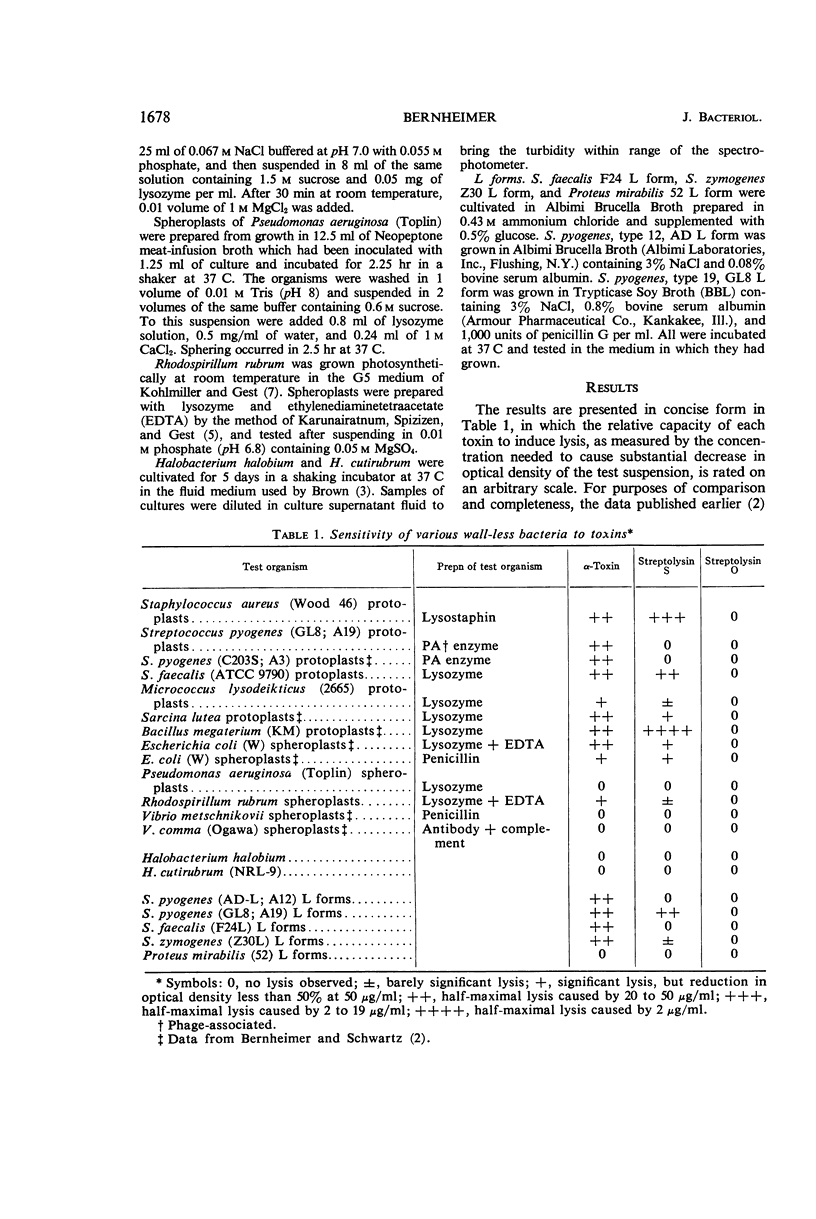
Abstract
Bernheimer, Alan W. (New York University School of Medicine, New York, N.Y.). Disruption of wall-less bacteria by streptococcal and staphylococcal toxins. J. Bacteriol. 91:1677–1680. 1966.—Earlier studies demonstrating that staphylococcal α-toxin and streptolysin S have the capacity to lyse protoplasts and spheroplasts of certain species of bacteria and Mycoplasma have been extended to encompass additional kinds of wall-less bacteria including L forms. It is suggested that sensitivity to staphylococcal α-toxin and streptolysin S may be explicable in terms of specific phospholipid composition of cell membranes, whereas sensitivity to streptolysin O is dependent upon the presence in cell membranes of cholesterol. The results suggest that streptolysin O might prove to be a useful reagent for differentiating L forms from parasitic pleuropneumonia-like organisms.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERNHEIMER A. W., DAVIDSON M. LYSIS OF PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS BY STAPHYLOCOCCAL AND STREPTOCOCCAL TOXINS. Science. 1965 May 28;148(3674):1229–1231. doi: 10.1126/science.148.3674.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNHEIMER A. W., SCHWARTZ L. L. LYSIS OF BACTERIAL PROTOPLASTS AND SPHEROPLASTS BY STAPHYLOCOCCAL ALPHA-TOXIN AND STREPTOLYSIN S. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1387–1392. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1387-1392.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN A. D. THE PERIPHERAL STRUCTURES OF GRAM-NEGATIVE BACTERIA.IV. THE CATION-SENSITIVE DISSOLUTION OF THE CELL MEMBRANE OF THE HALOPHILIC BACTERIUM, HALOBACTERIUM HALOBIUM. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Nov 29;75:425–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90630-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie J. M., Brock T. D. Action of streptolysin S, the group D hemolysin, and phospholipase C on whole cells and spheroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):595–600. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.595-600.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARUNAIRATNAM M. C., SPIZIZEN J., GEST H. Preparation and properties of protoplasts of Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Sep;29(3):649–650. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOHLMILLER E. F., Jr, GEST H. A comparative study of the light and dark fermentations of organic acids by Rhodo-spirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1951 Mar;61(3):269–282. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.3.269-282.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates M. Bacterial lipids. Adv Lipid Res. 1964;2:17–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHINDLER C. A., SCHUHARDT V. T. LYSOSTAPHIN: A NEW BACTERIOLYTIC AGENT FOR THE STAPHYLOCOCCUS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Mar;51:414–421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.3.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOCKMAN G. D., SLADE H. D. THE CELLULAR LOCATION OF THE STREPTOCOCCAL GROUP D ANTIGEN. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Dec;37:297–305. doi: 10.1099/00221287-37-3-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F. COMPARATIVE PHYSIOLOGY OF PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE AND L-TYPE ORGANISMS. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Jun;28:97–125. doi: 10.1128/br.28.2.97-125.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


