Abstract
Background. Previous studies have shown that the interaction of CD200R, a myeloid inhibitory receptor, with its ligand, CD200, is critical in the control of innate immune activation in the lung.
Methods and Results. Using a mouse model of bacterial superinfection following influenza, we show that an absence of CD200R (a negative regulator highly expressed by macrophages and dendritic cells), restricts commensal and exogenous bacterial invasiveness and completely prevents the mortality observed in wild-type mice. This benefit is due to a heightened innate immune response to influenza virus in cd200r knockout mice that limits immune pathogenesis and viral load. In wild-type mice, apoptotic cells expressing CD200 that we believe contribute to the suppressed innate immune response to bacteria dominate during the resolution phase of influenza-induced inflammation. We also show for the first time the presence of a variety of previously unidentified bacterial species in the lower airways that are significantly adjusted by influenza virus infection and may contribute to the pathophysiology of disease.
Conclusions. The interaction of CD200 with CD200R therefore contributes to the hyporesponsive innate immune state following influenza virus infection that predisposes to secondary bacterial infection, a phenomenon that has the potential for immune modulation.
Following severe influenza infection, secondary bacterial superinfections (including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus aureus, and Haemophilus influenzae) are prevalent and lead to a significantly worse prognosis [1, 2]. Increased mucus production, decreased ciliary beat frequency, and an upregulation of bacterial adhesins [3, 4] provide an environment conducive to bacterial persistence. Bacterial propagation leading to sepsis occurs following a loss of lung epithelial integrity that is caused by viral-induced cytopathology and/or lysis of virus-infected epithelial cells by recruited natural killer (NK) cells, cytotoxic T cells, and apoptosis-inducing cytokines [5–7] and the binding of TRAIL on recruited macrophages to death receptor 5 on the epithelium [8]. Bacterial colonization is also promoted by the apoptosis of neutrophils and macrophages during influenza-induced inflammation [9, 10] or reduced neutrophil recruitment [11, 12] due to a viral-driven type 1 interferon (IFN) reduction of appropriate chemokines [12].
Following an exuberant antiviral response, a period of time ensues in some patients where the lung is refractory to further stimulation. First, IFN-γ, though a key antiviral cytokine, also decreases bacterial scavenger receptors such as MARCO on macrophages [13]. Second, clearance of the large apoptotic immune cell infiltrate by macrophages produces a reduced bacteriocidal environment [14–16]. We have previously reported [17] (and it has subsequently been confirmed [18]) that mice lacking CD200 develop severe inflammation following influenza infection. CD200 is widely distributed in the central nervous system, on activated T cells, B cells, some dendritic cells, and cells of the glomeruli and vascular endothelium [19–21], and on epithelial-derived tissues including the thymus, retina, and hair follicle [22–24]. We and others also find CD200 on airway epithelial cells in mice [17] and rats [25]. CD200 lacks a cytoplasmic motif capable of recruiting adapter proteins, but instead imparts a unidirectional inhibitory signal to cells expressing CD200 receptor (CD200R); predominantly myeloid cells [26] (among others [27]). The extent of CD200-bearing cells from the outset therefore defines a site-specific threshold of innate immune cell activity.
Resolution of lung inflammatory disease sets a different threshold for innate immune activation that depends on the extent of original regulation, the pathogenicity of the infecting viral/bacterial strain, and the exuberance of inflammation required to clear it. This altered homeostasis could have a significant impact on the threshold of responsiveness to the next pathogen. We now report that an absence of the inhibitory CD200R reduces the outgrowth of endogenous bacterial species and prevents the sepsis and death observed following exogenous bacterial administration to influenza-infected mice. Furthermore, we show that during inflammatory resolution, apoptotic immune cells upregulate CD200, which may desensitize alveolar macrophages expressing higher levels of CD200R and contribute to the bacterial superinfections common following influenza infection.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Mouse Infection and Treatment
Eight- to 12-week-old female C57BL/6 (littermate controls) and cd200r -/- mice were bred in-house and kept in specific pathogen-free conditions in accordance with Home Office guidelines. Mice were anesthetized using isoflurane and infected intranasally with 50 μL influenza (as specified) or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) alone. At specified times after influenza infection, 104 bacterial colony-forming units (CFU) of Streptococcus pneumoniae (serotype 2), strain D39 (National Collection of Type Cultures [NCTC] 7466), was administered intranasally in a volume of 50 μL. In some experiments bacterial infection was administered 16 hours following intranasal inoculation of 106 CD200−/− or wild-type splenocytes incubated 5 hours previously with 1 μg/mL dimethyl sulfoxide at 37°C to induce apoptosis (confirmed by Annexin V and propodium iodide staining).
Cell Recovery and Isolation
Lung tissue, whole blood, and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), recovered by inflation of the lungs 4 times with 1.5 mL 5 mM EDTA in Hanks balanced salt solution via an intratracheal cannula, were collected. Lung tissue was disrupted through a 100 μM sieve and subsequently centrifuged for 5 minutes at 240 × g. At this stage 100 μL of each tissue was used for bacterial CFU enumeration, and the remainder was treated with red blood cell lysis buffer (0.15 M ammonium chloride, 1 M potassium hydrogen carbonate, and 0.01 mM EDTA, pH 7.2) for 3 minutes at room temperature (RT) before centrifugation (240 × g for 5 minutes). Cell viability was assessed by trypan blue exclusion and cells were resuspended in R10F at 1 × 106 cells/mL. In some studies lungs were inflation fixed with 10% neutral-buffered formalin in PBS and embedded in paraffin wax, and 4-μm sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin.
