Abstract
Antibiotics targeting the bacterial ribosome typically bind to highly conserved rRNA regions with only minor phylogenetic sequence variations. It is unclear whether these sequence variations affect antibiotic susceptibility or resistance development. To address this question, we have investigated the drug binding pockets of aminoglycosides and macrolides/ketolides. The binding site of aminoglycosides is located within helix 44 of the 16S rRNA (A site); macrolides/ketolides bind to domain V of the 23S rRNA (peptidyltransferase center). We have used mutagenesis of rRNA sequences in Mycobacterium smegmatis ribosomes to reconstruct the different bacterial drug binding sites and to study the effects of rRNA sequence variations on drug activity. Our results provide a rationale for differences in species-specific drug susceptibility patterns and species-specific resistance phenotypes associated with mutational alterations in the drug binding pocket.
INTRODUCTION
The bacterial ribosome is a target for many antibacterial agents that interfere with protein synthesis, such as aminoglycosides, macrolides, ketolides, oxazolidinones, and lincosamides (23). These compounds target different steps in translation, including decoding, peptide bond formation, and translocation (33, 37, 40). While different classes of antibiotics bind to different ribosomal regions and interfere with different steps in translation, they all interact directly with rRNA nucleotides at or near functionally important sites (38, 39). These rRNA residues typically show high phylogenetic sequence conservation within bacteria. It is largely unclear whether the minor sequence variations present in the bacterial drug binding sites affect antibiotic susceptibility and/or resistance development.
Structures of antibiotics bound to the ribosome have been resolved primarily with extremophiles such as Thermus thermophilus, Deinococcus radiodurans, or Haloarcula morismortui (2, 9, 30). Most genetic data, however, have been generated with Escherichia coli and Mycobacterium smegmatis (4–6, 10, 14, 15, 20–22, 26, 28, 29, 32). It has still to be established whether the conclusions drawn from diverse model organisms hold true for other bacterial clades as well. To address this question, we investigated rRNA alterations corresponding to phylogenetic sequence variations that are found in bacteria and which are located in two major drug binding sites, the 23S rRNA peptidyltransferase region and the 16S rRNA-decoding region. These two regions are targeted by different classes of antibiotic compounds: macrolides/ketolides (23S rRNA) and aminoglycosides (16S rRNA) (23, 37).
Macrolide/ketolide antibiotics are a diverse class of naturally occurring and synthetic compounds based on a polyketide macrolactone ring substituted with one or more nonnitrogenous and/or amino sugar moieties (27). These compounds exert their inhibitory effect on protein synthesis by binding to the opening of the ribosomal polypeptide exit tunnel to obstruct elongation of the nascent polypeptide chain (30, 34). Aminoglycosides form a large family of water-soluble, polycationic amino sugars (18). Common to all aminoglycosides is the neamine core. Additional sugars are attached to give rise to a variety of compounds categorized as 4,5- or 4,6-aminoglycosides. An important substituent in aminoglycoside specificity is the chemical group at position 6′ of ring I, i.e., 6′-NH2 or 6′-OH (36). Aminoglycosides target the ribosome by direct interaction with rRNA, and they affect protein synthesis by inducing codon misreading and by inhibiting translocation of the tRNA-mRNA complex (2, 3).
We here used previously described procedures for rRNA mutagenesis in M. smegmatis (15) to reconstruct the different bacterial sequence variants as found in the drug binding pockets of both macrolides/ketolides and aminoglycosides. The resulting recombinants were then investigated for drug susceptibility.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains and DNA techniques.
Mycobacterium smegmatis rRNA mutants were generated by the following procedures. (i) rRNA gene fragments coding for mutant rRNA were generated by PCR mutagenesis and cloned into an integration-proficient plasmid. RecA-mediated homologous recombination and selective plating were used to introduce point mutations into the single functional rRNA gene operon of M. smegmatis ΔrrnB (20). DNA sequencing was used to confirm that the point mutation had been introduced and that additional mutations in the area involved in homologous recombination were absent. (ii) Plasmid exchange mutagenesis was done as described previously (13). In brief, DNA sequences coding for mutant rRNA were generated by PCR mutagenesis and cloned into an integration-proficient plasmid with a fully functional rRNA operon. These plasmids with mutant rRNA genes were then used to replace the single rRNA operon present in M. smegmatis Δrrn/pMIG-rrnB+-sacB by plasmid exchange. Successful gene exchange was controlled by DNA sequence analysis.
