Abstract
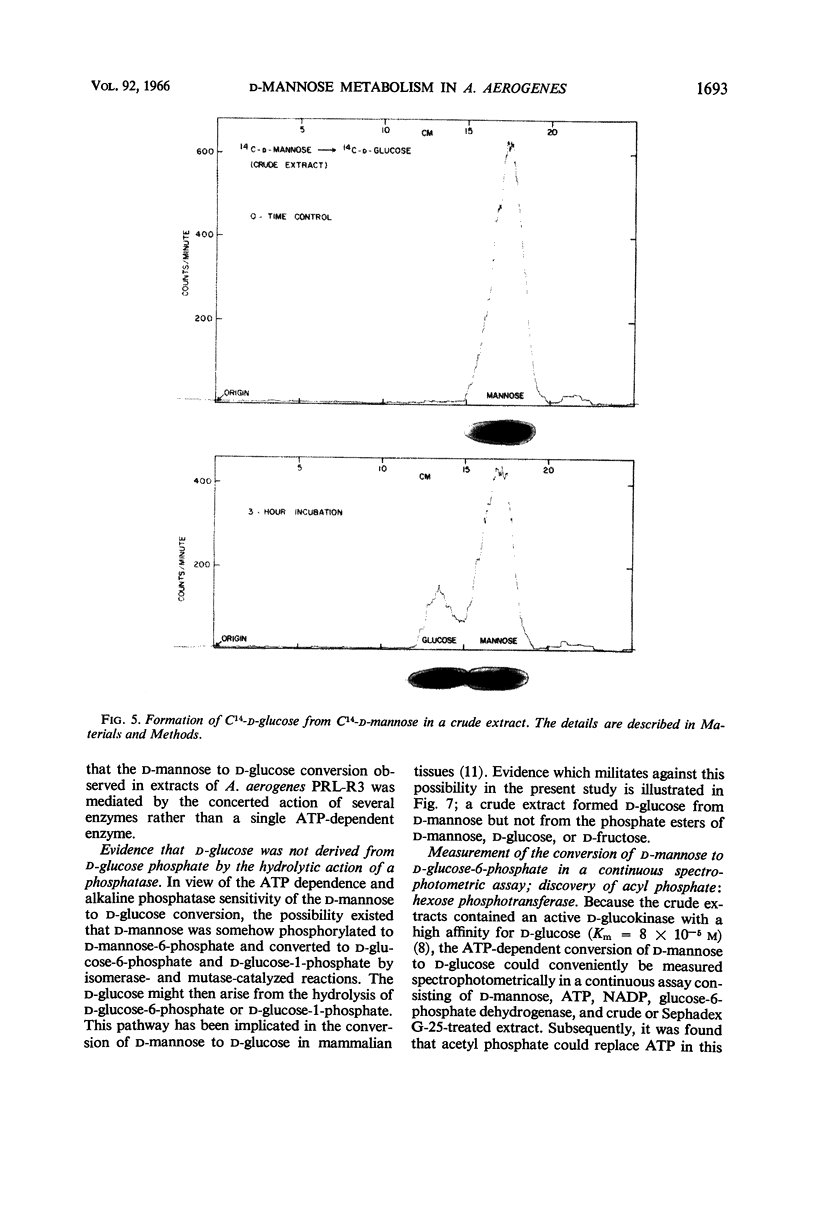
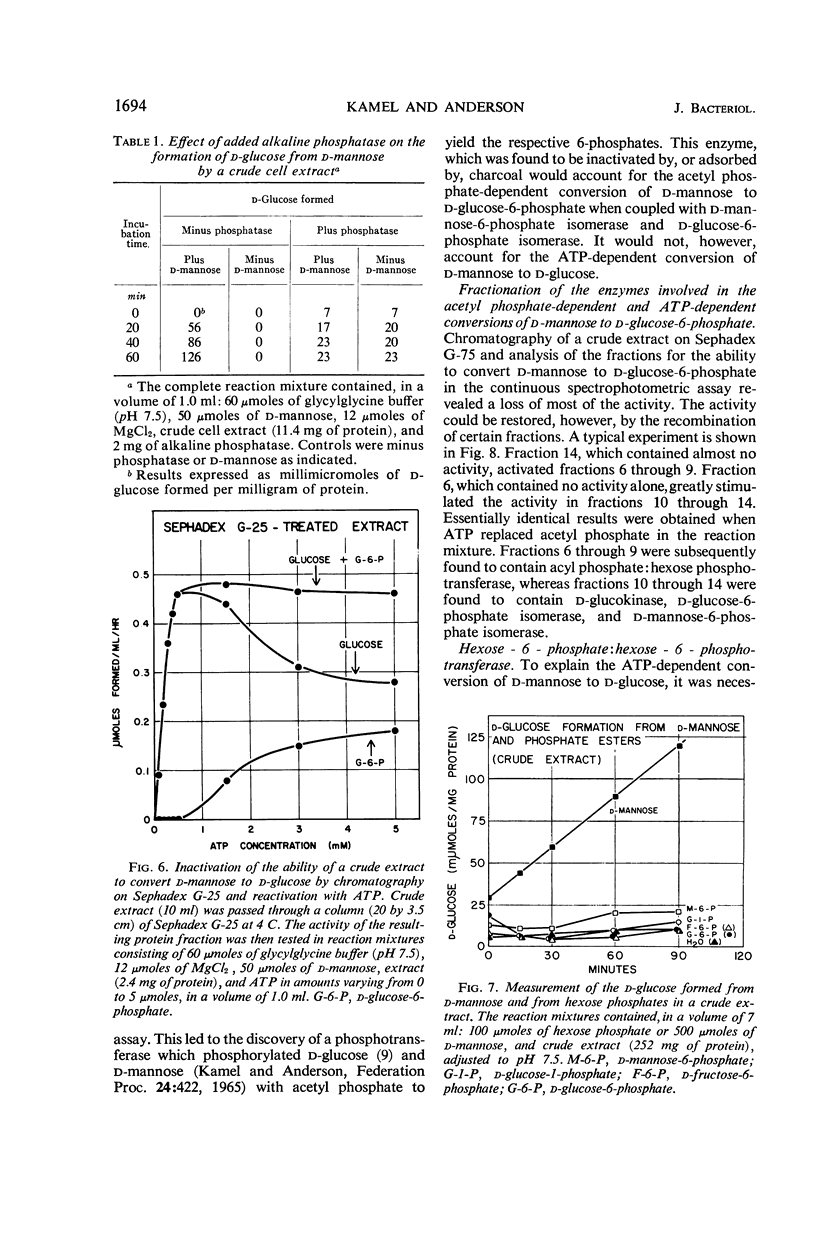
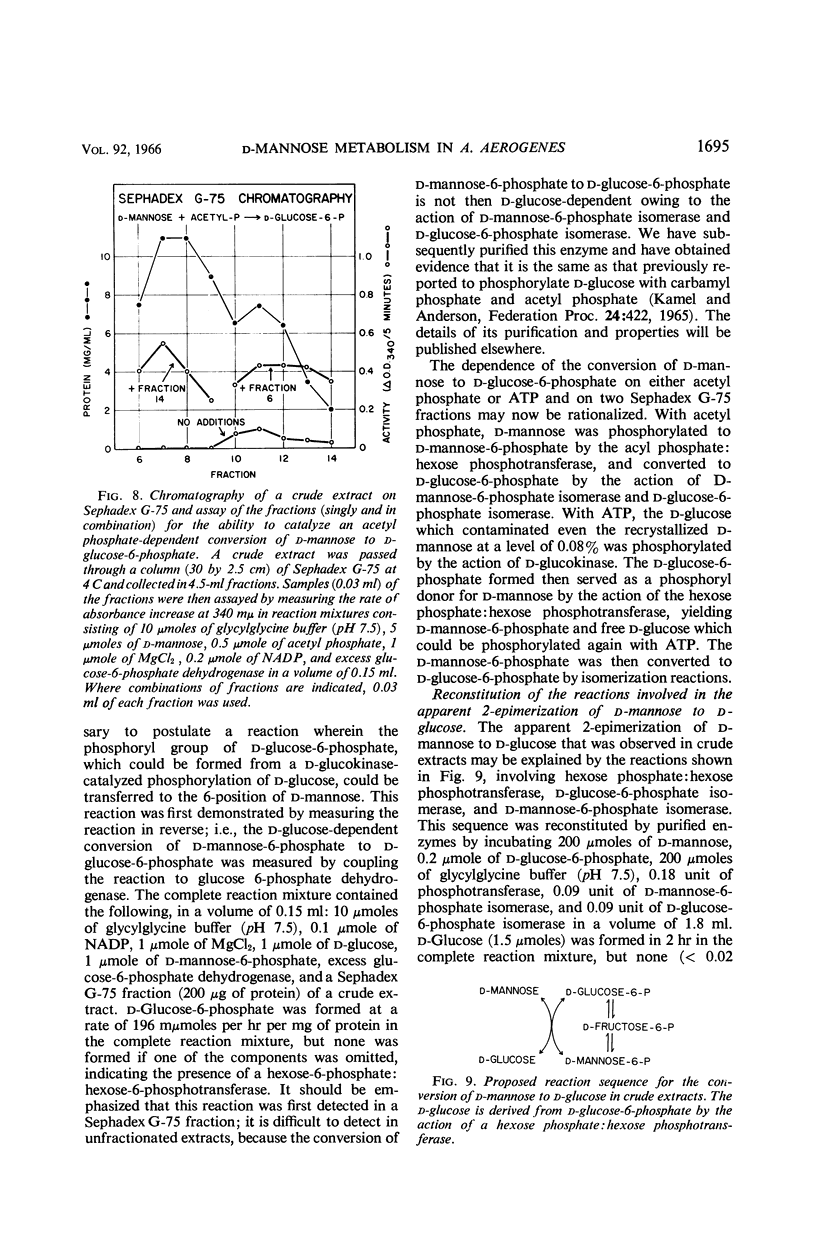
Kamel, M. Y. (Michigan State University, East Lansing), and R. L. Anderson. Metabolism of d-mannose in Aerobacter aerogenes: evidence for a cyclic pathway. J. Bacteriol. 92:1689–1697. 1966.—Evidence is presented which suggests a cyclic pathway for the constitutive utilization of d-mannose in extracts of Aerobacter aerogenes PRL-R3. d-Mannose is phosphorylated with d-glucose-6-phosphate to yield d-mannose-6-phosphate and d-glucose. d-Glucose-6-phosphate may be regenerated by isomerization of d-mannose-6-phosphate through d-fructose-6-phosphate, or by phosphorylation of d-glucose with adenosine-5′-triphosphate. The pathway involves the participation of four constitutive enzymes: d-glucose-6-phosphate isomerase, d-mannose-6-phosphate isomerase, a stereospecific d-glucokinase, and a phosphotransferase which phosphorylates d-mannose with d-glucose-6-phosphate, acetyl phosphate, or carbamyl phosphate. The absence of d-mannokinase (adenosine-5′-triphosphate:d-mannose phosphotransferase) activity in extracts of this organism suggests that the pathway may be of functional significance. Also, the pathway accounts for an apparent 2-epimerization of d-mannose to d-glucose that was observed in extracts.