Airway Macrophage Stimulation and Cytokine Quantification
Alveolar macrophages from cd200r−/− and littermate control mice were isolated by adherence of BAL for 1 hour in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium at 37°C, 5% CO2 (>97% pure by flow cytometry), and plated at 2 × 106 cells/mL in 200 μL R10F. Wild-type S. pneumoniae or a transformant strain expressing green fluorescent protein (kindly provided by P. Andrews, University of Nottingham, United Kingdom) was then added and incubated at 37°C for 24 hours. All supernatant and in vivo cytokine concentrations were quantified using OptEIA kits (Pharmingen).
Airway Albumin Quantification
Airway albumin was quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Bethyl Laboratories). The mean optical density of wells containing no albumin was subtracted from the results and the albumin concentration calculated from a standard curve.
Flow Cytometric Analysis
Cells were stained for surface markers (as indicated in the text) in PBS containing 0.1% sodium azide and 1% bovine serum albumin (PBA) for 30 minutes at 4°C and then fixed with 2% paraformaldehye. All antibodies were purchased from BD Pharmingen. Cells were then washed in PBA; data were acquired on a BD FACS LSR II and 30 000 lymphocyte or myeloid events analyzed with FACS Diva software version 6.1.3 (BD Biosciences) or the FlowJo version 7.6.1 analysis software package. Apoptotic cells were detected using the method described in the in situ cell death detection kit (Roche).
Influenza-Specific Plaque Assay and Bacterial Titer
Lung homogenates were freeze-thawed 3 times and centrifuged at 4000 × g, and the supernatants were titrated in doubling dilutions on Madin-Darby canine kidney cell monolayers at RT for 3 hours, overlayed with 1% methylcellulose, incubated for 72 hours at 37°C, washed, and incubated with anti-influenza antibody (Serotec) followed by antimouse–horseradish peroxidase (Dako). Infected cells were detected using 3-amino-9-ethylcarbazole substrate, enumerated by light microscopy and total plaque-forming units per lung quantified. S. pneumoniae titer was determined by serial dilution in PBS of 20 μL aliquots from single-cell suspensions, plated on Columbia agar supplemented with 5% defibrinated horse blood and incubation overnight at 37°C. Gram staining, colony morphology, α-hemolysis, and optochin sensitivity tests confirmed S. pneumoniae presence.
16s rRNA Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis
Bacterial 16s rRNA amplicon pools were generated using the 339F-5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAGT-3′ and 907R-5′-CCGTCAATTCMTTTGAGTTT-3′ primer pairs. Subsequent denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and cloning analysis were performed using the methodology described in [28]. DNA sequence chromatograms were uploaded to the ribosomal database (http://rdp.cme.msu.edu/), vector sequences trimmed (using the LUCY program), and remaining sequences quality control checked (using PHRED). Sequences of high quality were downloaded and primer regions additionally trimmed, and only full-length sequences ranging from 359 to 906 (Escherichia coli numbering of 16S rRNA gene) were included for further analysis. A total of 262 (including 52 from the migration marker) high-quality sequences were aligned with NAST (http://greengenes.lbl.gov) and manually curated to allow the creation of a phylogenetic tree. Refer to [28] for details regarding the calculation of distance matrix and operational taxonomic units (OTUs). A cutoff of 99% was set and each OTU was then assigned an organism name, based on the phylogenetic placement using sequence match of the ribosomal database (20 best-match sequences define taxanomic rank), and compared with NCBI BLAST results for the percentage of sequence identity. The numbers of 16S rRNA gene phylotypes were calculated at 99% sequence identity with the farthest neighbor clustering in the program DOTUR.
Statistical Analysis
Unpaired 2-tailed Student t-test, assuming unequal variance, was used to interrogate parametric data sets. Nonparametric data sets were analyzed using Mann–Whitney t tests. The log-rank Mantel–Cox test was employed to determine survival curve statistical significance. The Bonferroni correction was applied during multiple comparisons. Data presented represent the mean ± standard deviation (SD) unless otherwise stated. P values < .05 were considered significant.
RESULTS
Influenza Causes Bacterial Superinfection and Mortality
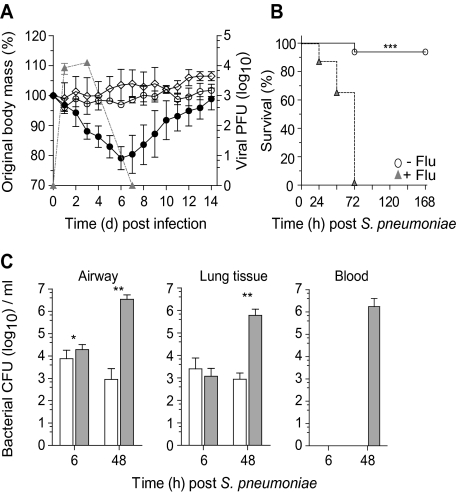
The murine model of bacterial superinfection following influenza virus was first used in 1945 [29] and has since been used with high reproducibility by many different researchers (eg, see [13, 30]). Similar to these prior studies, we show that uninfected mice gain weight with time whereas an intranasal influenza A virus infection caused substantial weight loss, peaking at days 5–6 (Figure 1A). Mice infected with 104 CFU of S. pneumoniae did not lose weight and were indistinguishable from uninfected littermate controls (Figure 1A). Bacterial administration 7 days after influenza infection, however, increased the already substantial weight loss caused by influenza alone, leading to 100% mortality 72 hours later (Figure 1B) (P < .0001 vs naive mice). Occasional mortality was observed in mice infected with 104 CFU S. pneumoniae alone (Figure 1B); however, this dose of S. pneumoniae was cleared rapidly from the airways within 3 days (data not shown). The combined infection, however, resulted in an increase in bacterial colonies in the airway (>1000 fold) and lung (Figure 1C) compared with mice infected with bacteria alone. In the absence of influenza infection, bacteria were rarely recovered from the blood. Bacterial infection 7 days after influenza, however, produced a bacterial septicemia by 48 hours, which correlated with heightened disease and mortality (Figure 1C). Similar to the postviral complication observed in humans, this increased susceptibility occurred when bacteria were administered on days 3, 7, or 14 following influenza infection, but not when bacteria were coadministered with influenza (Supplementary Figure 1A).
