Abstract
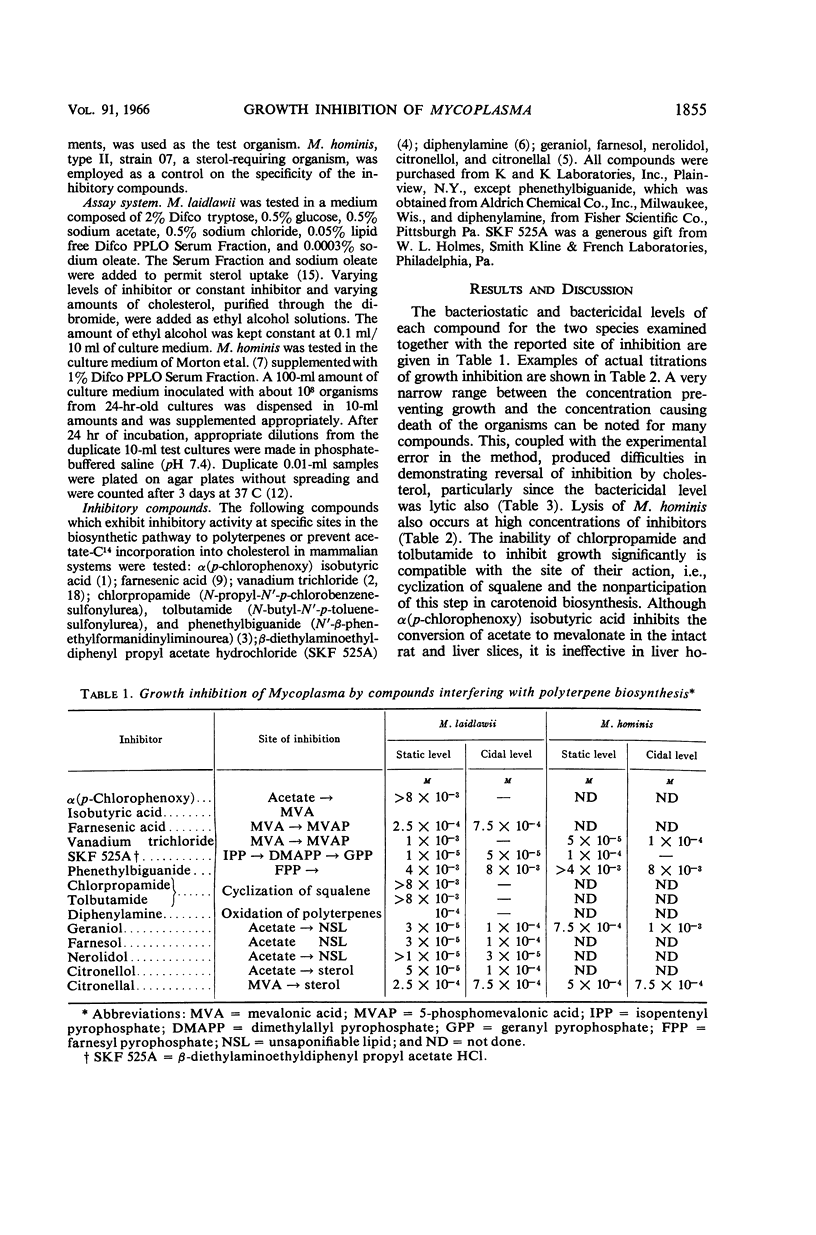
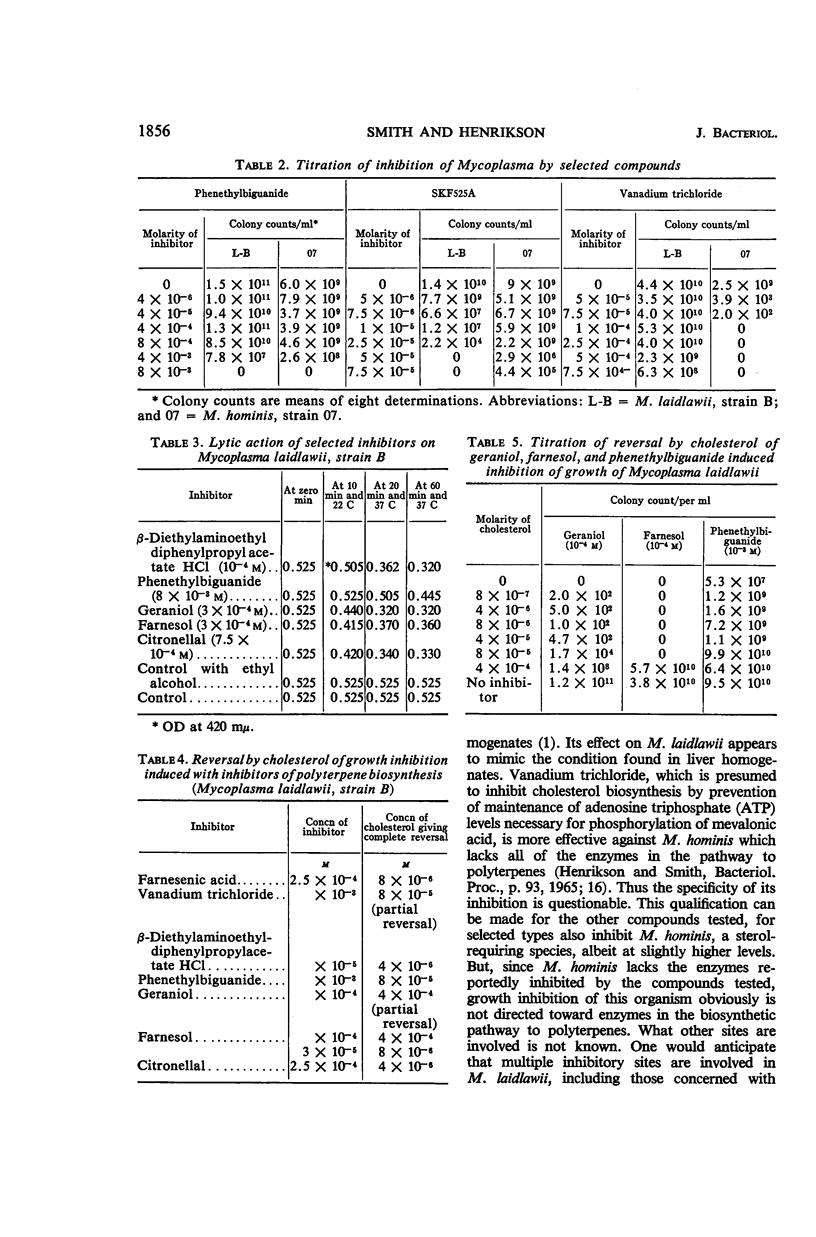
Smith, Paul F. (University of South Dakota, Vermillion), and Carl V. Henrikson. Growth inhibition of Mycoplasma by inhibitors of polyterpene biosynthesis and its reversal by cholesterol. J. Bacteriol. 91:1854–1858. 1966.—Compounds which inhibit enzymatic reactions in the biosynthetic pathway to carotenoids inhibited growth of a sterol-nonrequiring species, Mycoplasma laidlawii, strain B, and M. hominis, strain 07. Since M. hominis lacks the enzymes for polyterpene biosynthesis, the inhibitory compounds must act also at other sites. Most inhibitors exerted a lytic effect at bactericidal levels. The inhibition of M. laidlawii is reversed by exogenous cholesterol. M. laidlawii exhibited a greatly increased content of cholesterol and a greatly decreased content of carotenoids when grown in the presence of phenethylbiguanide and cholesterol. These results are considered as further evidence for a common function for sterols and carotenols in Mycoplasma.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVOY D. R., SWYRYD E. A., GOULD R. G. EFFECTS OF ALPHA-P-CHLOROPHENOXYISOBUTYRYL ETHYL ESTER (CPIB) WITH AND WITHOUT ANDROSTERONE ON CHOLESTEROL BIOSYNTHESIS IN RAT LIVER. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:369–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalidowicz J. E., McDonald H. J. Site of the in vitro inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis by tolbutamide and phenethylbiguanide. Biochemistry. 1965 Jun;4(6):1138–1143. doi: 10.1021/bi00882a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES W. L., DITULLIO N. W. Inhibitors of cholesterol biosynthesis which act at or beyond the mevalonic acid stage. Am J Clin Nutr. 1962 Apr;10:310–322. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/10.4.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENSEN S. L., COHEN-BAZIRE G., NAKAYAMA T. O., STANIER R. Y. The path of carotenoid synthesis in a photosynthetic bacterium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958 Sep;29(3):477–498. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(58)90003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON H. E., SMITH P. F., LEBERMAN P. R. Investigation of the cultivation of pleuropneumonia-like organisms from man. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1951 Jul;35(4):361–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPJAK G., CORNFORTH R. H., CLIFFORD K. Inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis by farnesoic acid and its analogues. Lancet. 1960 Jun 11;1(7137):1270–1273. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)92252-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollack J. D., Razin S., Pollack M. E., Cleverdon R. C. Fractionation of mycoplasma cells for enzyme localization. Life Sci. 1965 May;4(9):973–977. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90200-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., ARGAMAN M. Lysis of Mycoplasma, bacterial protoplasts, spheroplasts and L-forms by various agents. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jan;30:155–172. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-1-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHBLAT G. H., SMITH P. F. Nonsaponifiable lipids of representative pleuropneumonia-like organisms. J Bacteriol. 1961 Oct;82:479–491. doi: 10.1128/jb.82.4.479-491.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F. COMPARATIVE PHYSIOLOGY OF PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE AND L-TYPE ORGANISMS. Bacteriol Rev. 1964 Jun;28:97–125. doi: 10.1128/br.28.2.97-125.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F., HENRIKSON C. V. COMPARATIVE BIOSYNTHESIS OF MEVALONIC ACID BY MYCOPLASMA. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jan;89:146–153. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.1.146-153.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F. Quantitative measurement of the growth of pleuropneumonia-like organisms. Appl Microbiol. 1956 Sep;4(5):254–259. doi: 10.1128/am.4.5.254-259.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH P. F. THE CAROTENOID PIGMENTS OF MYCOPLASMA. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Sep;32:307–319. doi: 10.1099/00221287-32-3-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. F., Rothblat G. H. INCORPORATION OF CHOLESTEROL BY PLEUROPNEUMONIA-LIKE ORGANISMS. J Bacteriol. 1960 Dec;80(6):842–850. doi: 10.1128/jb.80.6.842-850.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT L. D., LI L. F., TRAGER R. The site of vanadyl inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis in liver homogenates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1960 Sep;3:264–267. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(60)90236-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


