Abstract
Aims
Rhodiola dumulosa (Crassulaceae) is a perennial diploid species found in high-montane areas. It is distributed in fragmented populations across northern, central and northwestern China. In this study, we aimed to (i) measure the genetic diversity of this species and that of its populations; (ii) describe the genetic structure of these populations across the entire distribution range in China; and (iii) evaluate the extent of gene flow among the naturally fragmented populations.
Methods
Samples from 1089 individuals within 35 populations of R. dumulosa were collected, covering as much of the entire distribution range of this species within China as possible. Population genetic diversity and structure were analyzed using AFLP molecular markers. Gene flow among populations was estimated according to the level of population differentiation.
Important Findings
The total genetic diversity of R. dumulosa was high but decreased with increasing altitude. Population-structure analysis indicated that the most closely related populations were geographically restricted and occurred in close proximity to each other. A significant isolation-by-distance pattern, caused by the naturally fragmented population distribution, was observed. At least two distinct gene pools were found in the 35 sampled populations, one composed of populations in northern China and the other composed of populations in central and northwestern China. The calculation of Nei's gene diversity index revealed that the genetic diversity in the northern China pool (0.1972) was lower than that in the central and northwestern China pool (0.2216). The populations were significantly isolated, and gene flow was restricted throughout the entire distribution. However, gene flow among populations on the same mountain appears to be unrestricted, as indicated by the weak genetic isolation among these populations.
Introduction
Habitat fragmentation is a significant threat to the maintenance of biodiversity in many terrestrial ecosystems [1]. Many studies have investigated the effects of fragmentation on the genetic diversity and population structure of plant species [2]–[4]. In general, fragmentation is expected to reduce genetic diversity and to increase interpopulation genetic divergence by restricting gene flow among fragmented populations, increasing inbreeding and increasing random genetic drift within populations [5]. However, habitat fragmentation does not always lead to reduced genetic variation [6]–[8]. In some cases, the genetic diversity of a fragmented population can be higher than that of a continuously distributed population [9]. This is because the effects of habitat fragmentation on genetic diversity and population structure can be affected by other factors, such as population size, gene flow and the time scale of fragmentation [10].
Fragmented distributions of plant populations are caused not only by human activity but also by natural factors, such as long-term, large-scale climate oscillations, topographical changes, the isolation of suitable habitats, or other ecological changes. Studies of the genetic diversity of naturally fragmented populations may not only reveal the ecological consequences of population fragmentation over long periods of time but also provide a frame of reference for predicting the consequences of habitat fragmentation by human activities [6]. Genetic analyses of naturally fragmented populations has been conducted in several studies [6], [11]–[14].
Rhodiola dumulosa (Crassulaceae) is a perennial plant species that is found in northern, central and northwestern China. R. dumulosa is suggested to be a diploid plant [15]. It uses a mixed-mating system, i.e., it is capable of self-fertilization but most often undergoes outbreeding via pollinators [16], [17]. This species lives exclusively between rocks on mountains at elevations of 1600 m to 4100 m. Wild populations of this species are uniquely adapted to scarce and highly fragmented rocky habitats. Its habituation to these ‘ecological islands’ has produced a naturally fragmented distribution, which may lead to the long-term genetic isolation of its populations. Most populations in our field investigation were of moderate size (around 50 to 80 individuals each population). However, we also found a few large populations, with more than 150 individuals, and very small populations, with fewer than 10 individuals.
In this study, we used AFLP analysis to assess the genetic diversity, differentiation and structure of isolated populations of R. dumulosa from different mountains across its entire distribution in China. We then used these results to address the following questions: (1) How much genetic diversity is maintained in these naturally fragmented populations of R. dumulosa? (2) How is the genetic diversity spatially structured across the entire distribution range of this species in China? (3) Is there any gene flow among these naturally fragmented populations?
Results
Four AFLP primer combinations were used to analyze 1,089 individual genotypes, resulting in 225 markers, 221 (98.22%) of which were polymorphic.
Population genetic structure
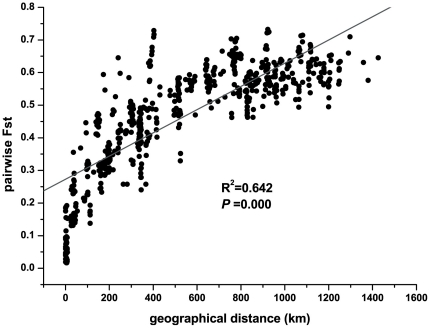
The Mantel test (Fig. 1) revealed a strong and significant positive relationship between geographical and genetic distances (r = 0.801; P<0.01) across the whole sampled region, indicating significant isolation-by-distance. We also conducted separate Mantel tests on the Donglingshan and Heyeping populations, in which populations were collected according to altitude, to determine whether isolation-by-distance also occurred on a smaller geographical scale. These results did not indicate any significant correlation between genetic differentiation and geographical distance within these populations (Donglingshan: r = 0.246; P = 0.186; Heyeping: r = 0.0852; P = 0.38).
Figure 1. The correlation between pairwise Fst and pairwise geographic distance among populations of Rhodiola dumulosa.