Figure 1.
Influenza infection increases susceptibility to Streptococcus pneumoniae superinfection. A, Body mass (left axis) and viral titer (triangles, right axis) of wild-type C57BL/6 mice infected with 1.25 × 105 plaque-forming units (PFU) of A/HK/X31 influenza (closed circle), 104 colony-forming units (CFU) Streptococcus pneumoniae (open circle), or vehicle control (diamonds). B, Survival of naive (open circle) or day 7 influenza-infected (triangles) wild-type mice infected with 104 CFU S. pneumoniae. C, Viable bacterial CFU recovered from the airway, lung tissue, and peripheral blood of naive (open bar) or day 7 postinfluenza (gray bar) mice at 6 hours and 48 hours following 104 CFU S. pneumoniae. Two-way ANOVA was used to interrogate weight loss, survival differences were determined using the log-rank Mantel–Cox test, and all other data were tested using a 2-tailed Mann–Whitney t test with 95% confidence intervals. Data are representative of 4 independent experiments (n = 5 mice per group). * P < .05, ** P < .01, *** P < .001 versus corresponding group.
Absence of CD200R Limits Bacterial Load and Prevents Systemic Dissemination
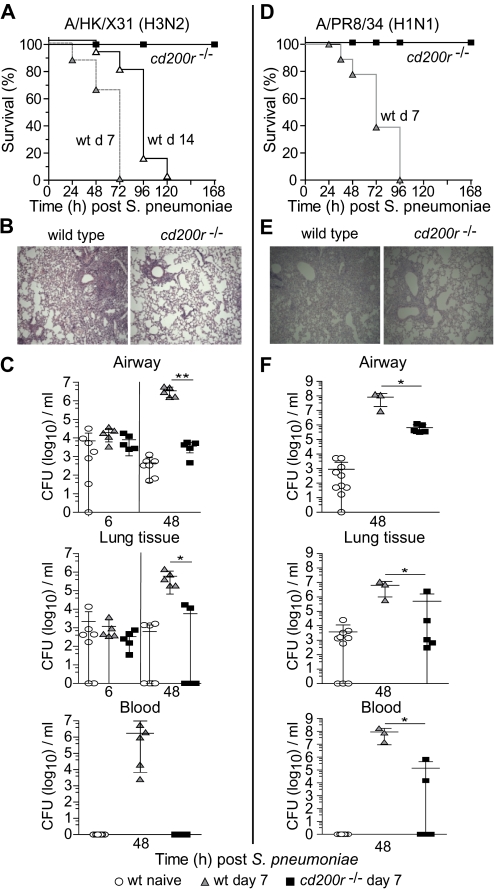
We next examined the consequences of bacterial administration to influenza-infected cd200r−/− mice. S. pneumoniae administration 7 days following influenza H3N2 (A/HK/X31) infection led to rapid mortality in all wild-type mice, but 100% survival in mice lacking CD200R (Figure 2A). This survival in cd200r−/− mice was accompanied by significantly improved lung histology with reduced inflammatory infiltrates (Figure 2B). S. pneumoniae administration to wild-type mice 7 days after influenza, as before, enhanced bacterial load in the airway, lung, and blood (Figure 2C). However, in cd200r−/− mice airway and lung bacterial titers were reduced and no colonies were recovered from the systemic circulation (Figure 2C). This protection in cd200r−/− mice was also observed in a repeat experiment where bacteria were administered 3, 7, and 14 days following influenza (A/HK/X31) infection (Supplemenatry Figure 1A) and also observed following infection with the H1N1 influenza strain (A/PR8/34) where, once again, all wild-type mice died (Figure 2D–F). Despite the increased virulence of this influenza strain in mice, all cd200r−/− mice displayed reduced cellularity (Figure 2E) and significantly fewer bacterial titers in the airway, lung, and blood (Figure 2F).
Figure 2.
Loss of CD200R prevents influenza-induced secondary bacterial superinfection. Survival of wild-type (wt) and cd200r−/− mice after infection with 104 colony-forming units (CFU) Streptococcus pneumoniae 7 days (gray triangles) or 14 days (open triangles) following A/HK/X31 (H3N2) (A) or A/PR8/34 (H1N1) (D) influenza virus infection. Representative hematoxylin and eosin–stained lung sections from day 7 A/X31 (H3N2) (B) or A/PR8/34 (H1N1) (E) influenza-infected wild-type and cd200r−/− mice 48 hours after S. pneumoniae infection. Total bacterial CFU recovered from the airway, lung tissue, and peripheral blood at 6 hours and 48 hours following 104 cfu S. pneumoniae in naive wild-type mice (circles) or those at day 7 of a A/HK/X31 (C) or A/PR8/34 (H1N1) (F) influenza infection. Survival differences were determined using the log-rank Mantel–Cox test, and all other data were tested using a 2-tailed Mann–Whitney t test with 95% confidence intervals. The data are representative of 3 independent experiments (n = 5–10 mice per group). * P < .05, ** P < .01, *** P < .001 versus corresponding group.