For a complete list of strains and plasmids, see Table 1 and Table S1 in the supplemental material, respectively.
Table 1.
Strains used in this study
| M. smegmatis strain(s) | Description | Parental strain | attB | rRNA mutation(s)f |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16S | 23S | ||||
| SZ379 | mc2155 | None | wt | wt | |
| SZ001d | mc2155 | SZ379 | None | wt | wt |
| SZ380e | ΔrrnB rrnA+ | SZ379 | None | wt | wt |
| SZ386d,e | ΔrrnA rrnB | SZ001 | None | wt | wt |
| SZ637e | ΔrrnA ΔrrnB attB: rrnB | SZ379 | pH 144 | wt | wt |
| SZ558d | ΔrrnA ΔrrnB attB: rrnB | SZ386 | pH 144 | wt | wt |
| SZ459-SZ461a,e | ΔrrnB rrnA (A1408G) | SZ380 | pH 128 | A1408G | wt |
| SZ463-SZ465a,e | ΔrrnB rrnA (G1491A) | SZ380 | PZ176 | G1491A | wt |
| SZ468-SZ470a,e | ΔrrnB rrnA (G1491C) | SZ380 | PZ178 | G1491C | wt |
| SZ505-SZ507a,e | ΔrrnB rrnA (G1491U) | SZ380 | PZ177 | G1491U | wt |
| SZ605c,e | ΔrrnB rrnA (C1409G · G1491C) | SZ469 | PZ178 | C1409G, G1491C | wt |
| SZ717-SZ720b,e | ΔrrnA ΔrrnB attB: rrnB (C1409U · G1491A) | SZ637 | pH 297 | C1409U, G1491A | wt |
| SZ721-SZ724b | ΔrrnA ΔrrnB attB: rrnB (Eco4) | SZ637 | pH 163 | G1410A, U1411C, A1489G, C1490U | wt |
| SZ725-SZ728b | ΔrrnA ΔrrnB attB: rrnB (Eco4 A1408G) | SZ637 | pH 205 | A1408G, G1410A, U1411C, A1489G, C1490U | wt |
| SZ706-SZ709b | ΔrrnA ΔrrnB attB: rrnB (Eco4 G1491A) | SZ637 | pH 294 | G1410A, U1411C, A1489G, C1490U, G1491A | wt |
| SZ710-SZ713b | ΔrrnA ΔrrnB attB: rrnB (Eco4 G1491C) | SZ637 | pH 295 | G1410A, U1411C, A1489G, C1490U, G1491C | wt |
| SZ714-SZ716b | ΔrrnA ΔrrnB attB: rrnB (Eco4 G1491U) | SZ637 | pH 296 | G1410A, U1411C, A1489G, C1490U, G1491U | wt |
| SZ763-SZ766b,e | ΔrrnA ΔrrnB attB: rrnB (Pac2) | SZ637 | pH 154 | C1409A, G1491U | wt |
| SZ832-SZ835b | ΔrrnA ΔrrnB attB: rrnB (Pac2 A1408G) | SZ637 | pH 349 | A1408G, C1409A, G1491U | wt |
| SZ678-SZ680b,d | ΔrrnA ΔrrnB attB: rrnB | SZ558 | pH 203 | wt | wt |
| SZ674-SZ677b,d | ΔrrnA ΔrrnB attB: rrnB (A2058G) | SZ558 | pH 191 | wt | A2058G |
| SZ681-SZ684b,d | ΔrrnA ΔrrnB attB: rrnB (A2057G · U2611C) | SZ558 | pH 219 | wt | A2057G, U2611C |
| SZ685-SZ687b,d | ΔrrnA ΔrrnB attB: rrnB (A2058G A2057G · U2611C) | SZ558 | pH 221 | wt | A2058G, A2057G, U2611C |
Mutagenesis by RecA-mediated gene conversion.
Mutagenesis by replacing the wild-type rrnB+ plasmid with a mutant rrnB plasmid.
Spontaneous C1409G mutation in an G1491C genetic background.
These strains were generated in a rpsL K43R background (K43 in M. smegmatis is homologous to K42 in E. coli [28]).
These strains have been described previously (31).
wt, wild type.
Susceptibility testing.
