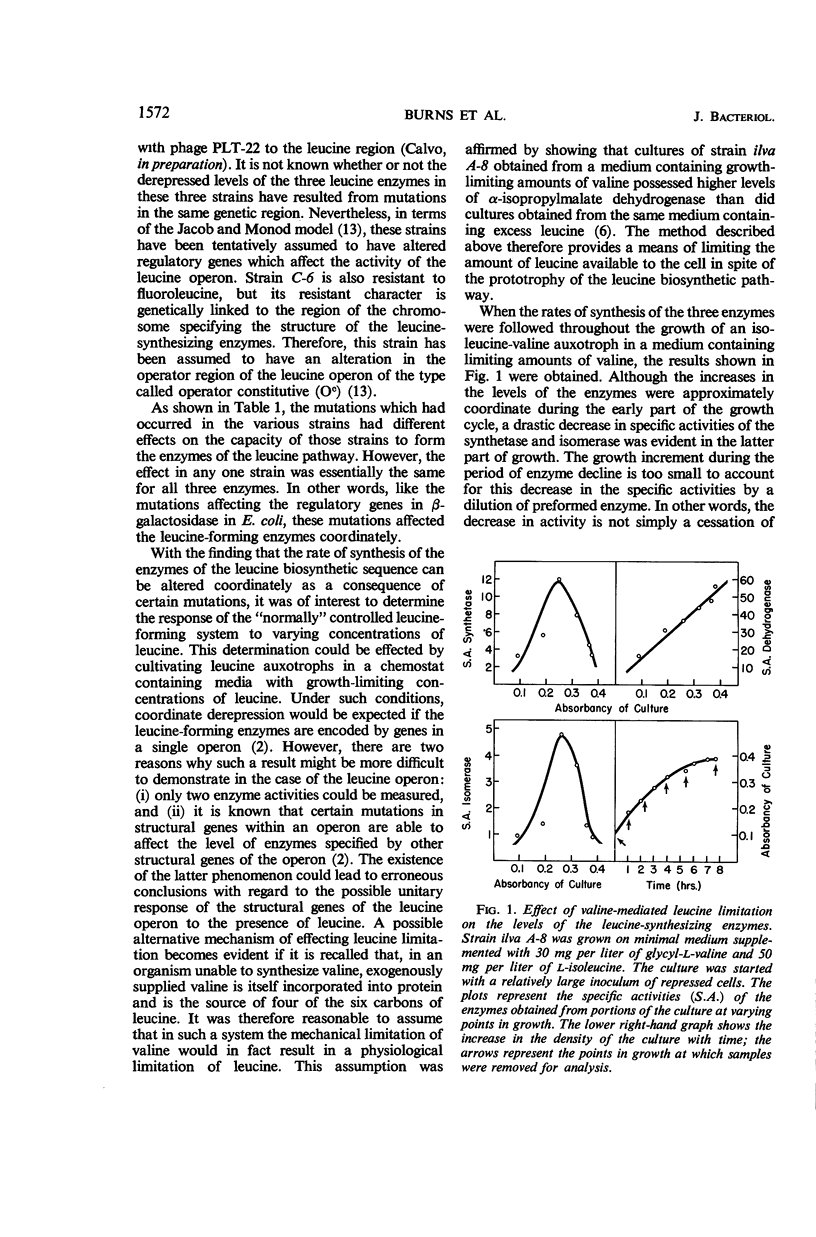
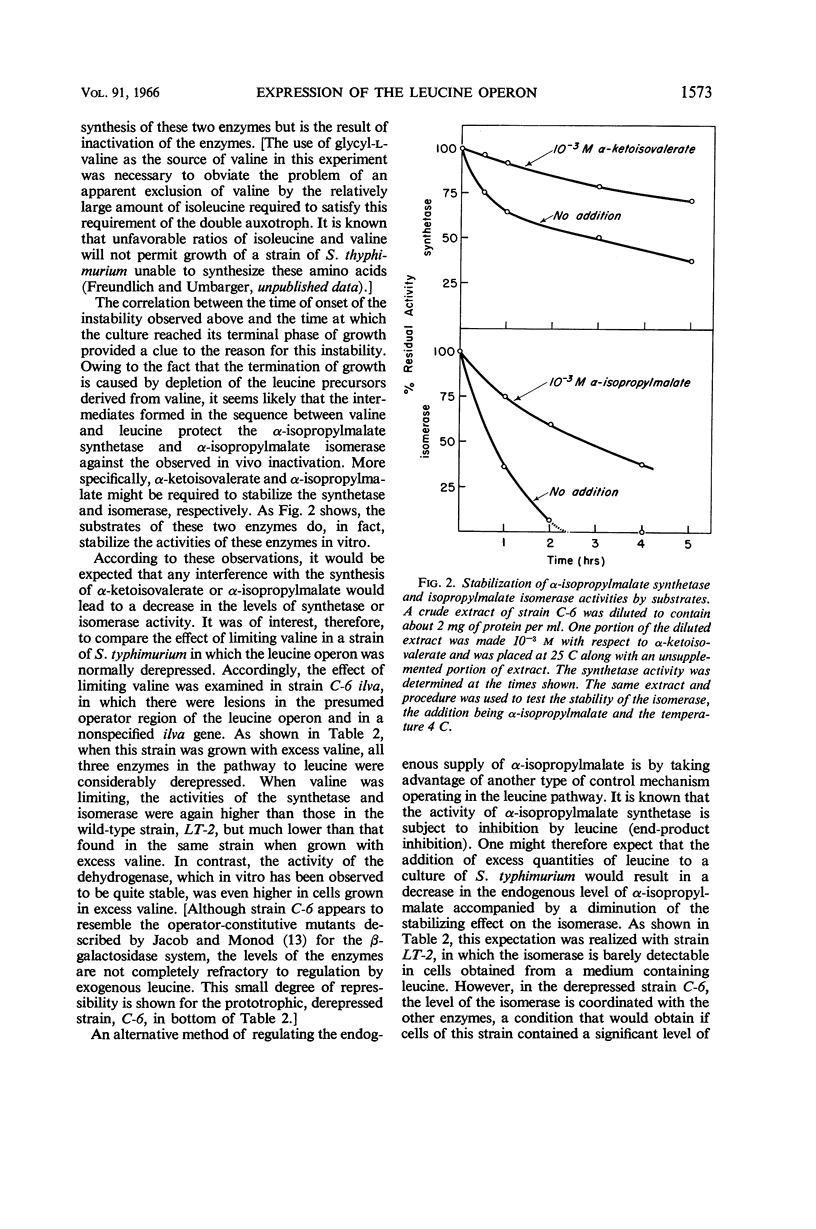
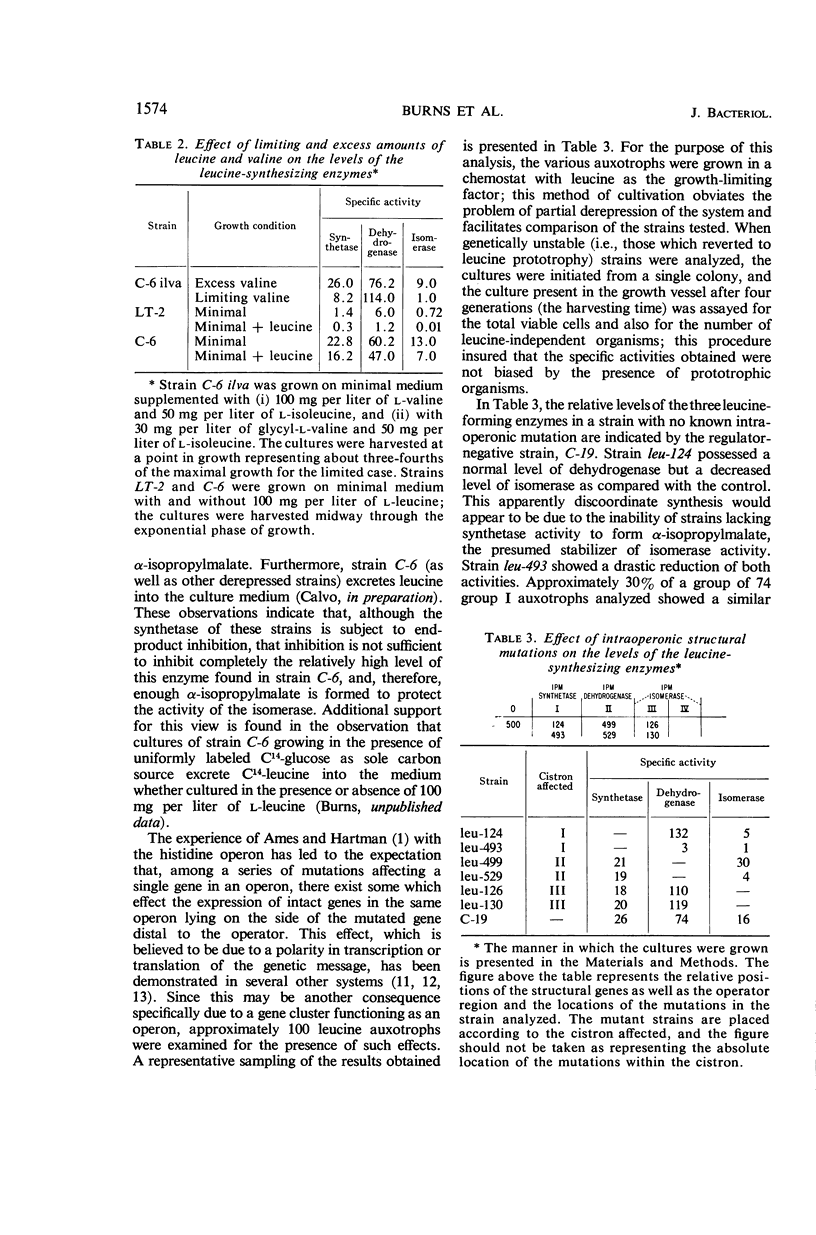
Abstract
Burns, R. O. (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratories of Quantitative Biology, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.), J. Calvo, P. Margolin, and H. E. Umbarger. Expression of the leucine operon. J. Bacteriol. 91:1570–1576. 1966.—The four genes which specify the structure of the three enzymes specifically involved in the biosynthesis of leucine in Salmonella typhimurium constitute a single operon. Three types of control mutants have been delineated on the basis of their location on the Salmonella chromosome and the manner in which they coordinately affect the rates of synthesis of the pertinent enzymes. The three types of mutants correspond to operator-negative, operator-constitutive, and regulator-negative. The rate of synthesis of the enzymes can also be altered by varying the amount of leucine made available to the cell. Leucine can be effectively limited by limiting the supply of α-ketoisovalerate, but in doing so two of the three enzymes, α-isopropylmalate synthetase and isopropylmalate isomerase, are labilized. This observation was correlated with an in vivo diminution of the levels of the substrates of these enzymes and the fact that α-ketoisovalerate and α-isoporpylmalate protect the respective enzymes against thermal inactivation in vitro. The functional association of the structural genes is also illustrated by the presence of polarity mutations; that is, certain structural gene mutations lower the rates of synthesis of the enzymes specified by genes located distally to the mutated gene and the operator segment of the operon.