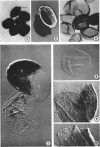
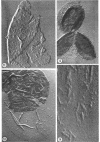
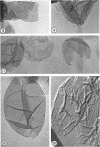
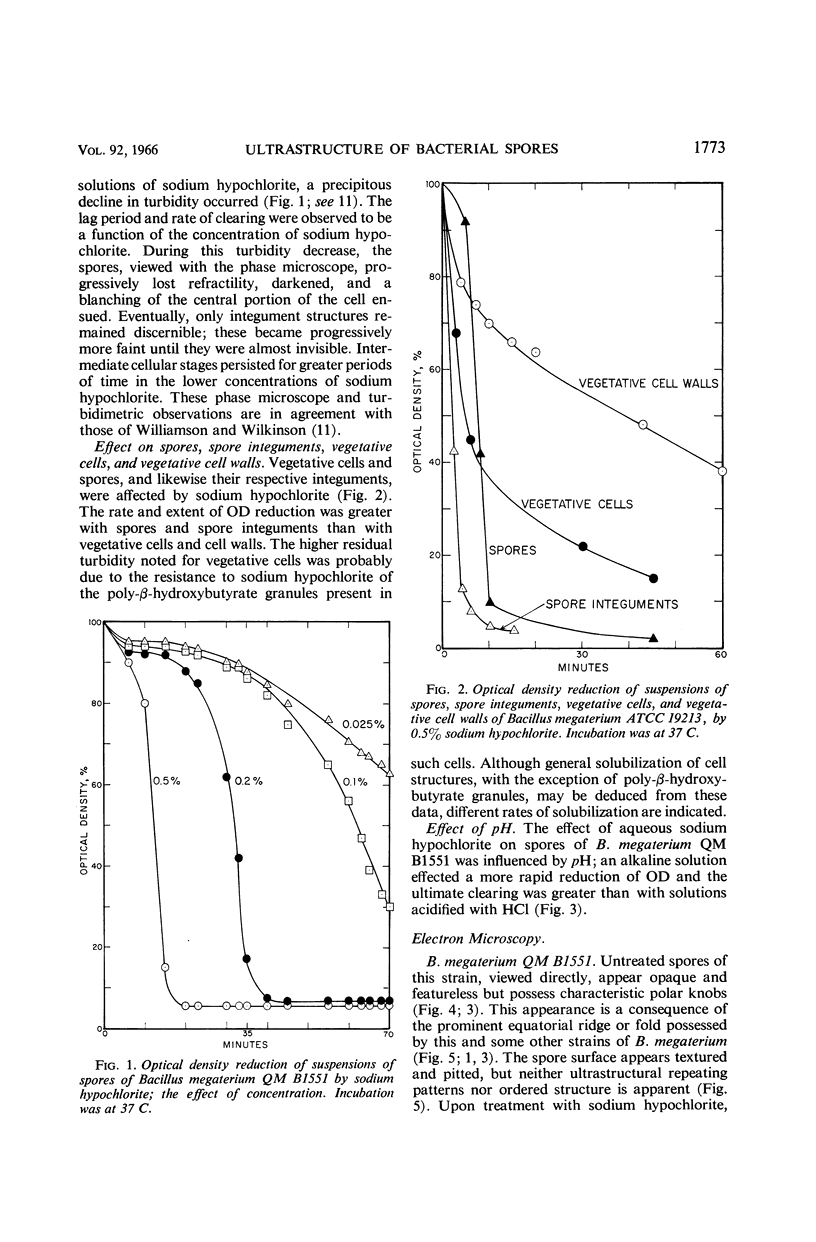
Abstract
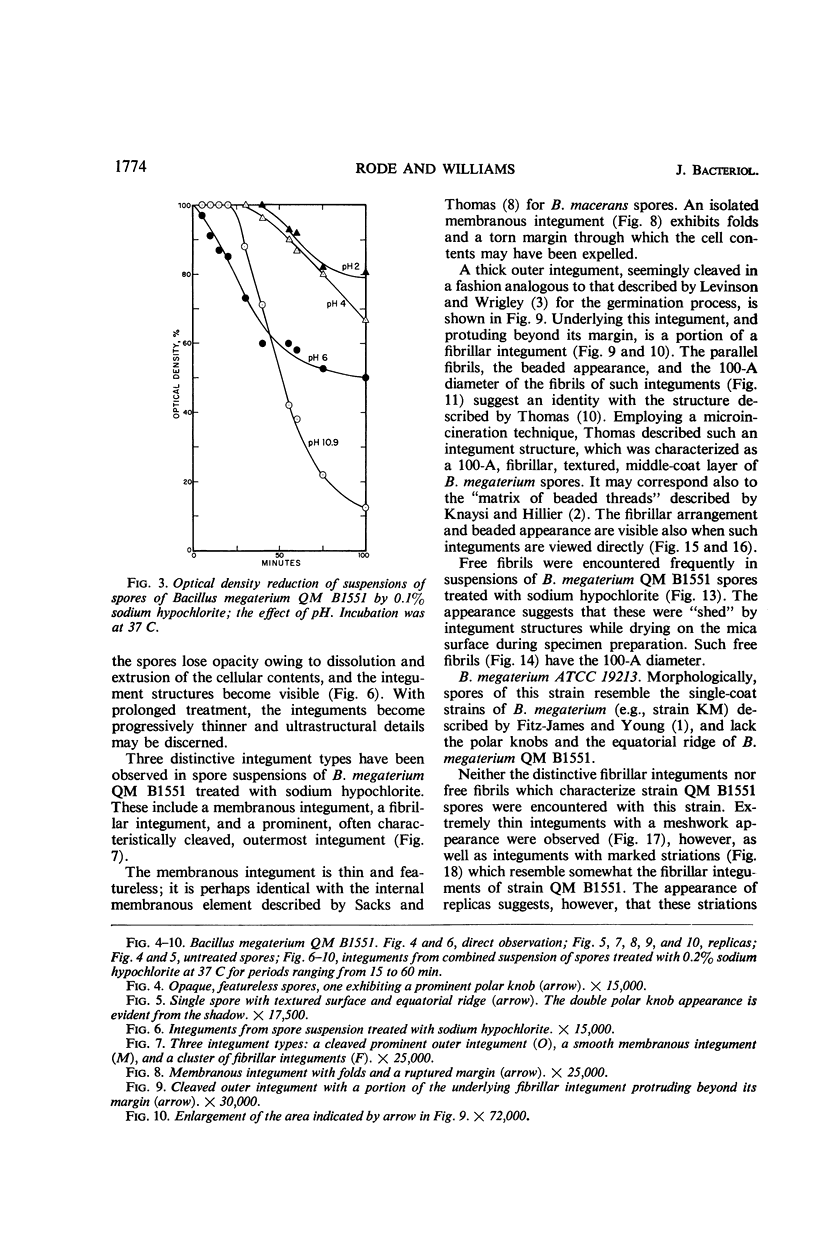
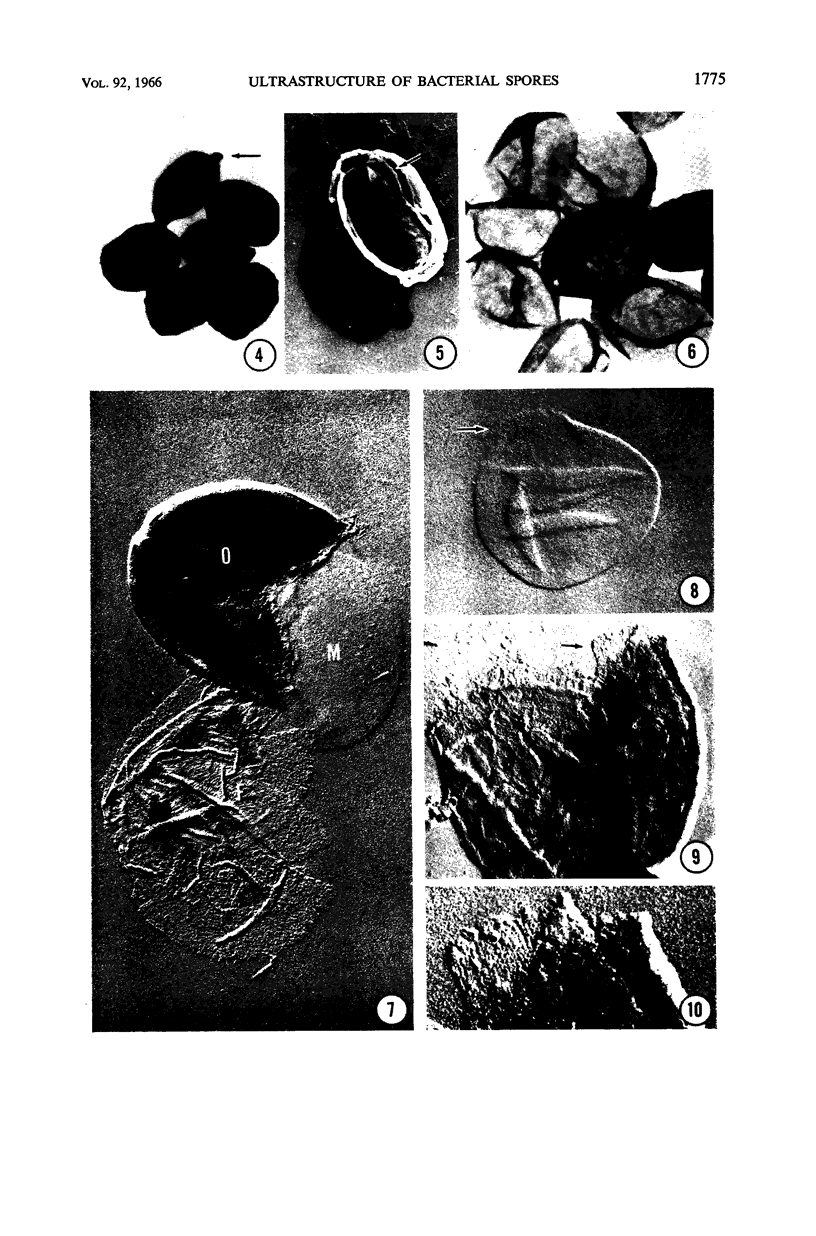
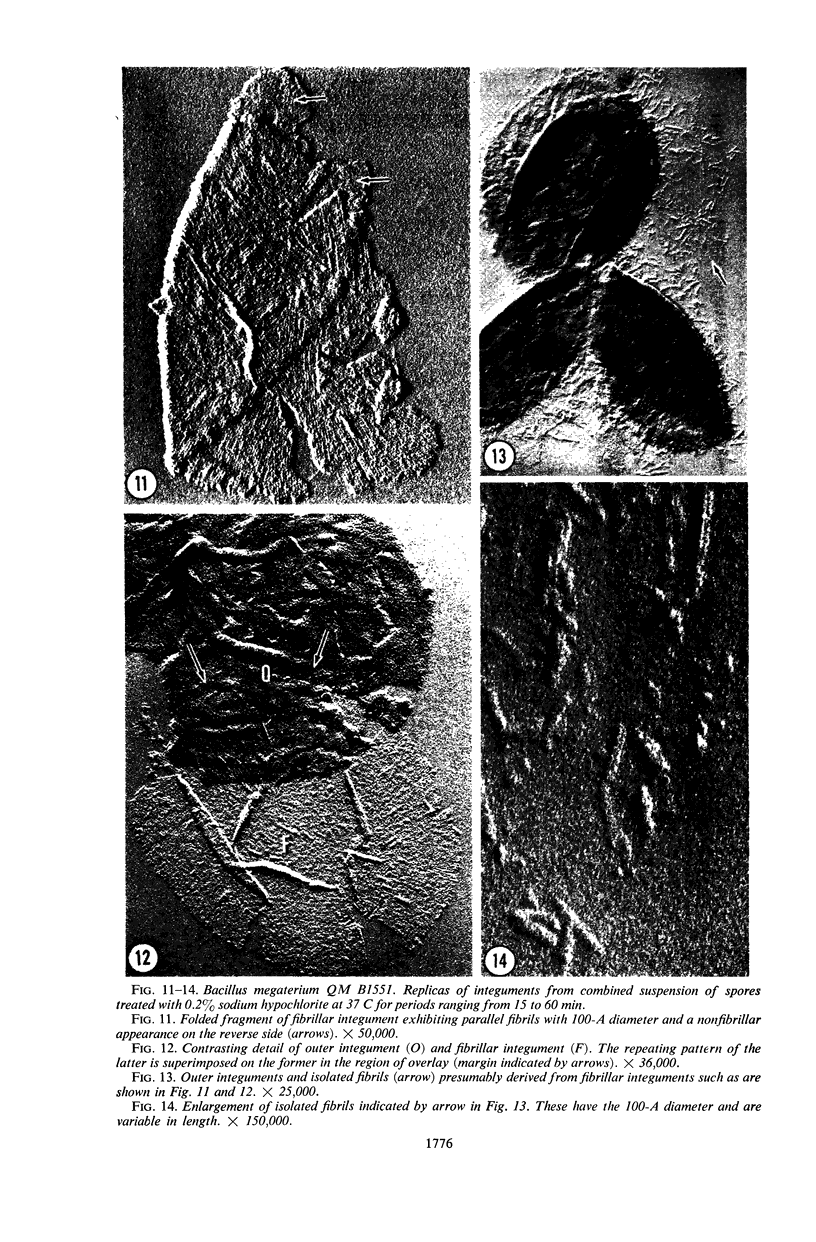
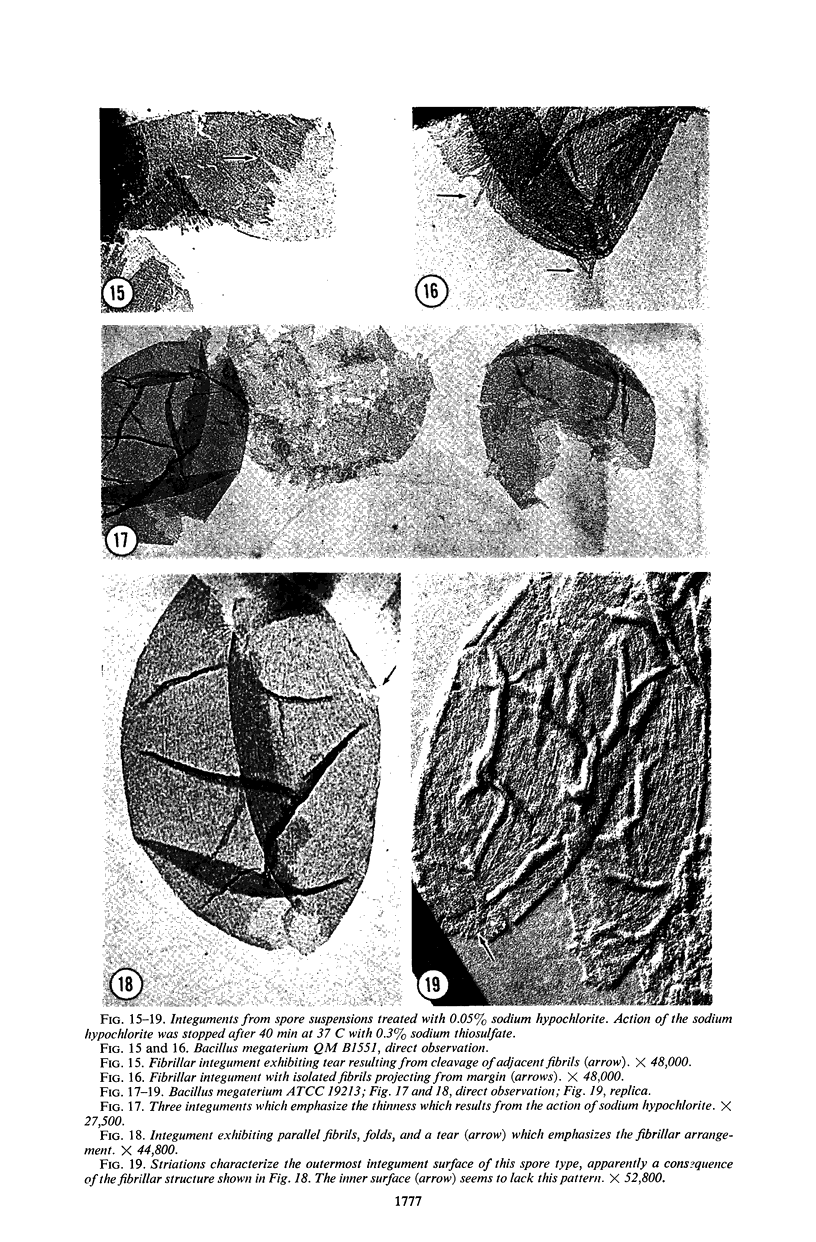
Rode, L. J. (The University of Texas, Austin), and M. Glenn Williams. Utility of sodium hypochlorite for ultrastructure study of bacterial spore integuments. J. Bacteriol. 92:1772–1778. 1966.—Spores of Bacillus megaterium are partially dissolved by sodium hypochlorite. Spore integuments become visible during the dissolution, and