Abstract
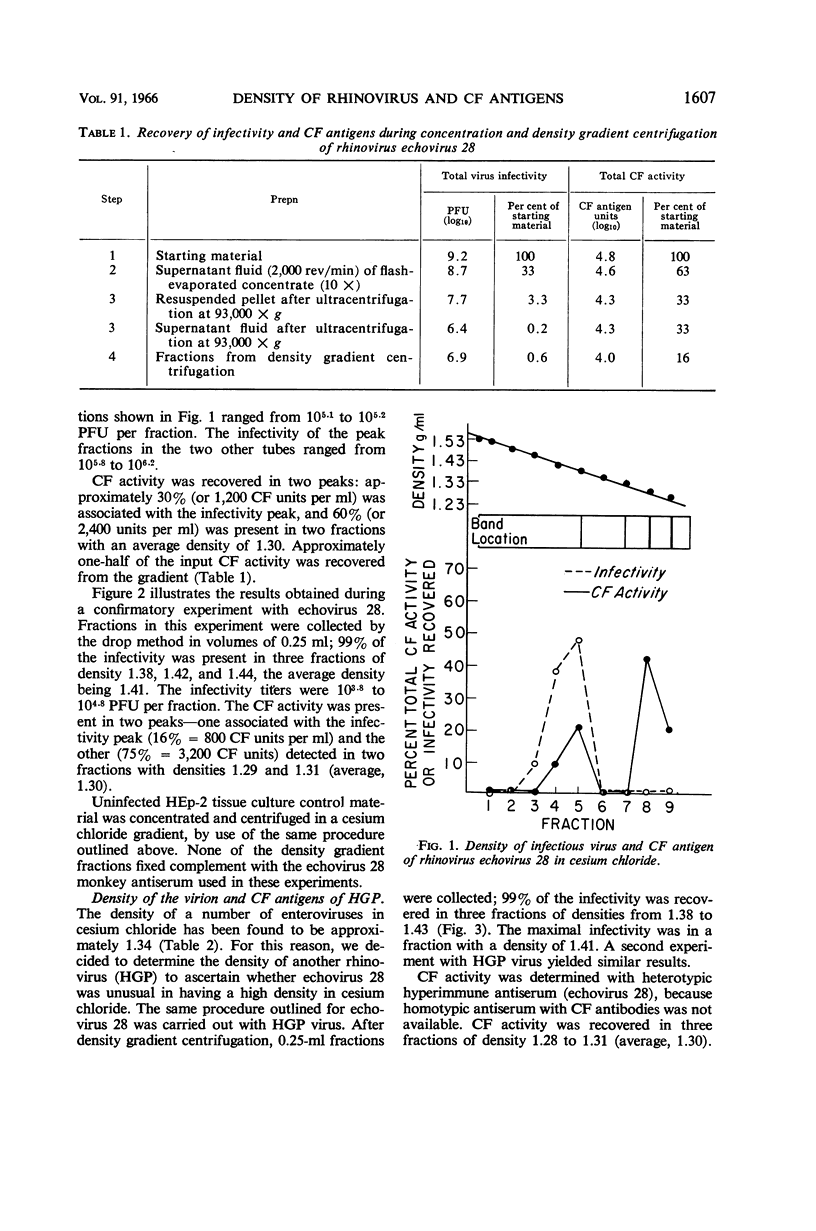
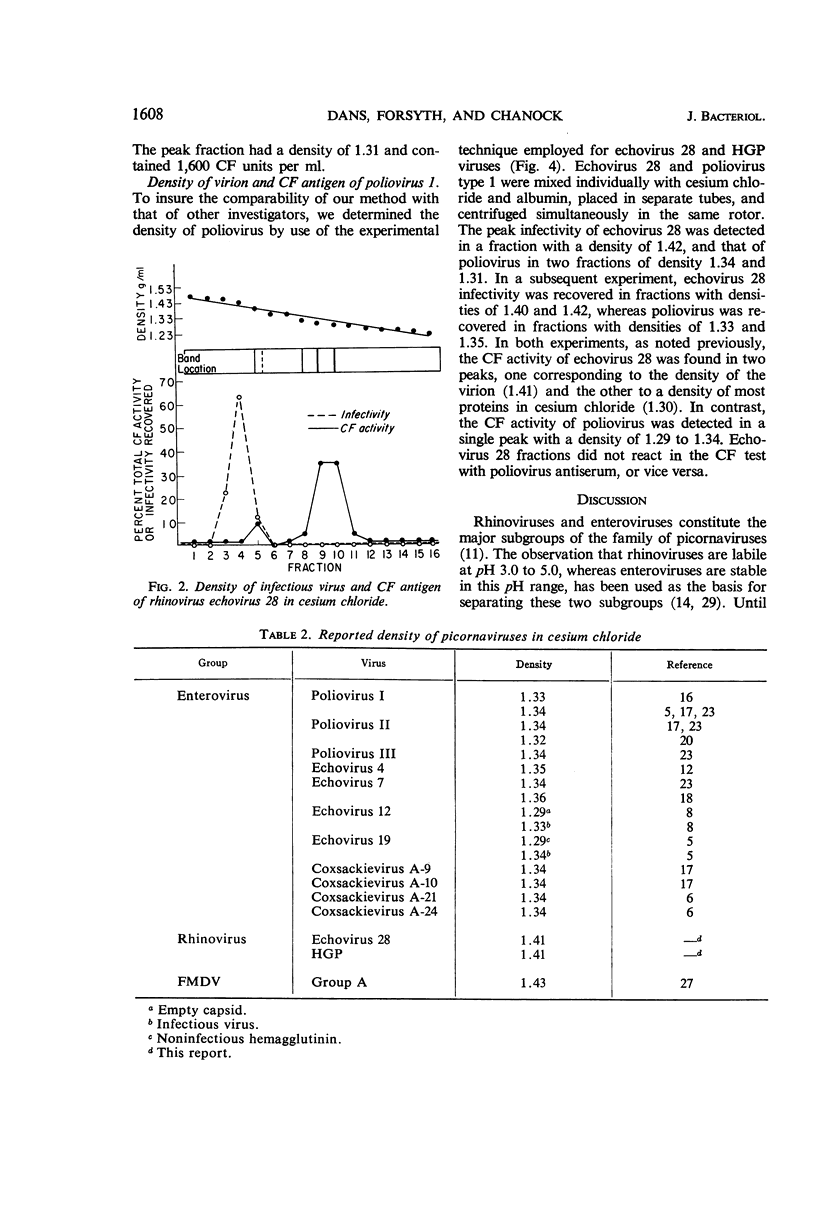
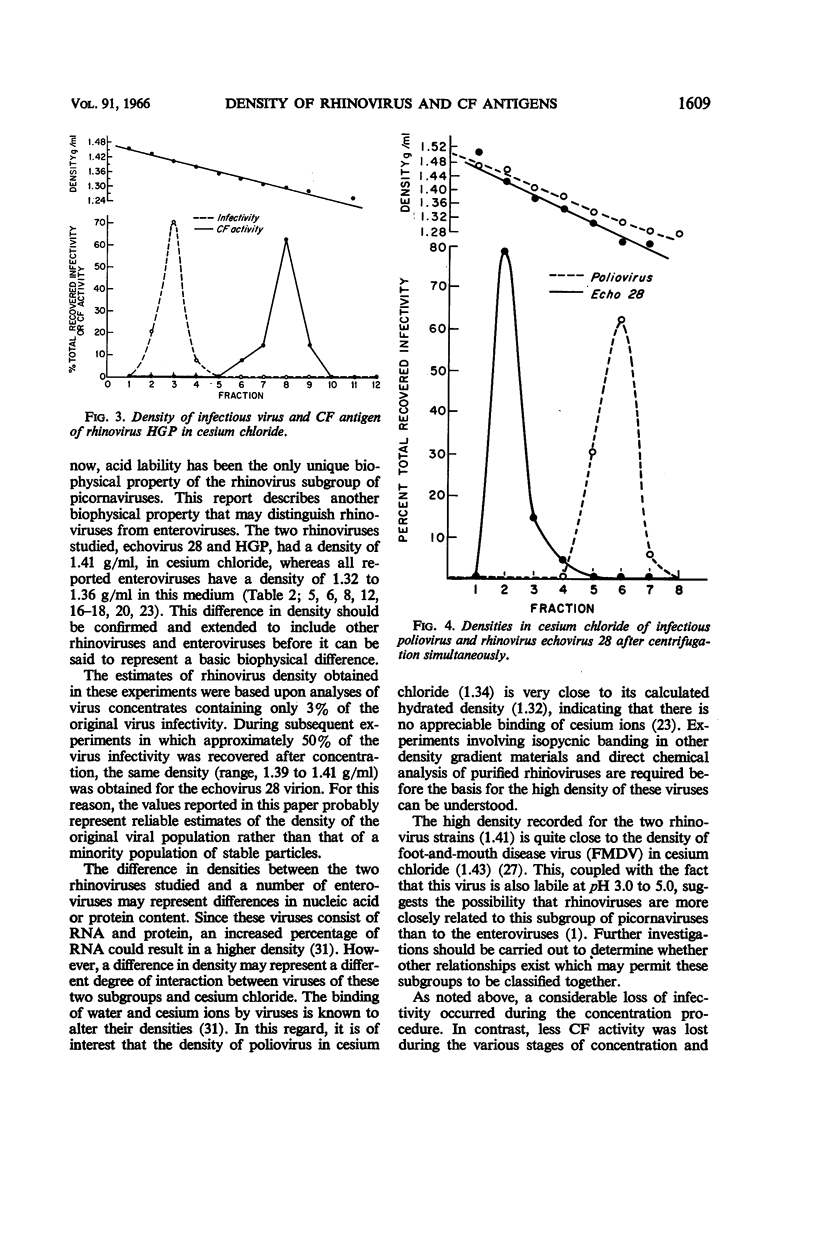
Dans, P. E. (National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, Bethesda, Md.), B. R. Forsyth, and R. M. Chanock. Density of infectious virus and complement-fixing antigens of two rhinovirus strains. J. Bacteriol. 91:1605–1611. 1966.—Two rhinovirus serotypes (echovirus 28 and HGP) and poliovirus type 1 were banded by isopycnic centrifugation in cesium chloride. The rhinovirus virions had a density of 1.41 g/ml, whereas that of poliovirus was 1.34. Since a number of other enteroviruses also have a density of 1.34 g/ml in cesium chloride, a basic difference in density may exist between the rhinovirus and enterovirus subgroups of the picornavirus family. Whether this difference reflects differences in ribonucleic acid content or binding of cesium ions remains to be determined. In tests with echovirus 28 two peaks of CF activity were detected: one in association with the virion (1.41 g/ml), and a larger peak of lower density (1.30 g/ml). With echovirus 28 antiserum, a heterotypically reactive complement-fixing (CF) antigen was detected in the HGP virus suspension at a density less than that of the virion (1.30 g/ml). This antigen corresponded in density to the less dense CF antigen of echovirus 28.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BACHRACH H. L., BREESE S. S., Jr, CALLIS J. J., HESS W. R., PATTY R. E. Inactivation of foot-and-mouth disease virus by pH and temperature changes and by formaldehyde. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 May;95(1):147–152. doi: 10.3181/00379727-95-23148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOOM H. H., FORSYTH B. R., JOHNSON K. M., CHANOCK R. M. RELATIONSHIP OF RHINOVIRUS INFECTION TO MILD UPPER RESPIRATORY DISEASE. 1. RESULTS OF A SURVEY IN YOUNG ADULTS AND CHILDREN. JAMA. 1963 Oct 5;186:38–45. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.63710010001012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOEYE A. MOLECULAR WEIGHT OF A POLIOVIRUS PROTEIN. Virology. 