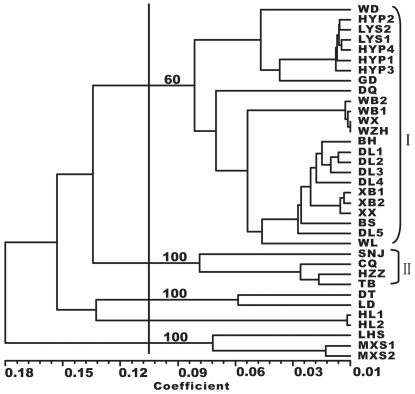
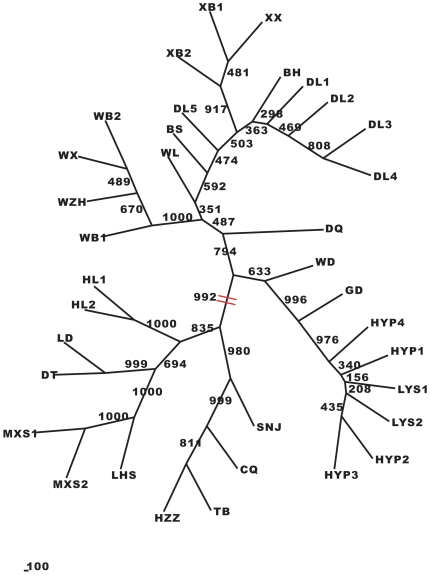
Hierarchical cluster analysis (UPGMA) showed that populations sampled from northern China and central China were grouped separately according to their geographical distribution (Fig. 2). Cluster I, with a bootstrap value of 60%, contained all populations in northern China, including 6 populations in Beijing, 5 populations in Hebei province, 12 populations in Shanxi province and 1 population in the Inner Mongolia autonomous region. Cluster II, with a bootstrap value of 100%, contained all populations in central China, including 1 population in Hubei province and 3 populations in Shaanxi province. The remaining northwestern populations could not be grouped in a single cluster, but the most closely related populations were geographically restricted and occurred in close proximity to each other. The NJ dendrogram revealed an obvious split between the populations in northern China and the other populations, with a bootstrap value of 99.2% (Fig. 3).
Figure 2. UPGMA tree of 35 Rhodiola dumulosa populations (numbers indicate bootstrap support values).
Figure 3. NJ tree of 35 Rhodiola dumulosa populations (numbers indicate bootstrap support values).
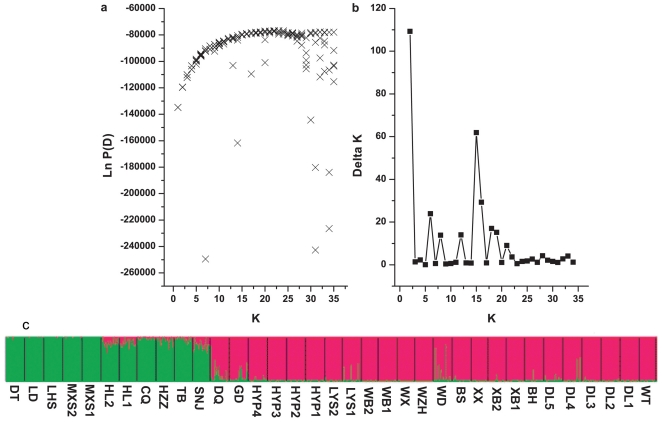
To further test this population structure, a model-based clustering method was implemented in the program STRUCTURE [18]–[20]. Without prior information about the populations and under an admixed model, STRUCTURE calculated that the estimate of the likelihood of the data (LnP(D)) was greatest when K = 2. For K>2, LnP(D) increased slightly but more or less plateaued (Fig. 4a), i.e., ΔK reached its maximum at K = 2 (Fig. 4b), suggesting that all populations fell into one of the two clusters. These two genetically distinct clusters primarily correspond to the geographic distribution of these populations (Fig. 5), and the percent representation of each cluster in each sampled population was high (Table S1). The red cluster covered all populations in northern China, and the remaining populations were grouped in the green cluster(Fig. 4c). This result is identical to the splitting in the NJ tree. Furthermore, UPGMA Cluster I is identical to the red cluster, indicating that the grouping of northern populations is well supported. Overall, the cluster analysis strongly suggested that the 35 sampled populations can be divided into two clusters, one composed of populations in northern China (NC) and the other composed of populations in central and northwestern China (CNWC).
Figure 4. STRUCTURE analysis of Rhodiola dumulosa populations.
Based on AFLP data (a: the relationship between K and LnP(D); b: the relationship between K and ΔK; c: the grouping when K = 2).
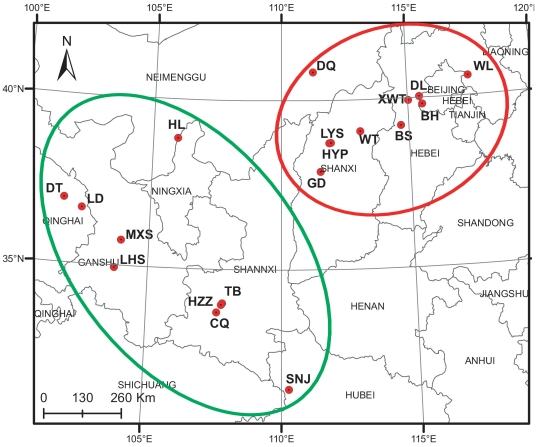
Figure 5. Distribution of the field sampling sites in China (the color of circles corresponds to two clusters resulted from STRUCTURE).