ultrastructural features may be detected. Three distinct integument types are described for B. megaterium QM B1551 with the use of this technique. Since a variety of microbial cells are affected by sodium hypochlorite, its use may be applicable to ultrastructure study of cells other than bacterial spores.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fitz-James P. C., Young I. E. CYTOLOGICAL COMPARISON OF SPORES OF DIFFERENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS MEGATERIUM. J Bacteriol. 1959 Dec;78(6):755–764. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.6.755-764.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaysi G., Hillier J. PRELIMINARY OBSERVATIONS ON THE GERMINATION OF THE ENDOSPORE IN BACILLUS MEGATHERIUM AND THE STRUCTURE OF THE SPORE COAT. J Bacteriol. 1949 Jan;57(1):23–29. doi: 10.1128/jb.57.1.23-29.1949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson H. S., Wrigley A. S. Spore Germination and Emergence of Bacillus megaterium. Science. 1960 May 6;131(3410):1382–1382. doi: 10.1126/science.131.3410.1382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode L. J., Foster J. W. Influence of exchangeable ions on germinability of bacterial spores. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1582–1588. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1582-1588.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode L. J., Foster J. W. MECHANICAL GERMINATION OF BACTERIAL SPORES. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Jan;46(1):118–128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rode L. J., Foster J. W. Quantitative aspects of exchangeable calcium in spores of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1589–1593. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1589-1593.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACKS L. E., THOMAS R. S. INTERNAL MEMBRANOUS STRUCTURE IN BACILLUS MACERANS SPORES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jun;89:1615–1616. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.6.1615-1616.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS R. S. ULTRASTRUCTURAL LOCALIZATION OF MINERAL MATTER IN BACTERIAL SPORES BY MICRONINCINERATION. J Cell Biol. 1964 Oct;23:113–133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.23.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMSON D. H., WILKINSON J. F. The isolation and estimation of the poly-beta-hydroxybutyrate inclusions of Bacillus species. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Aug;19(1):198–209. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-1-198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]