Drug susceptibility was assessed by determination of MICs. MICs were determined by broth microdilution assays as described previously (19). In brief, bacterial strains were cultured on Luria-Bertani (LB) agar plates at 37°C. Freshly grown cultures were resuspended in LB broth supplemented with 0.05% Tween 80, diluted to an absorbance at 600 nm of 0.025, and incubated in the presence of 2-fold serial dilutions of antibiotics (Sigma). After incubation at 37°C for 72 h, the MIC was recorded as the lowest concentration of drug inhibiting visible growth. Three to five independent clones were analyzed per mutation. Linezolid was included as unrelated ribosomal inhibitor representative of a different compound class to control for the class specificity of the effects.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Phylogenetic sequence variations in the 23S rRNA peptidyltransferase region.
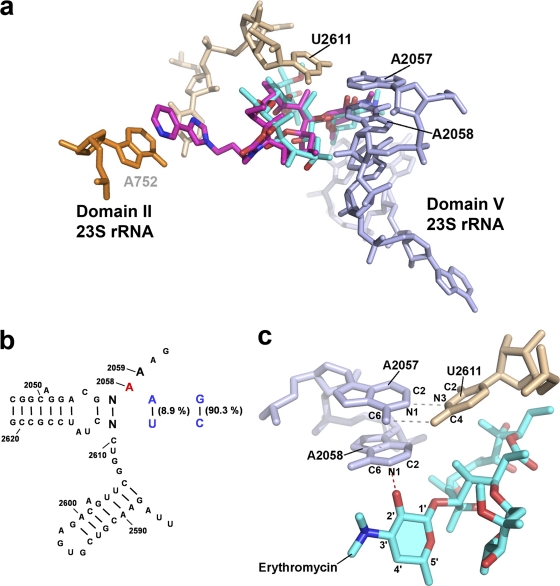
Most rRNA nucleotides in the inner peptidyltransferase region of the large ribosomal subunit are phylogenetically conserved (8). The macrolide/ketolide family of antibiotics binds to a hydrophobic cleft formed by residues 2058, 2059, and 2611 (E. coli numbering is used throughout) in domain V of 23S rRNA, with some drugs making additional contacts in domain II (9, 10, 30) (Fig. 1). The adenines at 23S rRNA positions 2058 and 2059 are phylogenetically conserved in bacteria and play an important role in compound binding, emergence of resistance, and drug selectivity (1, 22).
Fig. 1.
(a) Structures of erythromycin (blue) (PDB accession code 3OHJ) and telithromycin (pink) (PDB accession code 3OI3) bound to the Thermus thermophilus ribosome. Nucleotides investigated in this study are indicated in black. (b) Secondary structure of domain V of the 23S rRNA and sequence conservation in eubacteria. rRNA residues are numbered according to their homologous positions in E. coli 23S rRNA. Phylogenetic sequence variations analyzed in this study are highlighted in colors: base pair 2057 · 2611 is represented in blue and the adenine at position 2058 in red. (c) Detailed view of the hydrogen bond interaction between N-1 of A2058 and the 2′-OH moiety of erythromycin's deosamine sugar (the desosamine sugar is highlighted, and the hydrogen bond interaction is shown as a red dotted line). The hydrogen bond interactions between A2057 and U2611 are indicated by gray dotted lines.
One key interaction appears to be the hydrogen bond between N-1 of A2058 and the 2′-hydroxyl group of the macrolides' desosamine sugar (Fig. 1c) (30, 34). Mutation of A2058 to a guanine (A2058G) greatly impairs the binding of macrolides to ribosomes by both chemical and steric alteration of the binding site (9, 22). Ribosomal susceptibility to macrolides and ketolides is also affected by proper Watson-Crick base pairing between nucleotides at positions 2057 and 2611 (6), which are typically G · C (e.g., in Proteobacteria) and A · U (e.g., in Mycobacteria) (Fig. 1; for a phylogenetic comparison of the 2057 · 2611 interaction in clinically relevant phyla, see Table S2 in the supplemental material). The composition of the base pair between nucleotides 2057 and 2611 has been shown to affect the resistance phenotype of the A2058G mutation toward ketolides (19). However, the effect of an A2057G-U2611C substitution in the context of a wild-type A2058 has remained elusive. Changing the A2057 · U2611 base pair in M. smegmatis to G2057 · C2611, as it is typically found in Proteobacteria, had no effect on susceptibility to any of the macrolides or ketolides tested (Table 2). Similarly, the composition of this base pair had no effect on resistance to erythromycin, clarithromycin, azithromycin, spiramycin, tylosin, and josamycin as conferred by the A2058G mutation. However, we confirmed that the ketolide resistance phenotype of A2058G is indeed dependent on the nature of the 2057 · 2611 base pair, as the A2058G mutant is 16-fold more susceptible to telithromycin in the context of a proteobacterial G2057 · C2611 sequence than in the context of a mycobacterial A2057 · U2611 (Table 2).