1965 Apr;25:550–559. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90083-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIMMOCK N. J., TYRRELL D. A. Physicochemical properties of some viruses isolated from common colds (rhinoviruses). Lancet. 1962 Sep 15;2(7255):536–537. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)90404-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FABIYI A., ENGLER R., MARTIN D. C. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF INFECTIOUS UNIT, HEMAGGLUTININ AND COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGEN OF ECHO VIRUS 19. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1964 Jun 17;14:621–627. doi: 10.1007/BF01555119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FROMMHAGEN L. H., MARTINS M. J. The purification and physicochemical properties of two viruses associated with respiratory disease. Virology. 1961 Sep;15:30–35. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GWALTNEY J. M., Jr, JORDAN W. S., Jr RHINOVIRUSES AND RESPIRATORY DISEASE. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Dec;28:409–422. doi: 10.1128/br.28.4.409-422.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPEREN S., EGGERS H. J., TAMM I. COMPLETE AND CORELESS HEMAGGLUTINATING PARTICLES PRODUCED IN ECHO 12 VIRUS-INFECTED CELLS. Virology. 1964 May;23:81–89. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(64)80010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMPARIAN V. V., LEAGUS M. B., HILLEMAN M. R. ADDITIONAL RHINOVIRUS SEROTYPES. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Aug-Sep;116:976–984. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMELER K., HAMPARIAN V. V. Studies on the complement fixing antigens of poliomyelitis. I. Demonstration of type and group specific antigens in native and heated viral preparations. J Immunol. 1958 Dec;81(6):499–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON K. M., BLOOM H. H., FORSYTH B. R., CHANOCK R. M. RELATIONSHIP OF RHINOVIRUS INFECTION TO MILD UPPER RESPIRATORY DISEASE. II. EPIDEMIOLOGIC OBSERVATIONS IN MALE MILITARY TRAINEES. Am J Epidemiol. 