Analysis of Molecular Variance (AMOVA) based on the two genetic clusters indicated that majority of genetic variation (43.49%) occurred within populations, while the variation between the two clusters was 23.68% (Table 1). AMOVA based on three major distribution regions gave a very similar result (42.59% variation within populations, 29.39% variation among the three regions). Moreover, AMOVA that treated the central population as one group calculated much higher genetic variation within populations (65.44%) than that among populations (34.56%), which may partly explain why the northern populations always clustered together as a group. The central populations also exhibited a higher genetic variation within populations (58.87% variation within the population and 41.13% variation among the three regions), while the northwestern populations had a slightly higher variation among populations than within populations (52.41% and 47.59%, respectively). When the central and northwestern populations were pooled together, AMOVA calculated somewhat higher genetic variation among populations (56.90%). We also treated the 35 populations as one group and compared the variation within and among populations. The Fst value was 0.49922 (P<0.001) with 50.08% within populations and 49.92% among populations, indicating that the total genetic variation was almost equally divided between intrapopulation and interpopulation variations. This approximately equal partitioning could have been the result of significant differentiation among the populations in northwestern China and frequent gene flow among some populations in northern China; we sampled more closely distributed populations in northern China than in northwestern China. Therefore, we randomly chose one population from each locality (resulting in the exclusion of populations DL2, DL3, DL4, DL5, XB1, XX, WD, WB1, WB2, WX, LYS2, HYP2, HYP3, HYP4, HL2, and MXS2) and repeated the analyses (Table 1). After excluding these populations, the Fst became 0.54252 (P<0.001) with 54.25% of variation occurring among populations, only slightly higher than the variation within populations. Therefore, we conclude that the differentiation among groups was significant, but the genetic variation within populations was maintained.
Table 1. Results of AMOVA for R. dumulosa individuals based on 225 AFLP markers.
| Group | Partitioning | d.f. | Sum of squares | Variance components | Percentage of variation | F-statistics |
| two genetic clusters (NC & CNWC) | Among groups | 1 | 3686.335 | 7.15780 | 23.68 | Fct = 0.23679* |
| Among populations within groups | 33 | 10623.007 | 9.92465 | 32.83 | Fsc = 0.43019* | |
| Within populations | 1054 | 13855.386 | 13.14553 | 43.49 | Fst = 0.56512* | |
| Total | 1088 | 28164.728 | 30.22798 | |||
| three geographical regions (northern, central, northwestern) | Among groups | 2 | 5277.625 | 9.07061 | 29.39 | Fct = 0.29388* |
| Among populations within groups | 32 | 9031.718 | 8.64878 | 28.02 | Fsc = 0.39684* | |
| Within populations | 1054 | 13855.386 | 13.14553 | 42.59 | Fst = 0.57409* | |
| Total | 1088 | 28164.728 | 30.86492 | |||
| Northern populations | Among populations | 23 | 5408.968 | 7.13192 | 34.56 | Fst = 0.34560* |
| Within populations | 722 | 9750.255 | 13.50451 | 65.44 | ||
| Total | 745 | 15159.224 | 20.63643 | |||
| Central populations | Among populations | 3 | 643.064 | 6.66237 | 41.13 | Fst = 0.41129* |
| Within populations | 119 | 1134.839 | 9.53646 | 58.87 | ||
| Total | 122 | 1777.902 | 16.19883 | |||
| Northwestern populations | Among populations | 6 | 2979.686 | 15.35977 | 52.41 | Fst = 0.52414* |
| Within populations | 213 | 2970.292 | 13.94503 | 47.59 | ||
| Total | 219 | 5949.977 | 29.30480 | |||
| Central and Northwestern populations | Among populations | 10 | 5214.039 | 16.32634 | 56.90 | Fst = 0.56904* |
| Within populations | 332 | 4105.130 | 12.36485 | 43.10 | ||
| Total | 342 | 9319.169 | 28.69119 | |||
| 19 populations from each locality | Among populations | 18 | 8801.864 | 15.25624 | 54.25 | Fst = 0.54252* |
| Within populations | 574 | 7384.328 | 12.86468 | 45.75 | ||
| Total | 592 | 16186.192 | 28.12092 |
Population genetic diversity
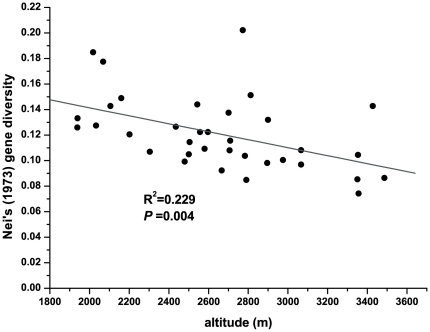
The genetic diversity of each population was calculated based on the genotypes present (Table S2). The expected heterozygosity (or Nei's gene diversity, Hj) varied from 0.09690 in population MXS1 to 0.22679 in population WD. Similar numbers were calculated for the Shannon diversity index, which varied from 0.1171 in population MXS1 to 0.3174 in population WD. The total diversity of the species (Ht) was 0.2473. When the populations were divided into two clusters based on the STRUCTURE analyses, the Nei's gene diversity index was lower in the northern region of China (0.1972) than in the central and northwestern areas (0.2216). There was a significant negative correlation between population genetic diversity and altitude (r = −0.478, P = 0.004) across the entire range of R. dumulosa. A regression analysis of Nei's genetic diversity and altitude using SPSS 15.0 revealed that population diversity decreases with increasing altitude (Fig. 6).
Figure 6. Scatter diagram of Nei's gene diversity and altitude.
Gene flow
The genetic differentiation among 35 populations of R. dumulosa was high and significant (Fst = 0.3942, P<0.001; Gst = 0.4675). The estimated gene flow, Nm (Nm = 0.5(1− Gst)/Gst), was 0.5695. The results of this analysis reveal that the genetic differentiation among populations throughout the entire distribution area is significant and that gene flow is restricted. Furthermore, the populations in northern China always congregated together as a cluster (UPGMA tree, NJ tree and STRUCTURE analysis results). The genetic differentiation, Gst, among all northern populations was 0.3155, and the Nm was 1.0847. Thus, the gene flow among populations in northern China was much higher than that across the entire range.