Table 2.
MICs of various macrolides/ketolides in M. smegmatis 23S rRNA variants
| Clade homology (mutation) | Strains | Base(s) at 23S rRNA position(s): |
MIC (μg/ml)a |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2058 | 2057 · 2611 | ERY | CLR | AZM | SPM | TYL | JSM | TEL | LZ (control) | ||
| e.g., Mycobacteria | SZ678-SZ680 | A | A · U | 8 | 1 | 4–8 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0.25–0.5 | 1 |
| e.g., Proteobacteria | SZ681-SZ684 | A | G · C | 8–16 | 1 | 2–4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.25–0.5 | 1 |
| Mycobacterial (A2058G) | SZ674-SZ677 | G | A · U | >512 | >512 | >512 | 128 | 8 | 8 | 128 | 1 |
| Proteobacterial (A2058G) | SZ685-SZ687 | G | G · C | >512 | >512 | >512 | 64 | 4 | 8 | 8 | 1 |
ERY, erythromycin; CLR, clarithromycin; AZM, azithromycin; SPM, spiramycin; TYL, tylosin; JSM, josamycin; TEL, telithromycin; LZ, linezolid. The MIC ranges shown are for at least 3 independent clones of the same mutation analyzed in 3 different experiments.
Phylogenetic sequence variations in 16S rRNA helix 44.
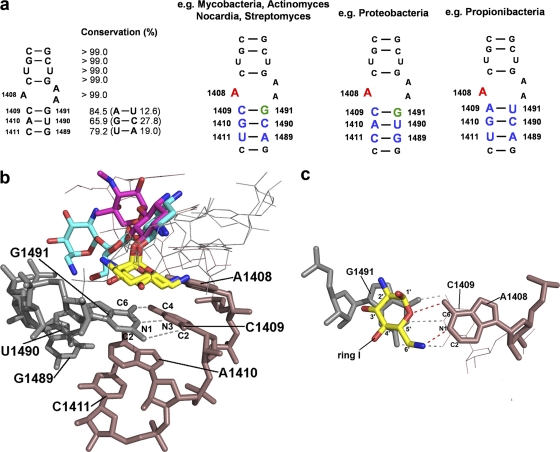
Nucleotides of 16S rRNA helix 44 are part of the aminoacyl-tRNA acceptor site (A site) and are highly conserved (Fig. 2) (7). Aminoglycoside antibiotics bind to the A site by direct contacts to helix 44 (2). While aminoglycosides form a number of hydrogen bonds with different nucleotides in helix 44, their interactions with rRNA residues 1408, 1409, and 1491 (E. coli numbering) appear to be most critical for drug binding (11, 14, 15, 20) (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
(a) Secondary structure of 16S rRNA helix 44 decoding site and sequence conservation in eubacteria. rRNA residues are numbered according to their homologous positions in E. coli 16S rRNA. Phylogenetic sequence variations analyzed in this study are highlighted in colors: 1409, 1410, 1411, 1489, and 1490 in blue; the adenine at position 1408 in red; and the guanine at 1491 in green. (b) Structures of neomycin (blue) (PDB accession code 2QOY) and gentamicin (pink) (PDB accession code 2QB9) bound to the Escherichia coli A site. Ring 1 of the aminoglycosides is highlighted in yellow, nucleotides investigated in this study are numbered in black, and the hydrogen bond interactions between C1409 and G1491 are indicated by gray dotted lines. (c) Detailed view of the hydrogen bond and stacking interactions of neomycin's ring 1 with A1408 (shown as red dotted lines) and G1491, respectively. The gray dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonding between C1409 and G1491.
16S rRNA residue 1408 is an adenine in all wild-type bacteria. Among all A-site mutations that confer aminoglycoside resistance, the 1408 adenine-to-guanine mutation (A1408G) is the predominant alteration in clinical drug-resistant strains (24, 28). This transition mutation alone is sufficient to confer high-level resistance to 6′-NH2 aminoglycosides by disrupting the interaction between A1408 and the compound's ring 1 amino sugar (21). It is also thought to function as the main specificity determinant of aminoglycosides, because the cytoplasmic ribosomes of higher eukaryotes carry a guanine at this position (1, 25).
