Figure 8. Comparison of mouse H4 Site II sequences and H4 mRNA levels.
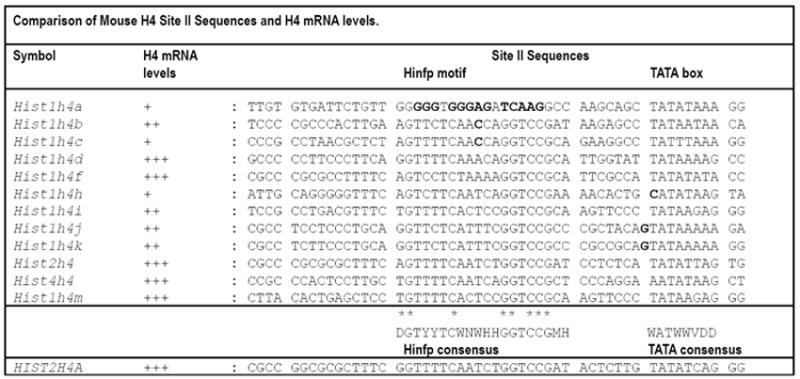
Alignment of the DNA sequences of the Site II cell cycle regulatory domain element (containing Hinfp and TATA elements) in the full complement of mouse histone H4 genes (top) compared to the prototypical human histone H4 gene HIST2H4A (bottom; see (Holmes et al., 2005)). Residues of Hinfp contact within the consensus element are indicated by asterisks (*). Redundant nucleotides (nt) are indicated as follows: D = A, G, or T; H = A, C, or T; M = A or C; W = A or T; Y = C or T; V = A, G or C. Mismatches in mouse Site II sequences (bold), which spans the Hinfp binding site consensus and the TATA box, are indicated in relation to H4 mRNA expression. H4 mRNA expression data in cells, tissues and developmental stages are summarized as follows: +, below average levels; ++, intermediate levels; +++, above average expression. Point-mutations in the Hinfp motif or the TATA-box correlate with decreased H4 gene expression.