On some mountains, more than one population was sampled. For instance, there were five populations in Donglingshan and four populations in Heyeping (Table 2). To investigate the gene flow among populations in these smaller geographical regions, the Gst and Nm of Donglingshan (DL1, DL2, DL3, DL4, DL5) and Heyeping (HYP1, HYP2, HYP3, HYP4) populations were calculated. The Gst of the five populations in Donglingshan was 0.1125, and the Nm was 3.9438. Meanwhile, the Gst of the four populations in Heyeping was 0.0728, and the Nm was 6.6390. These results indicated weak genetic differentiation and frequent gene flow within these small geographical regions. Consequently, to avoid the over-estimation of gene flow caused by frequent gene flow among populations on one mountain, we calculated the Gst and Nm of 19 populations with 593 individuals from only one population from each locality (as we did for AMOVA). These results revealed that the gene flow in small regions had a clear influence (Gst19 = 0.5437, Nm19 = 0.4197) on the gene flow in the entire region (Gst = 0.4675, Nm = 0.5695).
Table 2. Localities and sizes of the 35 R. dumulosa populations sampled in this study.
| Sampling Locality | Population ID | Longitude (E) | Latitude (N) | Altitude (m) | Population size |
| Wulingshan, Hebei province | WL | 117.461° | 40.577° | 1939 | 29 |
| Donglingshan (1), Beijing | DL1 | 115.454° | 40.031° | 2303 | 32 |
| Donglingshan (2), Beijing | DL2 | 115.462° | 40.031° | 2202 | 32 |
| Donglingshan (3), Beijing | DL3 | 115.471° | 40.034° | 2106 | 32 |
| Donglingshan (4), Beijing | DL4 | 115.475° | 40.033° | 2018 | 31 |
| Donglingshan (5), Beijing | DL5 | 115.451° | 40.029° | 2160 | 32 |
| Baihuashan, Beijing | BH | 115.582° | 39.813° | 2033 | 32 |
| Xiaowutaishan (beitai 1), Hebei | XB1 | 115.061° | 39.945° | 2500 | 31 |
| Xiaowutaishan (beitai 2), Hebei | XB2 | 115.047° | 39.943° | 2706 | 30 |
| Xiaowutaishan (xitai), Hebei | XX | 114.968° | 39.912° | 2480 | 29 |
| Baishishan, Hebei | BS | 114.698° | 39.208° | 1940 | 32 |
| Wutaishan (dongtai), Shanxi | WD | 111.662° | 39.041° | 2773 | 32 |
| Wutaishan (zhongtai), Shanxi | WZH | 113.531° | 39.047° | 2895 | 30 |
| Wutaishan (xitai), Shanxi | WX | 113.492° | 39.037° | 2783 | 29 |
| Wutaishan (beitai 1), Shanxi | WB1 | 113.568° | 39.080° | 3066 | 32 |
| Wutaishan (beitai 2), Shanxi | WB2 | 113.568° | 39.080° | 3066 | 28 |
| Luyashan (1), Shanxi | LYS1 | 111.926° | 38.750° | 2701 | 32 |
| Luyashan (2), Shanxi | LYS2 | 111.926° | 38.744° | 2580 | 30 |
| Heyeping (1), Shanxi | HYP1 | 111.837° | 38.722° | 2709 | 32 |
| Heyeping (2), Shanxi | HYP2 | 111.862° | 38.729° | 2596 | 32 |
| Heyeping (3), Shanxi | HYP3 | 111.874° | 38.729° | 2504 | 32 |
| Heyeping (4), Shanxi | HYP4 | 111.885° | 38.730° | 2435 | 32 |
| Guandishan, Shanxi | GD | 111.518° | 37.895° | 2557 | 32 |
| Daqingshan, Inner Mongolia | DQ | 111.259° | 40.838° | 2068 | 31 |
| Shennongjia, Hubei | SNJ | 110.258° | 31.446° | 2974 | 30 |
| Taibaishan, Shaanxi | TB | 107.806° | 33.997° | 3486 | 30 |
| Houzhenzi, Shaanxi | HZZ | 107.767° | 33.950° | 3350 | 31 |
| Changqing, Shaanxi | CQ | 107.600° | 33.717° | 2790 | 32 |
| Helanshan (west), Ningxia | HL1 | 105.944° | 38.838° | 3428 | 30 |
| Helanshan (north), Ningxia | HL2 | 105.944° | 38.846° | 2900 | 30 |
| Maxianshan (west), Gansu | MXS1 | 103.950° | 35.750° | 3356 | 32 |
| Maxianshan (east), Gansu | MXS2 | 103.950° | 35.750° | 3353 | 32 |
| Lianhuashan, Gansu | LHS | 103.750° | 34.933° | 2812 | 32 |
| Ledu, Qinghai | LD | 102.389° | 36.655° | 2543 | 32 |
| Datong, Qinghai | DT | 101.691° | 36.930° | 2666 | 32 |
Discussion
Population diversity and its relationship to geographical distance and altitude
Our analysis of AFLP molecular markers indicated that R. dumulosa has maintained a high overall genetic diversity (Ht = 0.2473), similar to that of the two other species of Rhodiola but much higher than that of other perennial plants (Table 3). Thus, the expectation that genetic variability would decline due to population fragmentation was not supported in this case. This result might be observed because R. dumulosa still occurs in medium or large population sizes (40 to over 150 individuals) in some localities. Moreover, the gene flow among populations on the same mountain was high (Gst and Nm for Donglingshan and Heyeping populations). Another explanation could be that this high genetic diversity is a reflection of high historic genetic variability, which is quite common in long-lived perennial plant species [21]–[22].