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., MARTIN R. G. BIOCHEMICAL ASPECTS OF GENETICS: THE OPERON. Annu Rev Biochem. 1964;33:235–258. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.33.070164.001315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURNS R. O., UMBARGER H. E., GROSS S. R. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF LEUCINE. III. THE CONVERSION OF ALPHA-HYDROXY-BETA-CARBOXYISOCAPROATE TO ALPHA-KETOISOCAPROATE. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:1053–1058. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKLIN N. C., LURIA S. E. Transduction by bacteriophage P-1 and the properties of the lac genetic region in E. coli and S. dysenteriae. Virology. 1961 Nov;15:299–311. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90362-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREUNDLICH M., BURNS R. O., UMBARGER H. E. Control of isoleucine, valine, and leucine biosynthesis. I. Multivalent repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Oct 15;48:1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.10.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORINI L., KATAJA E. PHENOTYPIC REPAIR BY STREPTOMYCIN OF DEFECTIVE GENOTYPES IN E. COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Mar;51:487–493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.3.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS S. R., BURNS R. O., UMBARGER H. E. THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF LEUCINE. II. THE ENZYMIC ISOMERIZATION OF BETA-CARBOXY-BETA-HYDROXYISOCAPROATE AND ALPHA-HYDROXY-BETA-CARBOXYISOCAPROATE. Biochemistry. 