Absence of CD200R Reduces Influenza-Associated Cytokine Storm and Promotes Natural Killer Cells
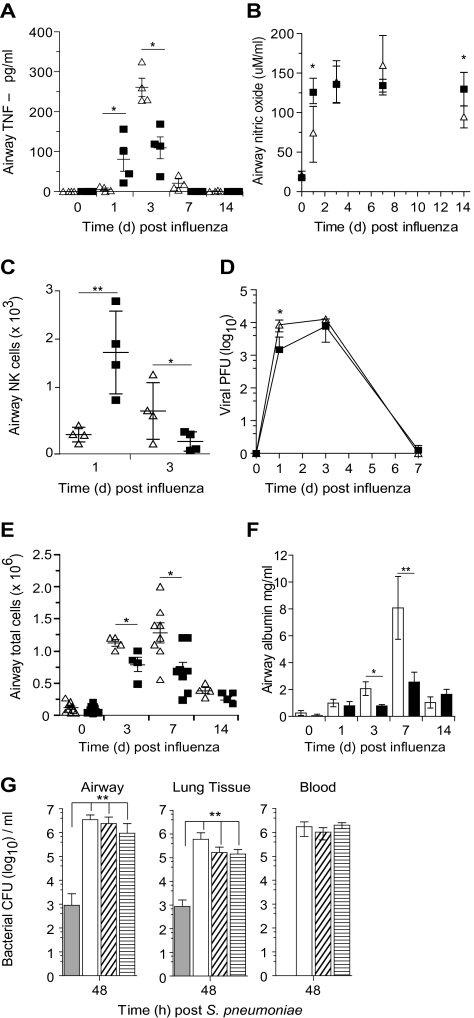
A reduced susceptibility to bacterial superinfections following influenza virus may result from a tempering of viral-induced damage in the first place. We have previously reported that a lack of CD200 causes exaggerated inflammation to influenza virus [17], but the impact of removing a single receptor (CD200R) for CD200 is unknown. In cd200r−/− mice we observed heightened airway tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–α (Figure 3A), nitric oxide (Figure 3B), and NK cells (Figure 3C) at early time points, suggesting heightened innate inflammation. Viral titers, however, were only partially reduced and showed no difference by day 3 (Figure 3D). This more rapid innate response resulted in less cellular recruitment in cd200r−/− mice at later time points (Figure 3E) and reduced epithelium permeability, as depicted by the leakage of serum albumin into the airspaces (Figure 3F). This heightened early innate immune response is therefore possibly beneficial as viral load and associated damage appear to be reduced. However, this alone cannot explain the reduced susceptibility to bacterial complications because titrating the influenza viral dose downward still resulted in bacterial superinfection in wild-type mice (Figure 3G).
Figure 3.
Antiviral immunity is enhanced in cd200r−/− mice. Airway levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–α (A) and nitric oxide (B) at homeostasis (naive) and 1, 3, 7, and 14 days after infection with A/HK/X31 (H3N2) influenza virus in wild-type (triangles) and cd200r−/− (squares) mice. Natural killer (NK) cell number (C) and lung tissue viral titer (D) in wild-type (triangles) and cd200r−/− mice (squares) at 1, 3, and 7 days following A/HK/X31 (H3N2) influenza infection. Total airway cellularity (E) and albumin (F) following infection with A/HK/X31 (H3N2) influenza virus in wild-type (triangles, open bars) and cd200r−/− mice (squares, closed bars). G, Viable bacterial colony-forming units (CFU) recovered from the airway, lung tissue, and peripheral blood of naive wild-type mice (closed bar) or those at day 7 after infection with 1.25 × 105 (open bar), 3.13 × 104 (diagonal lines), or 2.08 × 104 (horizontal lines) plaque-forming units (PFU) of influenza virus at 48 hours following 104 CFU Streptococcus pneumoniae. Cytokine data were analyzed using an unpaired 2-tailed Student t-test, assuming unequal variance. All other data were tested using a 2-tailed Mann–Whitney t test with 95% confidence intervals. Bonferroni correction was used for multiple comparisons. Data are representative of 4 independent experiments (n = 6–8 mice per group). * P < .05, ** P < .01, *** P < .001 versus corresponding group.
Cd200r−/− Mice Are More Responsive to Respiratory Bacteria
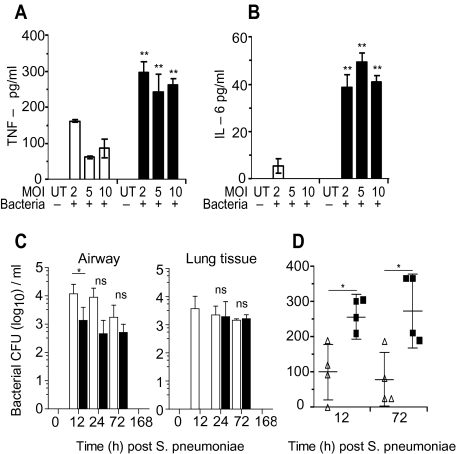
We next ascertained whether bacterial replication alone was altered in cd200r−/− mice. Isolated airway macrophages from naive cd200r−/− mice produced more TNF-α and interleukin (IL)–6 than wild-type littermate controls when cultured with varying doses of S. pneumoniae (Figure 4A and B). This was not due to enhanced uptake of bacteria or levels of FcγR/MARCO (data not shown), but may reflect the presence of marginally more macrophages expressing a higher intensity of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR-4 (data not shown).
Figure 4.