Bacterial A-site sequence variations within the aminoglycoside binding pocket involve base pair interactions 1409 · 1491, 1410 · 1490, and 1411 · 1489 (Fig. 2). The 1410 · 1490 pair is always a purine/pyrimidine interaction, either G · C (e.g., in Actinomycetales) or A · U (e.g., in Proteobacteria). The 1411 · 1489 interaction involves a pyrimidine/purine interaction, either U · A (e.g., in Actinomycetales) or C · G (e.g., in Proteobacteria). The 1409 · 1491 interaction involves a purine-pyrimidine switch: C · G (a pyrimidine/purine interaction) or A · U (a purine/pyrimidine interaction) (7). The majority of eubacteria are characterized by a 1409 pyrimidine · 1491 purine (C · G) interaction, while Propionibacteria carry a 1409 purine · 1491 pyrimidine (A · U) base pair (Fig. 2; for a phylogenetic comparison with clinically relevant phyla, see Table S2 in the supplemental material).
Bacterial sequence polymorphism of residues 1410 · 1490 and 1411 · 1489 was found not to affect the susceptibility of the wild-type drug binding pocket to aminoglycoside antibiotics, as the corresponding drug binding sites are highly susceptible to these compounds (Table 3, compare, e.g., Mycobacteria with Proteobacteria). Likewise, these sequence polymorphisms do not affect the resistance phenotype associated with the predominant mutational resistance alteration A1408G. Independent of the bacterial sequence polymorphism involving residues 1410 · 1490 and 1411 · 1489, an A1408G mutation results in high-level resistance to aminoglycosides with a 6′-NH2 group, such as gentamicin and neomycin, but only limited resistance to aminoglycosides with a 6′-OH group, such as paromomycin (Table 3).
Table 3.
MICs of various aminoglycosides in M. smegmatis 16S rRNA variants
| Clade homology (mutation) | Strain(s) | Base(s) at 16S rRNA position(s): |
MIC (μg/ml)a |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1408 | 1409 · 1491 | 1410 · 1490 | 1411 · 1489 | 4,5-substituted compounds |
4,6-substituted compounds |
LZ (control) | ||||||
| 6′-OH |
6′-NH2 |
6′-NH2 |
||||||||||
| PAR | NEO | GEN | TOB | KAN | AMK | |||||||
| e.g., Mycobacteria | SZ380 | A | C · G | G · C | U · A | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 |
| e.g., Proteobacteria | SZ721-SZ724 | A | C · G | A · U | C · G | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5–1 | 0.5–1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1–2 |
| e.g., Propionibacteria | SZ763-SZ766 | A | A · U | G · C | U · A | 64 | 8–16 | 16 | 32 | 16 | 2 | 1 |
| Mycobacterial (C1409U · G1491A) | SZ717-SZ720 | A | U · A | G · C | U · A | 8–16 | 1–2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 |
| Mycobacterial (C1409G · G1491C) | SZ605 | A | G · C | G · C | U · A | 32 | 2–4 | 4 | 4 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.5–1 |
| Mycobacterial (A1408G) | SZ459-SZ462 | G | C · G | G · C | U · A | 64 | >1,024 | >1,024 | >1,024 | >1,024 | >1,024 | 1 |
| Proteobacterial (A1408G) | SZ725-SZ728 | G | C · G | A · U | C · G | 64 | >1,024 | >1,024 | 1,024 | >1,024 | >1,024 | 1 |
| Propionibacterial (A1408G) | SZ832-SZ835 | G | A · U | G · C | U · A | >1,024 | >1,024 | >1,024 | >1,024 | >1,024 | >1,024 | 1 |
PAR, paromomycin; NEO, neomycin; GEN, gentamicin; TOB, tobramycin; KAN, kanamycin A; AMK, amikacin; LZ, linezolid. The MIC ranges shown are for at least 3 independent clones of the same mutation analyzed in 3 different experiments.
The sequence polymorphism at residues 1409 · 1491, which involves a purine/pyrimidine switch, was found to significantly affect the aminoglycoside susceptibility of the wild-type drug binding pocket. Replacing the C · G base pair in M. smegmatis with a propionibacterial A · U considerably reduced susceptibility to all 4,5- and 4,6-aminoglycosides tested (Table 3). This observation is in agreement with the lower aminoglycoside susceptibility of Propionibacteria reported previously (16). Amikacin is the least affected among the aminoglycosides tested, presumably because its l-haba group interacts with additional nucleotides within helix 44 and stabilizes drug binding (17).