1965 Jan;81:131–139. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KETLER A., HAMPARIAN V. V., HILLEMAN M. R. Characterization and classification of ECHO 28-rhinovirus-coryzavirus agents. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Aug-Sep;110:821–831. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNETTE E. H., SCHMIDT N. J., MAGOFFIN R. L., HAGENS S. J., DUKELLIS E. J. A COMPARISON OF THE REACTIVITY OF POLIOVIRUS COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGENS (NATIVE, HEATED AND SUCROSE DENSITY GRADIENT C AND D) WITH HUMAN SERA. J Immunol. 1964 Feb;92:261–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINTOW L., DARNELL J. E., Jr A simplified procedure for purification of large amounts of poliovirus: characterization and amino acid analysis of Type 1 poliovirus. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jan;235:70–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTERN C. F. Some physical and chemical properties of Coxsackie viruses A9 and A10. Virology. 1962 Aug;17:520–532. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90151-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILIPSON L., LIND M. ENTEROVIRUS ECLIPSE IN A CELL-FREE SYSTEM. Virology. 1964 Jul;23:322–332. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS C. A., RIGGS S., MELNICK J. L., GRIM C. A. RHINOVIRUSES ASSOCIATED WITH COMMON COLDS IN A STUDENT POPULATION. JAMA. 1965 Apr 26;192:277–280. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080170005001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLSON A., LEVITT J. DENSITY DETERMINATION IN A PREFORMED GRADIENT OF CAESIUM CHLORIDE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Jul 23;75:88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90582-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABIN A. B. Properties and behavior of orally administered attenuated poliovirus vaccine. J Am Med Assoc. 1957 Jul 13;164(11):1216–1223. doi: 10.1001/jama.1957.62980110008008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAFFER F. L., FROMMHAGEN L. H. SIMILARITIES OF BIOPHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF SEVERAL HUMAN ENTEROVIRUSES AS SHOWN BY DENSITY GRADIENT ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF MIXTURES OF THE VIRUSES. Virology. 