Enhanced bacterial responses in cd200r−/− mice. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–α (A) and interleukin (IL)–6 (B) liberated from wild-type (open bars) and cd200r−/− (closed bars) alveolar macrophages 24 hours following incubation with varying multiplicities of infection (MOI) of Streptococcus pneumoniae. C, Total colony-forming units (CFU) recovered from the airway and lung tissue of wild-type (open bar) and cd200r−/− mice (closed bar) at 12, 72, and 168 hours after 104 CFU S. pneumoniae infection. D, Airway levels of TNF-α in wild-type (triangles) and cd200r−/− mice (squares) 12 hours and 72 hours after S. pneumoniae infection. Cytokine data were analyzed using an unpaired 2-tailed Student t-test, assuming unequal variance. All other data were tested using a 2-tailed Mann–Whitney t test with 95% confidence intervals. Bonferroni correction was used for multiple comparisons. The data are representative of 4 independent experiments (n = 4 mice per group). * P < .05, ** P < .01, *** P < .001 versus corresponding group.
Without a coexisting morbidity in humans, bacteria do not often cause complications in the lower respiratory tract. We found this to be the case in wild-type and cd200r−/− mice. However, even in this self-limiting infection, cd200r−/− mice still displayed slightly lower airway CFU and a delay in their invasiveness into the lung parenchyma (Figure 4C), and heightened TNF-α secretion into the airway (Figure 4D). The cd200r−/− mice therefore display heightened responses to a self-limiting bacterial infection in the lung.
Role for CD200R in Inflammatory Resolution in the Lung
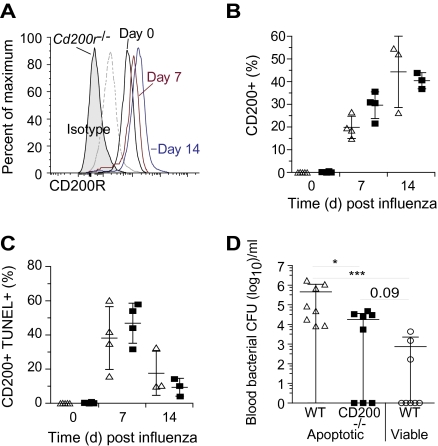
CD200 and its receptors are likely to play an important role in resolving lung inflammation that requires the clearance of recruited immune cells that have undergone apoptosis. Since presentation of self-antigens is undesirable, mechanisms to prevent macrophage activation during efferocytosis of apoptotic cells exist that cause the production of IL-10 and PGE2. However, the precise signaling molecules involved in delivering these inhibitory signals are not completely understood. We hypothesized that the increased intensity of CD200R on airway macrophages during resolution of influenza infection (Figure 5A) provides such a signal as we now show that TUNEL+ apoptotic cells express high levels of CD200 (Figure 5B and C). These apoptotic CD200+ cells are equally present in influenza-infected wild-type and cd200r−/− mice, though in the latter this suppression will not occur as CD200R is not expressed. Furthermore, intratracheal instillation of apoptotic cd200−/− splenocytes followed by administration of 105 CFU S. pneumoniae resulted in a reduced level of bacteremia compared with controls that received CD200 expressing apoptotic cells (Figure 5D). Regulation of lung innate immunity during resolution of inflammation may therefore render the lung susceptible to bacterial superinfection.
Figure 5.
CD200 is expressed on apoptotic leukocytes in the airway during the resolution of influenza infection. A, Relative CD200R levels at day 0 (black), day 7 (red), and day 14 (blue) in wild-type (WT) mice compared with isotype matched control (dotted line) or staining of cd200r−/− airway macrophages (shaded). Percentage of CD200+ (B) and TUNEL+ CD200+ (C) airway monocytes/macrophages 0, 7, and 14 days after A/HK/X31 (H3N2) influenza infection. D, Intratracheal transfer of apoptotic WT (triangles), apoptotic cd200−/− (squares), or viable WT (circles) splenocytes into naive WT mice 16 hours prior to infection with 105 CFU Streptococcus pneumoniae. Data represents resultant blood colony-forming units (CFU) per mouse with mean ± SD after 48 hours. All data were tested using a 2-tailed Mann–Whitney t test with 95% confidence intervals. Bonferroni correction was used for multiple comparisons. The data are representative of 3 independent experiments (n = 6–8 per group). * P < .05, ** P < .01, *** P < .001 versus corresponding group.
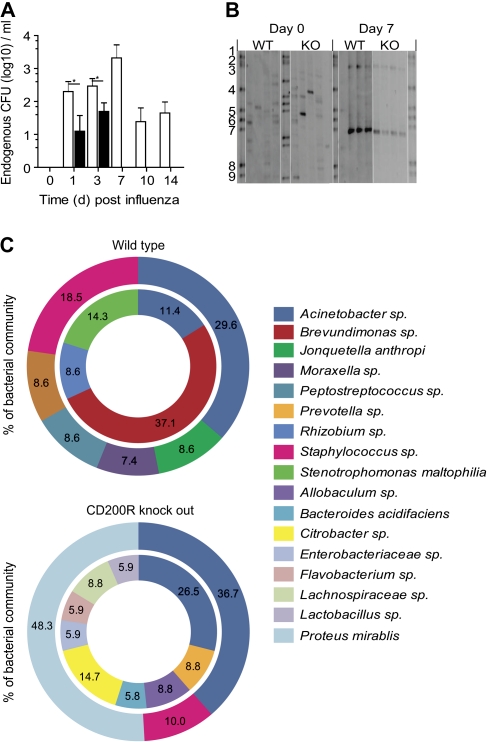
Regulation of Commensal Bacterial Species by CD200R
The initial reactivity of innate immunity is likely to be important in containing the density and diversity of commensal bacterial species. In our studies we observed a population of endogenous commensal bacteria in the airways during influenza infection that were not present at homeostasis (Figure 6A). Their density was reduced and better contained by an absence of CD200R. Because culture is not the most sensitive method for examining microbiota (as 95% of bacterial species are not recoverable under these conditions), we undertook a preliminary screen of commensal bacteria by polymorphic 16s ribosomal RNA gene analysis of airway lavage and showed a significant diversity of bacterial genera in both wild-type and cd200r−/− mice that at day 7 following influenza had concentrated into 2 dominant regions (Figure 6B) predominantly containing Acinetobacter, Staphylococcus, Prevotella, Moraxella, and Proteus mirabilis spp (Figure 6C). A full species identification and clone frequency are shown in Supplemenatry Figure 1B and C.