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON R. L., ALLISON D. P. PURIFICATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF D-LYXOSE ISOMERASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jun;240:2367–2372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSON R. L., WOOD W. A. Purification and properties of L-xylulokinase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1029–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUJIMOTO A., INGRAM P., SMITH R. A. D-GLUCOSE-I-PHOSPHATE:D-GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHOTRANSFERASE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jan;96:91–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90613-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GHOSH S., ROSEMAN S. THE SIALIC ACIDS. V. N-ACYL-D-GLUCOSAMINE 2-EPIMERASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Apr;240:1531–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAMEL M. Y., ANDERSON R. L. ENZYMATIC PHOSPHORYLATION OF D-GLUCOSE WITH ACETYL PHOSPHATE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:PC3607–PC3608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNDIG W., GHOSH S., ROSEMAN S. PHOSPHATE BOUND TO HISTIDINE IN A PROTEIN AS AN INTERMEDIATE IN A NOVEL PHOSPHO-TRANSFERASE SYSTEM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Oct;52:1067–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.4.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamel M. Y., Allison D. P., Anderson R. L. Stereospecific D-glucokinase of Aerobacter aerogenes. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1966 Feb 10;241(3):690–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs H. A., Lund P. Formation of glucose from hexoses, pentoses, polyols and related substances in kidney cortex. Biochem J. 1966 Jan;98(1):210–214. doi: 10.1042/bj0980210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTLOCK R. P., WOOD W. A. METABOLISM OF PENTOSES AND PENTITOLS BY AEROBACTER AEROGENES. I. DEMONSTRATION OF PENTOSE ISOMERASE, PENTULOKINASE, AND PENTITOL DEHYDROGENASE ENZYME FAMILIES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:838–844. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.838-844.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMPSON F. J., WOOD W. A. Degradation of L-arabinose by Aerobacter aerogenes. II. Purification and properties of L-ribulokinase. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jan;230(1):473–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TREVELYAN W. E., PROCTER D. P., HARRISON J. S. Detection of sugars on paper chromatograms. Nature. 1950 Sep 9;166(4219):444–445. doi: 10.1038/166444b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]