Table 3. Comparison of genetic diversity of R. dumulosa with values from other Rhodiola species and selected other plant species.
| Species | Genetic diversity | Marker | References conclusion |
| Rhodiola species | |||
| Rhodiola dumulosa | PPL = 98.22% | AFLP | Present study |
| Ht = 0.2473 | |||
| I = 0.3625 | |||
| Rhodiola rosea | PPL = 95.3% | AFLP | high total genetic diversity [53] |
| Ht = 0.266 | |||
| I = 0.420 | |||
| Rhodiola fastigiata | PPL = 96.61% | AFLP | high total genetic diversity [54] |
| Ht = 0.3329 | |||
| I = 0.4893 | |||
| Other plants | |||
| Incarvillea younghusbandii | Ht = 0.063 | AFLP | low genetic diversity [55] |
| I = 0.096 | |||
| Cedrela odorata | PPL = 98.8% | AFLP | high total genetic diversity [56] |
| Ht = 0.22 |
Analyses of the correlation between population genetic diversity and geographic altitude showed a weak but significant negative correlation. The lower genetic diversity of populations at higher altitudes might be the result of the smaller populations of pollinators in these areas; R. dumulosa is thought to breed by facultative xenogamy, which requires pollinators for outbreeding [16]. However, pollination biology studies of R. dumulosa concluded that populations in open fields, such as those near peaks, received more frequent pollinator visits than those at lower altitudes [17]. Therefore, we suggest that past climatic oscillations, which may have caused the local extinction and recolonization of populations at high altitudes, could have driven this pattern. The impacts of past climatic oscillations on species ranges and genetic structure have been addressed in several previous phylogeographic studies [23]–[25]. Here, we hypothesize that the extremely low temperatures experienced during glaciation resulted in the extirpation of R. dumulosa populations in high-altitude montane regions, whereas the populations in lower altitude areas with more favorable climate conditions survived. During interglacial periods, some offspring of the surviving low altitude populations recolonized the higher altitude. Thus, populations in higher altitude sites, derived from only a few individuals from lower altitude populations, would exhibit less genetic variation. Greater genetic diversity at in situ survival areas than at recolonized areas was also found in a number of phylogeographic studies, especially in the Alps [26]–[28]. For example, the genetic variation of a widespread alpine herb, Biscutella laevigata (Brassicaceae), reflected the influence of past climate changes on the species range as a gradient of genetic diversity along recolonization pathways [27], [29]. The study of these populations also revealed that the peripheral Alps are occupied by populations with significant haplotypic variation, whereas recently glaciated areas at high altitudes in the central Alps typically contain expanding populations with a single, fixed haplotype [29]. A third potential reason for the correlation between higher altitude and lower genetic diversity pattern is simply related to population size. It is widely accepted that genetic drift can have significant effects on small populations [30]. However, we did not observe an obvious gradient of population size according to altitude, and in some sampling areas, the populations on mountain peaks are larger because the mountain has a flat top (e.g., Wutaishan).
Population structure and gene flow among naturally isolated populations
A strong correlation between genetic and geographical distances (Mantel test: r = 0.801; P<0.01) revealed a pattern of isolation-by-distance across the distribution range of R. dumulosa in China. This pattern suggested that the dispersal of this species might be constrained by distance such that gene flow is most likely to occur between neighboring populations [31]–[32]. As a result, more closely situated populations tend to be more genetically similar to one another [33]. The population genetic structure analyses (UPGMA tree, NJ tree and STRUCTURE) showed that populations tend to cluster in the same group when they are geographically restricted and occur in close proximity to one another. The congruence between the geographical distribution of populations and their genetic relationships is generally interpreted as sign of a longstanding pattern of highly restricted gene flow [34]. Our AFLP analysis revealed significant genetic differentiation and restricted gene flow among all sampled populations throughout the distribution range, which is naturally fragmented (Gst = 0.4675, Nm = 0.5695). This finding may be the result of the “ecological island” distribution pattern of R. dumulosa across its range in China. However, we also found that the gene flow among populations on the same mountain is relatively unrestricted, and the genetic differentiation among these populations is weak. For example, the Gst and Nm of the five populations in Donglingshan were 0.1125 and 3.9438, respectively, while the Gst and Nm of the four populations in Heyeping were 0.0728 and 6.6390. Furthermore, Mantel tests conducted on these two groups of populations revealed no significant correlations between genetic and geographical distances. Thus, our AFLP data suggest that although an isolation-by-distance pattern may be detected across the whole range of R. dumulosa, the gene flow and the relationship between geographical and genetic distances have different patterns at different spatial scales. Similarly distinct patterns at different spatial scales were also found for some other plant species [35].
The results of our hierarchical and model-based cluster analyses of AFLP data strongly suggested that the 35 sampled populations of R. dumulosa could be split into two clusters, one in northern China (NC) and the other in central and northwestern China (CNWC). In particular, the populations collected from northern China always clustered together regardless of the approach used for genetic structure analysis. AMOVA within the northern populations also clearly indicated that the genetic variation within populations was higher than that among populations (65.44% and 34.56%, respectively). Thus, we treated the northern populations as a reasonable cluster. However, when the populations from central and northwestern China were pooled together, AMOVA indicated that there was greater genetic variation among populations than within populations (56.90% and 43.10%), and the variation between NC and CNWC clusters was only 23.68%. Thus, the central and northwestern populations may not form a good cluster. More data may help resolve the genetic relationship between populations in these two areas. Moreover, when AMOVA was conducted based on different grouping approaches, we always found high genetic variation within populations (at least above 40%, Table 1). This finding could be due to some gene flow among populations, especially at small distribution scales, as discussed above. Alternatively, this result could reflect the preservation of ancient genetic diversity within populations as we also found significant genetic differentiation among populations or groups (Table 1). However, additional data, such as detailed gene sequence data, will be required to further dissect the evolutionary history of R. dumulosa.