Figure 6.
Influenza infection causes a dysbiosis of the endogenous microbiota. A, Endogenous bacterial colony-forming units (CFU) recovered from the airway of wild-type (WT; open bar) and cd200r−/− (closed bar) mice following infection with A/HK/X31 (H3N2) influenza virus. Data were tested using a 2-tailed Mann–Whitney t test with 95% confidence intervals. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments (n = 5 mice per group). * P < .05, ** P < .01, *** P < .001 versus corresponding group. B, Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis of bacterial 16s ribosomal RNA gene amplicon pools from the airways of naive and day 7 influenza-infected WT and cd200r−/− (KO) mice (n = 4 mice per group). Bands 1–9 represent a standardized bacteria species marker. C, Phylogenetic analysis of endogenous airway bacteria, expressed as a percentage of the total microbiota, from naive (inner circle) and day 7 influenza-infected (outer circle) WT and cd200r−/− mice. Only bacteria representing >5% or designating a known species name are shown. The omitted bacteria can be found in Supplemenatry Figure 1A. Data represent 2 independent samples randomly picked from each experimental group for cloning analysis and species identification.
DISCUSSION
The activity of innate immunity is dictated by site-specific factors to ensure reactivity to potential pathogens but inactivity to harmless environmental antigens in mucosal tissues. We believe that this threshold is likely to be different due to regulatory receptor polymorphisms, or as a consequence of an attempt to return the lung to its normal state following inflammation. Such heterogeneity may explain why some respond inappropriately to environmental allergens or experience exacerbations of asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease more frequently; in this case the threshold for activation is set too low. On the other hand, a high threshold can be equally damaging, as we show here for lung bacterial superinfection and sepsis following influenza. An excess of soluble IL-10 [31] and enhanced CD200R expression on antigen presenting cells including macrophages and dendritic cells (APCs) [17], together with those pathways mentioned in the introduction, enhances the point of reactivity of lung APCs to bacteria and their products, meaning that bacterial titers exceed a containable threshold.
The excess of anti-inflammatory mechanisms following acute viral infection may be a consequence of local APCs attempting to clear apoptotic epithelial and immune cells. Such efferocytosis of apoptotic cells by macrophages liberates transforming growth factor-β, IL-10, and prostaglandins while reducing proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines [14, 15, 32], which may explain the long-term desensitization of airway APCs to subsequent bacterial products [11]. Intratracheal administration of apoptotic cells reduces acute inflammation to the bacterial product lipopolysaccharide [33] and impairs the clearance of S. pneumoniae by airway macrophages that are dependent on prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) [16]. PGE2 alone suppresses the antimicrobial activity of alveolar macrophages by inhibiting NADPH oxidase [34]. The role of CD200 in this process is not currently known. Here we report high expression of CD200 on apoptotic (TUNEL+) lung cells during influenza infection and also a sustained increase of CD200R on airway macrophages and neutrophils [17]. Furthermore, bacterial loads are much higher in mice given apoptotic cells from wild-type compared with CD200 knockout mice. This effect is not explained by other inherent differences between these 2 cell populations because CD200 does not possess a cytoplasmic signaling motif. Therefore, CD200-expressing apoptotic cells may inhibit the bacterial responsiveness of CD200R± lung myeloid cells and predispose to bacterial superinfection.
It is interesting to note that the inflammation generated in vivo during influenza infection of cd200r−/− mice is heightened, but less than we reported in cd200−/− knockout mice (where prolonged inflammation caused mice to succumb to inflammatory lung disease [17]). Macrophages from both CD200 [17] and CD200R knockout mice (this study) produce higher inflammatory cytokines in response to TLR agonists. We explain this difference based on the wide distribution of CD200 and the restricted expression of CD200R. In addition to the inhibitory CD200R, several activating CD200R-like molecules also exist (termed CD200R1-5 or CD200RLa-e) [35–38]. The ligand(s) for these are unknown and they either show no, or 100-fold weaker, binding to CD200 [39]. All mouse strains express the inhibitory CD200R (that is present in 2 allelic forms differing in only 7 amino acids in the variable domain) and up to 3 activating receptors [40]. Blocking or knocking out CD200 in murine models (that usually binds to several different inhibitory or activating CD200R or CD200R-like receptors) may have a different effect to knocking out or blocking an individual allelic variant of the inhibitory CD200R. Knocking out only CD200R does enhance innate inflammation, but this is ultimately beneficial in the context of a secondary bacterial pneumonia. CD200, on the other hand, is present on a wide variety of cells and vast surface area and may affect multiple receptors.
Although lowering the threshold of innate immune cell activation in cd200r−/− mice may directly enhance clearance of respiratory bacteria, we cannot rule out an indirect role of CD200R on epithelial permeability. In wild-type mice epithelial integrity depends on the pathogenicity of the infecting influenza strain [41, 42], the extent of the cytokine storm [43–45], and the activity of cytolytic and Th1 cytokine-secreting T cells and NK cells [5, 6]. The duration of these adverse factors may be reduced in cd200r−/− mice that display reduced inflammation to influenza.