1963 Sep-Oct;2:1046–1052. doi: 10.1021/bi00905a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS S. R., JUNGWIRTH C., UMBARGER E. Another intermediate in leucine biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Feb 20;7:5–9. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. R. The regulation of synthesis of leucine biosynthetic enzymes in Neurospora. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1538–1546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito J., Crawford I. P. Regulation of the enzymes of the tryptophan pathway in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1965 Dec;52(6):1303–1316. doi: 10.1093/genetics/52.6.1303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUNGWIRTH C., GROSS S. R., MARGOLIN P., UMBARGER H. E. The biosynthesis of leucine. I. The accumulation of beta-carboxy-beta-hydroxyisocaproate by leucine auxotrophs of Salmonella typhimurium and Neurospora crassa. Biochemistry. 1963 Jan-Feb;2:1–6. doi: 10.1021/bi00901a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE N., ENGLESBERG E. Dual effects of structural genes in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Mar 15;48:335–348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.3.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARGOLIN P. Genetic fine structure of the leucine operon in Salmonella. Genetics. 1963 Mar;48:441–457. doi: 10.1093/genetics/48.3.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK A., SZILARD L. Description of the chemostat. Science. 1950 Dec 15;112(2920):715–716. doi: 10.1126/science.112.2920.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