In conclusion, the total genetic diversity of R. dumulosa was high, and population diversity decreased with increasing altitude. The geographical distribution of populations and their genetic relationships were consistent and most likely due to the natural geographic fragmentation of this species. A significant isolation-by-distance pattern was found across the entire distribution range in China, and significant genetic differentiation and restricted gene flow were observed among populations. However, restricted gene flow and a correlation between genetic and geographical distance were not appreciated at smaller spatial scales.
Materials and Methods
Population sampling and DNA extraction
Thirty-five populations of R. dumulosa, including 1089 individuals (28–32 individuals per population), were sampled from 19 localities across the entire distribution of this species in 2005, 2006 and 2007. The sampling area ranged from the northernmost population “DQ” in the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region (40.838°N) to the southernmost population “SNJ” in Hubei province (31.446°N) and from the easternmost population “WL” in Hebei province (117.461°E) to the westernmost population “DT” in Qinghai province (101.691°E) (Fig. 5, Table 2). All sampled individuals were separated by at least five meters.
Leaf material was stored in zip-lock plastic bags with silica gel until DNA extraction. Sample vouchers were deposited in the collection at Beijing Normal University. Genomic DNA was extracted from silica gel-dried leaf material using a plant DNA extraction kit (Tiangen, Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer's protocol, with some modifications.
AFLP fingerprinting
AFLP fingerprinting was performed according to the original protocol presented by Vos et al. [36], with minor modifications. Four pairs of primers (combinations of FAM-labeled EcoRI-ATG, MseI-CTG, MseI-CAA, MseI-CAC and MseI-CAG) were used for selective amplification. Selective amplification products were separated using an ABI 3100 sequencer (Applied Biosystems) with a GeneScan ROX 500 internal size standard. Electropherograms were then analyzed using GENEMAPPER 3.7 software (Applied Biosystems). To create a binary matrix, amplified fragments of 80–500 base pairs were scored visually as having present (1), absent (0), or ambiguous (?) peaks in the output traces. Only distinct peaks were scored as present, and the manual scoring procedure was repeated twice on separate occasions to reduce scoring errors.
Genetic data analysis
The unweighted pair group method with averages (UPGMA) clustering analysis, derived from the Nei's minimum distance matrix [37], [38] as calculated in TFPGA v1.3 [39], was conducted using the SAHN module in NTSYS v2.10 [40]. One thousand bootstrapped replicate matrices of pairwise Fst among populations were calculated in AFLP-SURV. The results were used as inputs for computing Neighbor-Joining (NJ) dendrograms, using the NEIGHBOR module in the PHYLIP v3.68 [41] software package. An extended majority-rule consensus tree was produced using CONSENSE, a module for STRUCTURE v2.2 [20], adapted for dominant markers and used to assign an individual's probability of belonging to a homogeneous cluster (K populations) without prior population information. The correlated allele frequencies and admixed model were applied with a burn-in period of 100,000 and 1,000,000 MCMC replicates after burn-in. The range of clusters (K) was predefined from 1 to 35. From K = 1 to K = 10, ten runs were performed, whereas for K>10, five runs were performed. The Pr (X|K) (or “LnP(D)”) can be used as an indication of the most likely number of groups, and it usually plateaus or increases slightly after the “right K” is reached [42]. Therefore, the height of the modal value of the ΔK distribution was calculated to detect the true K [42] using Structure 2(1).2-sum [18]. The similarity coefficient of pair-wise runs for each value of K was also calculated in Structure 2(1).2-sum to control the stability of the results [43]. Permutations of the most likely results among different runs for each K were conducted in CLUMPP [44]. DISTRUCT [45] was used to visualize the STRUCTURE results. The partitioning of variation at different levels was calculated by Analysis of Molecular Variance (AMOVA) in ARLEQUIN v3.01 [46] using 1,000 permutations. The 35 populations were then grouped according to the clusters indicated by the UPGMA tree, NJ dendrograms and STRUCTURE analysis results, respectively. The correlation between the genetic (Fst) and geographic population pairwise distance matrices was evaluated using a Mantel test with 9999 permutations in ARLEQUIN v3.01, and the scatter plot was constructed in SPSS v15.0. The correlation between Nei's genetic diversity and altitude was calculated using SPSS v15.0. Genetic diversity and differentiation statistics were calculated using AFLP-SURV v1.0 [47], [48]. This program estimates allele frequencies at each marker locus in each population, assuming that the markers are dominant and that there are two alleles per locus (the presence of a band is considered dominant and its absence is considered recessive). A Bayesian method with a non-uniform prior distribution of allele frequencies [49] was used to estimate the allelic frequencies, which assumed Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. These allele frequencies were then used to analyze the genetic diversity within and between samples according to the method described by Lynch and Milligan [50]. The proportions of polymorphic loci at the 5% level (PPL), as well as the expected heterozygosity (or Nei's gene diversity, Hj), standard errors (S.E.(Hj)) and total variance (Var(Hj)) were computed for each population. Wright's fixation index, Fst [51], was computed using the Lynch and Milligan [50] method and tested with a permutation procedure of 1000 replicates. POPGENE v1.32 [52] was also used to conduct descriptive analysis for AFLP markers. Nei's gene diversity (H, analogous to Hj), the Shannon diversity index, population differentiation (Gst) and the estimate of gene flow, Nm (Nm = 0.5(1 – Gst)/Gst) were also calculated.
Supporting Information
Membership of each pre-defined population in each of the two clusters generated by CLUMPP based on the STRUCTURE v2.2 analysis (K = 2).
(DOC)
Population genetic diversity of R. dumulosa. (n: population size; PPL: proportion of polymorphic loci at the 5% level; Hj: expected heterozygosity or Nei's gene diversity; S.E.: standard error; Var: variance; H: Nei's gene diversity; I: Shannon diversity index; NC: northern China; CNWC: central and northwestern China).
