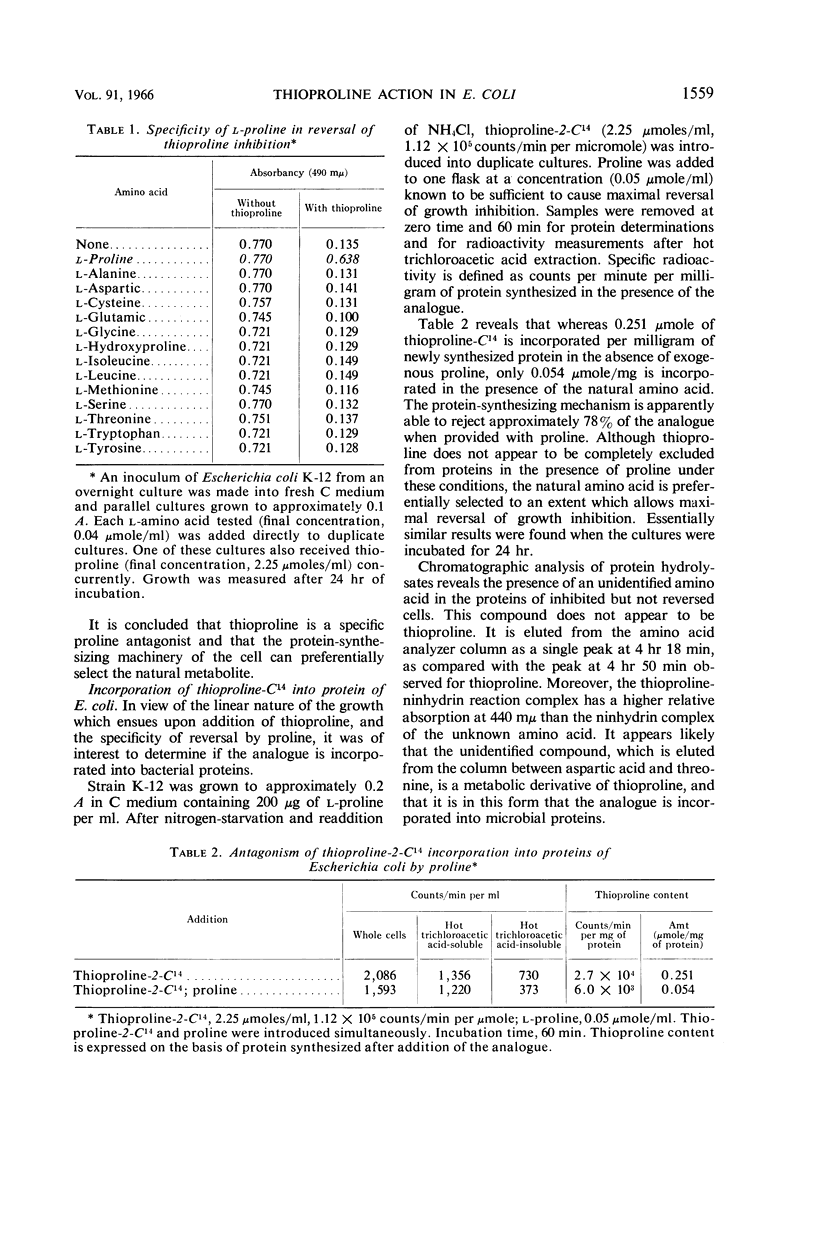
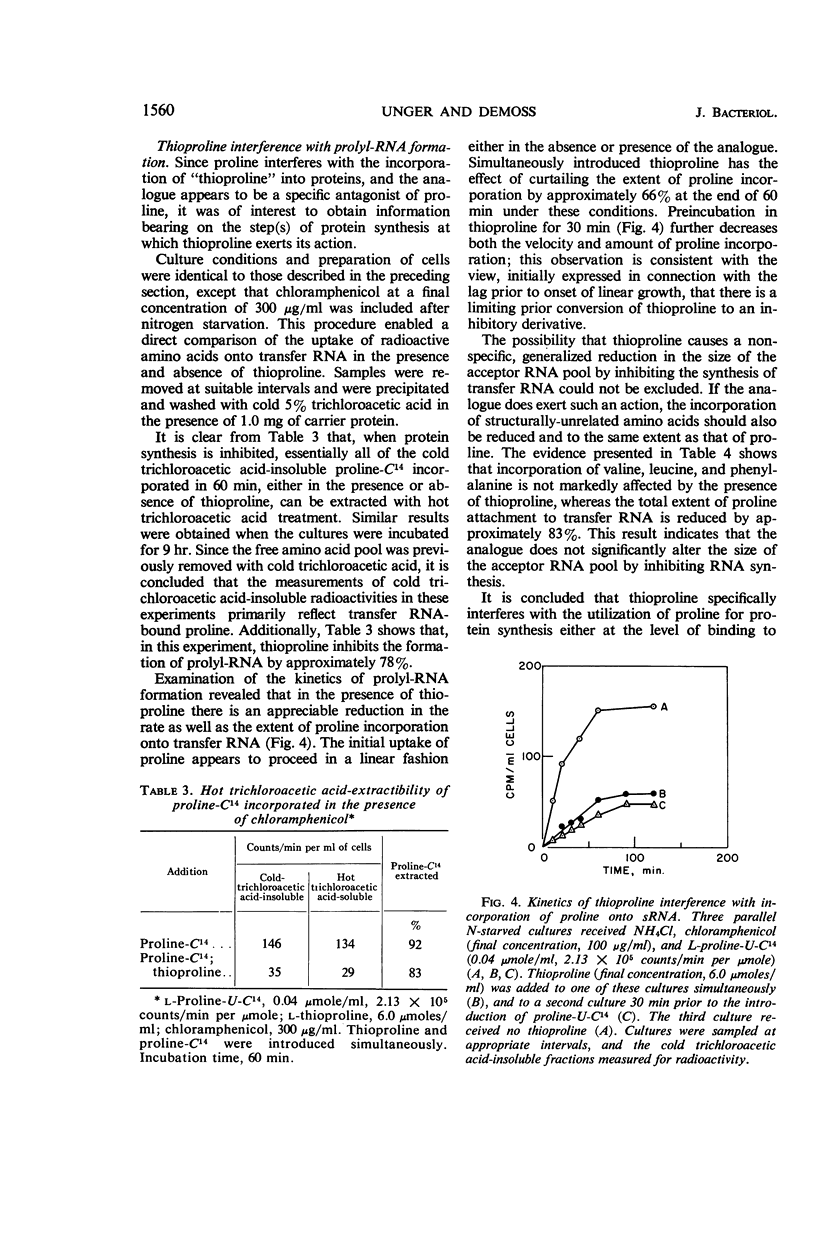
Unger, Leon (University of Illinois, Urbana), and R. D. DeMoss. Action of a proline analogue, l-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid, in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 91:1556–1563. 1966.—The effect of the proline analogue, l-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid (thioproline), on growth, and its relation to the metabolic function of proline in protein synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12, has been studied. Thioproline causes linear growth in E. coli within one generation. The inhibition is specifically reversed by the simultaneous addition of l-proline. Thioproline, or a closely related metabolic derivative, is incorporated into bacterial proteins. Proline antagonizes the incorporation of “thioproline” into protein. The analogue specifically inhibits the rate and extent of prolyl-ribonucleic acid formation. The effectiveness of thioproline as a proline analogue is attributed to its ability to interfere with the utilization of proline for protein synthesis and to mimic proline in its function of being incorporated into proteins. The effect of the incorporation of thioproline on protein structure and enzyme activity is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baich A., Pierson D. J. Control of proline synthesis in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 8;104(2):397–404. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(65)90345-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., GROS F. Protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1960;29:525–546. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.29.070160.002521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOWDEN L., NEALE S., TRISTRAM H. EFFECT OF 3,4-DEHYDRO-DL-PROLINE ON GROWTH AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Nature. 1963 Jul 6;199:35–38. doi: 10.1038/199035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRISELL W. R., MEECH L. A., MACKENZIE C. G. A simplified photometric analysis for serine and formaldehyde. J Biol Chem. 1954 Apr;207(2):709–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKENZIE C. G., HARRIS J. N-formylcysteine synthesis in mitochondria from formaldehyde and L-cysteine via thiazolidinecarboxylic acid. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jul;227(1):393–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. THE ENZYMIC BASIS OF SPECIFIC ANTIBACTERIAL ACTION BY STRUCTURAL ANALOGUES. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1965 Feb;40:93–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1965.tb00797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHMOND M. H. The effect of amino acid analogues on growth and protein synthesis in microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Dec;26:398–420. doi: 10.1128/br.26.4.398-420.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH L. C., RAVEL J. M., SKINNER C. G., SHIVE W. 3,4-Dehydroproline, a proline antagonist. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Oct;99:60–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRECKER H. J. The interconversion of glutamic acid and proline. I. The formation of delta1-pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid from glutamic acid in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1957 Apr;225(2):825–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger L., DeMoss R. D. Metabolism of a proline analogue, l-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid, by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1564–1569. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1564-1569.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