To study the contribution of a 1409 · 1491 purine/pyrimidine base pair switch to aminoglycoside susceptibility in more detail, we investigated base pair interactions U · A and G · C. Base pair U1409 · A1491 represents a pyrimidine/purine interaction similar to the C · G found in the majority of eubacteria. Introduction of the U · A base pair decreased susceptibility to paromomycin, a 4,5-substituted aminoglycoside with a 6′-OH group, while it had little if any effect on aminoglycosides with a 6′-NH2 group (Table 3). Introduction of a G1409 · C1491 purine/pyrimidine interaction similar to the A · U found in Propionibacteria resulted in minor but significant changes in susceptibility to both 4,5- and 4,6-aminoglycosides (with the exception of amikacin), with the 4,5-compounds being more affected (Table 3). From these data we infer that in the presence of an A1408 there is a gradient of drug susceptibility for the 1409 · 1491 interaction, indicating that both the purine/pyrimidine interaction and the specific nucleotide are relevant. In line with previous investigations and the different orientation of the aminoglycosides' sugars linked to position 5 or 6 of the neamine core (20) (Fig. 2), our results suggest that, in general, the 4,5-substituted compounds and in particular the 6′-OH paromomycin are more dependent on a proper 1409 · 1491 interaction than the 4,6-substituted compounds.
Combining the propionibacterial A1409 · U1491 pair further with an A1408G alteration resulted in high-level resistance to all aminoglycosides, including paromomycin (Table 3). Typically, binding of paromomycin, which carries a hydroxyl group at the 6′ position of ring I, is only moderately affected by the A1408G mutation, since it can accept a hydrogen bond from the N-1 and N-2 of G1408 (21, 35). Apparently, the high-level resistance to paromomycin is the result of a combined effect of perturbing contacts to both G1491 and A1408, which would be in agreement with previous data demonstrating that alteration of residue 1491 primarily increased resistance toward 6′-OH aminoglycosides such as paromomycin (20).
Given that stacking of aminoglycoside ring I on G1491 is important for binding (Fig. 2), we wished to study whether the bacterial 1410 · 1490 and 1411 · 1489 sequence variations affect the drug susceptibility pattern associated with C1409 · G1491 base pair disruptions. Accordingly, we replaced G1491 with A, C, or U in isogenic hybrid strains carrying the mycobacterial and proteobacterial A-site sequence. Drug susceptibility testing of the recombinant mutants revealed that the context of a mycobacterial or proteobacterial A site does not affect the specific drug resistance pattern associated with distinct alterations of residue 1491 (Table 4) (see reference 11 for a structural discussion of resistance patterns conferred by mutational alteration of G1491).
Table 4.
MICs of various aminoglycosides in M. smegmatis 16S rRNA variants with disruption of 1409 · 1491 base pairing
| Clade homology (mutation) | Strains | Base(s) at 16S rRNA position(s): |
MIC (μg/ml)a |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1408 | 1409 · 1491 | 1410 · 1490 | 1411 · 1489 | 4,5-substituted compounds |
4,6-substituted compounds |
LZ (control) | ||||||
| 6′-OH |
6′-NH2 |
6′-NH2 |
||||||||||
| PAR | NEO | GEN | TOB | KAN | AMK | |||||||
| Mycobacterial (G1491A) | SZ463-SZ466 | A | C · A | G · C | U · A | 32–64 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1–2 | 0.5 | 0.5–1 |
| Proteobacterial (G1491A) | SZ706-SZ709 | A | C · A | A · U | C · G | 64 | 2–4 | 2–4 | 2 | 1–2 | 0.5 | 1 |
| Mycobacterial (G1491C) | SZ467-SZ470 | A | C · C | G · C | U · A | 512 | 16 | 16–32 | 16 | 16–32 | 4 | 0.5–1 |
| Proteobacterial (G1491C) | SZ710-SZ713 | A | C · C | A · U | C · G | >1,024 | 8–16 | 32 | 16–32 | 32 | 8 | 1 |
| Mycobacterial (G1491U) | SZ505-SZ507 | A | C · U | G · C | U · A | 512–1,024 | 8–16 | 64 | 64–128 | 64 | 16 | 1 |
| Proteobacterial (G1491U) | SZ714-SZ716 | A | C · U | A · U | C · G | 512 | 8 | 64 | 64 | 32 | 8 | 1 |
PAR, paromomycin; NEO, neomycin; GEN, gentamicin; TOB, tobramycin; KAN, kanamycin A; AMK, amikacin; LZ, linezolid. The MIC ranges shown are for at least 3 independent clones of the same mutation analyzed in 3 different experiments.