(DOC)
Acknowledgments
We thank Yong Mu, Lin Zhu, Hao-Bin Zhang and associate professor Quan-Ru Liu of Beijing Normal University for assistance with field surveys and sample collections. We are also grateful to professor Da-Yong Zhang, Yan-Ping Guo and Guang-Yuan Rao for their helpful suggestions and discussions as well as Dr. Yan-Fei Zeng, Dr. Yuan-Ye Zhang, Dr. Wan-Jin Liao and Dr. Chuan Ni for their guidance and suggestions throughout the analysis process.
Footnotes
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Funding: This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30770356). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Young A, Boyle T, Brown T. The population genetic consequences of habitat fragmentation for plants. Tree. 1996;11:413–418. doi: 10.1016/0169-5347(96)10045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cardoso SRS, Provan J, Lira CDF, Pereira LDOR, Ferreira PCG, et al. High levels of genetic structuring as a result of population fragmentation in the tropical tree species Caesalpinia echinata Lam. Biodiversity and Conservation. 2005;14:1047–1057. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Prentice HC, Lönn M, Rosquist G, Ihse M, Kindströn M. Gene diversity in a fragmented population of Briza media: grassland continuity in a landscape context. Journal of Ecology. 2006;94:87–97. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yao XH, Ye QG, Kang M, Huang HW. Microsatellite analysis reveals interpopulation differentiation and gene flow in the endangered tree Changiostyrax dolichocarpa (Styracaceae) with fragmented distribution in central China. New Phytologist. 2007;176:472–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Aguilar R, Quesada M, Ashworth L, Herreriasdiego Y, Lobo J. Genetic consequences of habitat fragmentation in plant populations: susceptible signals in plant traits and methodological approaches. Molecular Ecology. 2008;17:5177–5188. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chen KX, Wang R, Chen XY. Genetic structure of Alpinia japonica populations in naturally fragmented habitats. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 2008;28(6):2480–2485. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Balal SR, Fore SA, Guttman SI. Apparent gene flow and genetic structure of Acer saccharum subpopulations in forest fragments. Canadian Journal of Botany. 1994;72(9):1311–1315. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Prober SM, Tompkins C, Moran CG, Bell JC. The conservation genetics of Eucalyptus paliformis L. Johnson et Blaxell and E. parviflora Cambage, two rare species from south-eastern Australia. Australian Journal of Botany. 1990;38(1):79–95. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Young AG, Merriam HG, Warwick SI. The effects of forest fragmentation on genetic variation in Acer saccharum Marsh. (sugar maple) population. Heredity. 1993;71:277–289. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chen XY. Effects of fragmentation on genetic structure of plant populations and implications for the biodiversity conservation. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 2000;20(5):884–892. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kuss P, Pluess AR, Ægisdóttir HH, Stöcklin J. Expand+Spatial isolation and genetic differentiation in naturally fragmented plant populations of the Swiss Alps. Journal of Plant Ecology. 2008;1(3):149–159. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Medrano M, Herrera CM. Geographical structuring of genetic diversity across the whole distribution range of Narcissus longispathus, a habitat-specialist, Mediterranean narrow endemic. Annals of Botany. 2008;102(2):183–194. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcn086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bossuyt B. Genetic rescue in an isolated metapopulation of a naturally fragmented plant species, Parnassia palustris. Conservation Biology, 2007;21:832–841. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1739.2006.00645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wesche K, Hensen I, Undrakh R. Range-wide genetic analysis provides evidence of natural isolation among populations of the Mongolian endemic Potentilla ikonnikovii Juz. (Rosaceae). Plant Species Biology. 2006;21:155–163. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Uhl CH. Heteroploidy in Sedum rosea (L.) Scop. Evolution. 1952;6:81–86. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Mu Y, Zhang YH, Lou AR. A preliminary study on floral syndrome and breeding system of the rare plant Rhodiola dumulosa. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 2007;31(3):528–535. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhu L, Lou AR. Mating system and pollination biology of a high-mountain perennial plant, Rhodiola dumulosa (Crassulaceae). Journal of Plant Ecology. 2010;3(3):219–227. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics. 2000;155:945–959. doi: 10.1093/genetics/155.2.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics. 2003;164:1567–1587. doi: 10.1093/genetics/164.4.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK. Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: dominant markers and null alleles. Molecular Ecology Notes. 2007;7:574–578. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-8286.2007.01758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Geert A, Rossum F, Triest L. Genetic diversity in adult and seedling populations of Primula vulgaris in a fragmented agricultural landscape. Conservation Genetics. 2008;9:845–853. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Honnay O, Jacquemyn H, Bossuyt B, Hermy M. Forest fragmentation effects on patch occupancy and population viability of herbaceous plant species. New Phytologist. 2005;166:723–736. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Beatty GE, Provan J. Comparative phylogeography of two related plant species with overlapping ranges in Europe, and the potential effects of climate change on their intraspecific genetic diversity. BMC Evolutionary Biology. 2011;11:29. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dubreuil M, Riba M, Mayol M. Genetic structure and diversity in Ramonda myconi (Gesneriaceae): effects of historical climate change on a preglacial relict species. American Journal of Botany. 2008;95:577–587. doi: 10.3732/ajb.2007320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Beck JB, Schmuths H, Schaal BA. Native range genetic variation in Arabidopsis thaliana is strongly geographically structured and reflects Pleistocene glacial dynamics. Molecular Ecology. 2008;17(3):902–915. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2007.03615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Parisod C. Postglacial recolonisation of plants in the western Alps of Switzerland. Botanica Helvetica. 2008;118:1–12. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Parisod C, Besnard G. Glacial in situ survival in the Western Alps and polytopic autopolyploidy in Biscutella laevigata L. (Brassicaceae). Molecular Ecology. 2007;16:2755–2767. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2007.03315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schönswetter P, Stehlik I, Holderegger R, Tribsch A. Molecular evidence for glacial refugia of mountain plants in the European Alps. Molecular Ecology. 