The appearance of culturable commensal bacterial species in the airways of influenza-infected mice and their reduction in cd200r−/− mice is interesting. These are likely to arise from the nasopharynx and may be washed into the airspaces during the intranasal infection and persist, or they arise from the increased commensal density observed in the nasopharynx during influenza infection. It is also interesting to note that the diversity of bacterial species was reduced following influenza infection. This suggests that the activity of innate immunity dictates the density and repertoire of commensal bacteria and that, in part, colonization is tolerated where site-specific factors exert their most restraint on innate immune cells. The change in the local microenvironment by influenza is likely to benefit certain commensal species as described for other areas of the body ([46] and references therein). Such outgrowths of particular commensals probably contribute to the severity of many inflammatory pathologies but have not been identified to date due to difficulties in culture methods. Whether acquired from an exogenous or endogenous source, our data suggest that modification of CD200R may reduce the severity of life-threatening bacterial superinfections that are common during seasonal and pandemic influenza virus infection.
Supplementary Data
Supplementary Data are available at The Journal of Infectious Diseases online.
Funding
This work was supported by the Medical Research Council (P171/03/C1/048); the National Institutes of Health (NGA:1 U01 AI070232-01), The Wellcome Trust (082727/Z/07/Z); and the European Union (contract number 032296).
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Professors Brigitte Askonas and Charles Bangham for critical reading of this manuscript, and The Centre for Respiratory Infection.
References
- 1.Brundage JF, Shanks GD. Deaths from bacterial pneumonia during 1918–19 influenza pandemic. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:1193–9. doi: 10.3201/eid1408.071313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Bacterial coinfections in lung tissue specimens from fatal cases of 2009 pandemic influenza A (H1N1)—United States, May–August 2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:1071–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cundell DR, Gerard NP, Gerard C, Idanpaan-Heikkila I, Tuomanen EI. Streptococcus pneumoniae anchor to activated human cells by the receptor for platelet-activating factor. Nature (London) 1995;377:435–8. doi: 10.1038/377435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McCullers JA, Bartmess KC. Role of neuraminidase in lethal synergism between influenza virus and Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 2003;187:1000–9. doi: 10.1086/368163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mandelboim O, Lieberman N, Lev M, et al. Recognition of haemagglutinins on virus-infected cells by NKp46 activates lysis by human NK cells. Nature (London) 2001;409:1055–60. doi: 10.1038/35059110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Daidoji T, Koma T, Du A, et al. H5N1 avian influenza virus induces apoptotic cell death in mammalian airway epithelial cells. J Virol. 2008;82:11294–307. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01192-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Topham DJ, Tripp RA, Doherty PC. CD8+ T cells clear influenza virus by perforin or Fas-dependent processes. J Immunol. 1997;159:5197–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Herold S, Steinmueller M, von WW, et al. Lung epithelial apoptosis in influenza virus pneumonia: the role of macrophage-expressed TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. J Exp Med. 2008;205:3065–77. doi: 10.1084/jem.20080201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.McNamee LA, Harmsen AG. Both influenza-induced neutrophil dysfunction and neutrophil-independent mechanisms contribute to increased susceptibility to a secondary Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. Infect Immun. 2006;74:6707–21. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00789-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Colamussi ML, White MR, Crouch E, Hartshorn KL. Influenza A virus accelerates neutrophil apoptosis and markedly potentiates apoptotic effects of bacteria. Blood. 1999;93:2395–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Didierlaurent A, Goulding J, Patel S, et al. Sustained desensitization to bacterial Toll-like receptor ligands after resolution of respiratory influenza infection. J Exp Med. 2008;205:323–9. doi: 10.1084/jem.20070891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shahangian A, Chow EK, Tian X, et al. Type I IFNs mediate development of postinfluenza bacterial pneumonia in mice. J Clin Invest. 2009;119:1910–20. doi: 10.1172/JCI35412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sun K, Metzger DW. Inhibition of pulmonary antibacterial defense by interferon-gamma during recovery from influenza infection. Nat Med. 2008;14:558–64. doi: 10.1038/nm1765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fadok VA, Bratton DL, Konowal A, Freed PW, Westcott JY, Henson PM. Macrophages that have ingested apoptotic cells in vitro inhibit proinflammatory cytokine production through autocrine/paracrine mechanisms involving TGF-beta, PGE2, and PAF. J Clin Invest. 1998;101:890–8. doi: 10.1172/JCI1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Voll RE, Herrmann M, Roth EA, Stach C, Kalden JR, Girkontaite I. Immunosuppressive effects of apoptotic cells. Nature (London) 1997;390:350–1. doi: 10.1038/37022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Medeiros AI, Serezani CH, Lee SP, Peters-Golden M. Efferocytosis impairs pulmonary macrophage and lung antibacterial function via PGE2/EP2 signaling. J Exp Med. 2009;206:61–8. doi: 10.1084/jem.20082058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Snelgrove RJ, Goulding J, Didierlaurent AM, et al. A critical function for CD200 in lung immune homeostasis and the severity of influenza infection. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:1074–83. doi: 10.1038/ni.1637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rygiel TP, Rijkers ES, de Ruiter T, et al. Lack of CD200 enhances pathological T cell responses during influenza infection. J Immunol. 2009;183:1990–6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0900252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Clark MJ, Gagnon J, Williams AF, Barclay AN. MRC OX-2 antigen: a lymphoid/neuronal membrane glycoprotein with a structure like a single immunoglobulin light chain. EMBO J. 1985;4:113–8. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Barclay AN, Clark MJ, McCaughan GW. Neuronal/lymphoid membrane glycoprotein MRC OX-2 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily with a light-chain-like structure. Biochem Soc Symp. 1986;51:149–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.McCaughan GW, Clark MJ, Barclay AN. Characterization of the human homolog of the rat MRC OX-2 membrane glycoprotein. Imm. 1987;25:329–35. doi: 10.1007/BF00404426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ragheb R, Abrahams S, Beecroft R, et al. Preparation and functional properties of monoclonal antibodies to human, mouse and rat OX-2. Immunol Lett. 1999;68:311–5. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(99)00060-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dick AD, Broderick C, Forrester JV, Wright GJ. Distribution of OX2 antigen and OX2 receptor within retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42:170–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rosenblum MD, Olasz EB, Yancey KB, et al. Expression of CD200 on epithelial cells of the murine hair follicle: a role in tissue-specific immune tolerance? J Invest Dermatol. 2004;123:880–7. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-202X.2004.23461.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jiang-Shieh YF, Chien HF, Chang CY, et al. Distribution and ex-pression of CD200 in the rat respiratory system under normal and endotoxin-induced pathological conditions. J Anat. 2010;216:407–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01190.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Barclay AN, Wright GJ, Brooke G, Brown MH. CD200 and membrane protein interactions in the control of myeloid cells. Trends Immunol. 2002;23:285–90. doi: 10.1016/s1471-4906(02)02223-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Minas K, Liversidge J. Is the CD200/CD200 receptor interactio/endo/n more than just a myeloid cell inhibitory signal? Crit Rev Immunol. 2006;26:213–30. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v26.i3.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hilty M, Burke C, Pedro H, et al. Disordered microbial communities in asthmatic airways. PLoS One. 2010;5:e8578. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Francis TE, de Torregrosa MV. Combined infection of mice with H. influenzae and influenza virus by the intranasal route. J Infect Dis. 1945;76:70–7. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Huber VC, Peltola V, Iverson AR, McCullers JA. Contribution of vaccine-induced immunity toward either the HA or the NA component of influenza viruses limits secondary bacterial complications. J Virol. 2010;84:4105–8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02621-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.van der Sluijs KF, van Elden LJ, Nijhuis M, et al. IL-10 is an important mediator of the enhanced susceptibility to pneumococcal pneumonia after influenza infection. J Immunol. 2004;172:7603–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.12.7603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.McDonald PP, Fadok VA, Bratton D, Henson PM. Transcriptional and translational regulation of inflammatory mediator production by endogenous TGF-beta in macrophages that have ingested apoptotic cells. J Immunol. 1999;163:6164–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Huynh ML, Fadok VA, Henson PM. Phosphatidylserine-dependent ingestion of apoptotic cells promotes TGF-beta1 secretion and the resolution of inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2002;109:41–50. doi: 10.1172/JCI11638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Serezani CH, Chung J, Ballinger MN, Moore BB, Aronoff DM, Peters-Golden M. Prostaglandin E2 suppresses bacterial killing in alveolar macrophages by inhibiting NADPH oxidase. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2007;37:562–70. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2007-0153OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Dittmer U, Werner T, Kraft AR. Co-immunization of mice with a retroviral DNA vaccine and GITRL-encoding plasmid augments vaccine-induced protection against retrovirus infection. Viral Immunol. 2008;21:459–67. doi: 10.1089/vim.2008.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Kojima T, Obata K, Mukai K, et al. Mast cells and basophils are selectively activated in vitro and in vivo through CD200R3 in an IgE-independent manner. J Immunol. 2007;179:7093–100. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.10.7093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Voehringer D, Rosen DB, Lanier LL, Locksley RM. CD200 receptor family members represent novel DAP12-associated activating receptors on basophils and mast cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:54117–23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406997200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wright GJ, Cherwinski H, Foster-Cuevas M, et al. Characterization of the CD200 receptor family in mice and humans and their interactions with CD200. J Immunol. 2003;171:3034–46. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.6.3034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hatherley D, Barclay AN. The CD200 and CD200 receptor cell surface proteins interact through their N-terminal immunoglobulin-like domains. Eur J Immunol. 2004;34:1688–94. doi: 10.1002/eji.200425080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Akkaya M, Barclay AN. Heterogeneity in the CD200R paired receptor family. Immunogenetics. 2010;62:15–22. doi: 10.1007/s00251-009-0415-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tumpey TM, Basler CF, Aguilar PV, et al. Characterization of the reconstructed 1918 Spanish influenza pandemic virus. Science. 2005;310:77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.1119392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Tumpey TM, Garcia-Sastre A, Taubenberger JK, et al. Pathogenicity of influenza viruses with genes from the 1918 pandemic virus: functional roles of alveolar macrophages and neutrophils in limiting virus replication and mortality in mice. J Virol. 2005;79:14933–44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.23.14933-14944.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Szretter KJ, Gangappa S, Lu X, et al. Role of host cytokine responses in the pathogenesis of avian H5N1 influenza viruses in mice. J Virol. 2007;81:2736–44. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02336-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cheung CY, Poon LL, Lau AS, et al. Induction of proinflammatory cytokines in human macrophages by influenza A (H5N1) viruses: a mechanism for the unusual severity of human disease? Lancet. 2002;360:1831–7. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(02)11772-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lee DC, Cheung CY, Law AH, Mok CK, Peiris M, Lau AS. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent hyperinduction of tumor necrosis factor alpha expression in response to avian influenza virus H5N1. J Virol. 2005;79:10147–54. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.16.10147-10154.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Artis D. Epithelial-cell recognition of commensal bacteria and maintenance of immune homeostasis in the gut. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:411–20. doi: 10.1038/nri2316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.