1965 Apr;25:662–664. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90095-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHARFF M. D., LEVINTOW L. Quantitative study of the formation of poliovirus antigens in infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1963 Apr;19:491–500. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMIDT N. J., DENNIS J., FROMMHAGEN L. H., LENNETTE E. H. SEROLOGIC REACTIVITY OF CERTAIN ANTIGENS OBTAINED BY FRACTIONATION OF COXSACKIE VIRUSES IN CESIUM CHLORIDE DENSITY GRADIENTS. J Immunol. 1963 Apr;90:654–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVER J. L. Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J Immunol. 1962 Mar;88:320–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRAUTMAN R., BREESE S. S., Jr Isodensity ultracentrifugation of foot-and-mouth disease virus in caesium chloride. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Feb;27:231–239. doi: 10.1099/00221287-27-2-231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TYRRELL D. A., BYNOE M. L. Some further virus isolations from common colds. Br Med J. 1961 Feb 11;1(5223):393–397. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5223.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TYRRELL D. A., CHANOCK R. M. Rhinoviruses: a description. Science. 1963 Jul 12;141(3576):152–153. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3576.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANOSS C. J., DHENNIN L., DHENNIN L. THE ANTIGENIC CONNECTION BETWEEN TWO DIFFERENT TYPES OF FOOT-AND-MOUTH DISEASE VIRUSES AND THEIR SUBPARTICLES. Virology. 1964 Mar;22:428–430. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90035-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VINOGRAD J., HEARST J. E. Equilibrium sedimentation of macromolecules and viruses in a density gradient. Fortschr Chem Org Naturst. 1962;20:373–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