2005;14:3547–3555. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Parisod C, Joost S. Divergent selection in trailing- versus leading-edge populations of Biscutella laevigata. Annals of Botany. 2010;105:655–660. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcq014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nei M, Maruyama T, Chakraborty R. The bottleneck effect and genetic variability in populations. Evolution. 1975;29:1–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1975.tb00807.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hutchison DW, Templeton AR. Correlation of pairwise genetic and geographic distance measures: inferring the relative influences of gene flow and drift on the distribution of genetic variability. Evolution. 1999;53:1898–1914. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1999.tb04571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Slatkin M. Isolation by distance in equilibrium and non-equilibrium populations. Evolution. 1993;47:264–279. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.1993.tb01215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wright S. Isolation by distance. Genetics. 1943;28:114–138. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.2.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schaal BA, Hayworth DA, Olsen KM, Rauscher JT, Smith WA. Phylogeographic studies in plants: problems and prospects. Molecular Ecology. 1998;7:465–474. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Medrano M, Herrera CM. Geographical structuring of genetic diversity across the whole distribution range of Narcissus longispathus, a habitat-specialist, Mediterranean narrow endemic. Annals of Botany. 2008;102:183–194. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcn086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, Lee T, et al. AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995;23(21):4407–7714. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.21.4407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nei M. Genetic distance between populations. Am Nat. 1972;106(949):283–292. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Nei M. Estimation of average heterozygosity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics. 1978;89:583–590. doi: 10.1093/genetics/89.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Miller MP. Tools for Population Genetic Analysis (TFPGA), version 1.3. Department of Biological Sciences, Northern Arizona University, Flagstaff, AZ, USA. 1997;16 Available: http://www.marksgeneticsoftware.net/tfpga.htm. Accessed 2011 Aug. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rohlf FJ. Exeter Publishing, Ltd, Setauket, NY; 2000. NTSYS-pc Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Felsenstein J. PHYLIP: Phylogeny inference package, version 3.68, August 2008. Seattle, WA: University of Washington. 2008;16 Available: http://evolution.gs.washington.edu/phylip.html. Accessed 2011 Aug. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J. Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol. 2005;14:2611–2620. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Nordborg M, Hu TT, Ishino Y, Jhaveri J, Toomajian C, et al. The pattern of polymorphism in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Biol. 2005;3:196. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Jakobsson M, Rosenberg NA. CLUMPP: a cluster matching and permutation program for dealing with label switching and multimodality in analysis of population structure. Bioinformatics. 2007;23:1801–1806. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rosenberg NA. DISTRUCT: a program for the graphical display of population structure. Mol Ecol Notes. 2004;4:137–138. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S. ARLEQUIN version 3.0: an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinform Online. 2005;1:47–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Vekemans X. AFLP-SURV version 1.0. Distributed by the author. Laboratoire de Génétique et Ecologie Végétale, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium. 2002;16 Available: http://www.ulb.be/sciences/lagev/aflp-surv.html. Accessed 2011 Aug. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Vekemans X, Beauwens T, Lemaire M, Roldan-Ruiz I. Data from amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) markers show indication of size homoplasy and of a relationship between degree of homoplasy and fragment size. Mol Ecol. 2002;11:139–151. doi: 10.1046/j.0962-1083.2001.01415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhivotovsky LA. Estimating population structure in diploids with multilocus dominant DNA markers. Mol Ecol. 1999;8:907–913. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294x.1999.00620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lynch M, Milligan BG. Analysis of population genetic structure with RAPD markers. Mol Ecol. 1994;3:91–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294x.1994.tb00109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Hartl DL, Clark AG. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates; 1997. Principles of population genetics, 3rd edition. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Yeh FC, Yang RC, Boyle T. POPGENE version 1.31, the user-friendly shareware for population genetic analysis. Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Center, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada. 1997;16 Available: http://www.ualberta.ca/~fyeh/index.htm. Accessed 2011 Aug. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Meng QW. Intra-species Genetic Diversity Analysis of Rhodiola Rosea L. Based on Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (AFLP) Marker, Xinjiang Agricultural University, China. 2007;16 Available: http://www.lunwentianxia.com/product.sf.3204045.1/. Accessed 2011 Aug. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Lv YL. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Rhodiola fastigiata in Tibet Based on Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism (AFLP) Marker, Tibet University, China. 2009;16 Available: http://so.med.wanfangdata.com.cn/ViewHTML/DegreePaper_D061963.aspx. Accessed 2011 Aug. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zhu Y, Geng Y, Tersing T, Liu N, Wang Q, et al. High genetic differentiation and low genetic diversity in Incarvillea younghusbandii, an endemic plant of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, revealed by AFLP markers. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology. 2009;37(5):589–596. [Google Scholar]
- 56.de la Torre A, Lopez C, Yglesias E, Cornelius JP. Genetic (AFLP) diversity of nine Cedrela odorata populations in Madre de Dios, southern Peruvian Amazon. Forest Ecology and Management. 2008;255(2):334–339. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Membership of each pre-defined population in each of the two clusters generated by CLUMPP based on the STRUCTURE v2.2 analysis (K = 2).
(DOC)
Population genetic diversity of R. dumulosa. (n: population size; PPL: proportion of polymorphic loci at the 5% level; Hj: expected heterozygosity or Nei's gene diversity; S.E.: standard error; Var: variance; H: Nei's gene diversity; I: Shannon diversity index; NC: northern China; CNWC: central and northwestern China).
(DOC)