Previously, limitations in genetic manipulation did not allow study of the effect of bacterial A-site polymorphism on aminoglycoside susceptibility in isogenic mutants. Rather, investigations were limited to testing different bacterial species representative of the corresponding sequence polymorphism. In these early studies it was concluded that the C1409 · G1491/A1409 · U1491 polymorphism is not associated with resistance (21). Using more recently developed genetic techniques, we have now been able to refine this statement and to define the role of the 1409 · 1491 base-pairing polymorphism in aminoglycoside susceptibility more precisely. In addition, we have recently observed that the 16S rRNA 1410 · 1490 interaction has a subtle influence on aminoglycoside susceptibility in ribosomes with a non-Watson-Crick 1409 · 1491 interaction, e.g., C1409 · C1491 (12). We extend these findings in our current study, which reveals that in the presence of a 1409 · 1491 base pair interaction, bacterial 1410 · 1490 sequence polymorphisms do not measurably affect aminoglycoside susceptibility.
Conclusions.
The ribosome is a target for many different classes of antibiotic compounds (23). We have studied the effects of minor phylogenetic differences in the species-specific compositions of the drug binding site on drug susceptibility and resistance. From our results we conclude that natural sequence variations in the ribosomal peptidyltransferase center of bacteria do not affect macrolide/ketolide susceptibility but do affect the resistance phenotype of the A2058G mutation, in particular resistance to the ketolide telithromycin. In contrast, natural sequence variations in the ribosomal A site of bacteria affect both the aminoglycoside susceptibility of the wild-type drug binding pocket and the resistance phenotype associated with the A1408G alteration.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Tanja Janušić for expert technical assistance.
This work was supported in part by grants from the University of Zürich and the European Community (PAR, FP7-HEALTH-2009-241476) and by a donation from BNP Paribas.
Footnotes
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://aac.asm.org/.
Published ahead of print on 5 July 2011.
REFERENCES
- 1. Böttger E. C., Springer B., Prammananan T., Kidan Y., Sander P. 2001. Structural basis for selectivity and toxicity of ribosomal antibiotics. EMBO Rep. 2:318–323 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Carter A. P., et al. 2000. Functional insights from the structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit and its interactions with antibiotics. Nature 407:340–348 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Davies J., Gorini L., Davis B. D. 1965. Misreading of RNA codewords induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Mol. Pharmacol. 1:93–106 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. De Stasio E. A., Dahlberg A. E. 1990. Effects of mutagenesis of a conserved base-paired site near the decoding region of Escherichia coli 16 S rRNA. J. Mol. Biol. 212:127–133 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. De Stasio E. A., Moazed D., Noller H. F., Dahlberg A. E. 1989. Mutations in 16S rRNA disrupt antibiotic-RNA interactions. EMBO J. 8:1213–1216 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Douthwaite S., Aagaard C. 1993. Erythromycin binding is reduced in ribosomes with conformational alterations in the 23 S rRNA peptidyl transferase loop. J. Mol. Biol. 232:725–731 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Gutell R. R. 1994. Collection of small subunit (16S- and 16S-like) rRNA structures: 1994. Nucleic Acids Res. 22:3502–3507 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Gutell R. R., Gray M. W., Schnare M. N. 1993. A compilation of large subunit (23S and 23S-like) rRNA structures: 1993. Nucleic Acids Res. 21:3055–3074 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Hansen J. L., et al. 2002. The structures of four macrolide antibiotics bound to the large ribosomal subunit. Mol. Cell 10:117–128 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Hansen L. H., Mauvais P., Douthwaite S. 1999. The macrolide-ketolide antibiotic binding site is formed by structures in domains II and V of 23S rRNA. Mol. Microbiol. 31:623–631 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Hobbie S. N., et al. 2006. A genetic model to investigate drug-target interactions at the ribosomal decoding site. Biochimie 88:1033–1043 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Hobbie S. N., et al. 2008. Mitochondrial deafness alleles confer misreading of the genetic code. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 105:3244–3249 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Hobbie S. N., et al. 2007. Engineering the rRNA decoding site of eukaryotic cytosolic ribosomes in bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 35:6086–6093 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Hobbie S. N., et al. 2006. Binding of neomycin-class aminoglycoside antibiotics to mutant ribosomes with alterations in the A-site of 16S rRNA. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50:1489–1496 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Hobbie S. N., Pfister P., Brull C., Westhof E., Böttger E. C. 2005. Analysis of the contribution of individual substituents in 4,6-aminoglycoside-ribosome interaction. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 49:5112–5118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Hoeffler U., Ko H. L., Pulverer G. 1976. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Propinibacterium acnes and related microbial species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 10:387–394 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Kondo J., Francois B., Russell R. J., Murray J. B., Westhof E. 2006. Crystal structure of the bacterial ribosomal decoding site complexed with amikacin containing the gamma-amino-alpha-hydroxybutyryl (haba) group. Biochimie 88:1027–1031 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Mingeot-Leclercq M. P., Glupczynski Y., Tulkens P. M. 1999. Aminoglycosides: activity and resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 43:727–737 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Pfister P., et al. 2005. 23S rRNA base pair 2057-2611 determines ketolide susceptibility and fitness cost of the macrolide resistance mutation 2058A→G. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102:5180–5185 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Pfister P., et al. 2005. Mutagenesis of 16S rRNA C1409-G1491 base-pair differentiates between 6′OH and 6′NH3+ aminoglycosides. J. Mol. Biol. 346:467–475 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Pfister P., Hobbie S., Vicens Q., Böttger E. C., Westhof E. 2003. The molecular basis for A-site mutations conferring aminoglycoside resistance: relationship between ribosomal susceptibility and X-ray crystal structures. Chem. Biochem. 4:1078–1088 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Pfister P., et al. 2004. The structural basis of macrolide-ribosome binding assessed using mutagenesis of 23S rRNA positions 2058 and 2059. J. Mol. Biol. 342:1569–1581 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Poehlsgaard J., Douthwaite S. 2005. The bacterial ribosome as a target for antibiotics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3:870–881 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Prammananan T., et al. 1998. A single 16S rRNA substitution is responsible for resistance to amikacin and other 2-deoxystreptamine aminoglycosides in Mycobacterium abscessus and Mycobacterium chelonae. J. Infect. Dis. 177:1573–1581 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Recht M. I., Douthwaite S., Dahlquist K. D., Puglisi J. D. 1999. Effect of mutations in the A site of 16 S rRNA on aminoglycoside antibiotic-ribosome interaction. J. Mol. Biol. 286:33–43 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Recht M. I., Puglisi J. D. 2001. Aminoglycoside resistance with homogeneous and heterogeneous populations of antibiotic-resistant ribosomes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 45:2414–2419 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Retsema J., Fu W. C. 2001. Macrolides: structures and microbial targets. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 18:S3–S10 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Sander P., Prammananan T., Böttger E. C. 1996. Introducing mutations into a chromosomal rRNA gene using a genetically modified eubacterial host with a single rRNA operon. Mol. Microbiol. 22:841–848 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Sander P., Prammananan T., Meier A., Frischkorn K., Bottger E. C. 1997. The role of ribosomal RNAs in macrolide resistance. Mol. Microbiol. 26:469–480 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Schluenzen F., et al. 2001. Structural basis for the interaction of antibiotics with the peptidyl transferase centre in eubacteria. Nature 413:814–821 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Shcherbakov D., Akbergenov R., Matt T., Sander P., Andersson D. I., Böttger E. C. 2010. Directed mutagenesis of Mycobacterium smegmatis 16S rRNA to reconstruct the in-vivo evolution of aminoglycoside resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Mol. Microbiol. 77:830–840 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Sigmund C. D., Ettayebi M., Morgan E. A. 1984. Antibiotic resistance mutations in 16S and 23S rRNA genes of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 12:4653–4663 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Tenson T., Mankin A. 2006. Antibiotics and the ribosome. Mol. Microbiol. 59:1664–1677 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Tu D., Blaha G., Moore P. B., Steitz T. A. 2005. Structures of MLSBK antibiotics bound to mutated large ribosomal subunits provide a structural explanation for resistance. Cell 121:257–270 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Vicens Q., Westhof E. 2001. Crystal structure of paromomycin docked into the eubacterial ribosomal decoding A site. Structure (Camb.) 9:647–658 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Walter F., Vicens Q., Westhof E. 1999. Aminoglycoside-RNA interactions. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 3:694–704 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Wilson D. N. 2009. The A-Z of bacterial translation inhibitors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 44:393–433 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Yassin A., Fredrick K., Mankin A. S. 2005. Deleterious mutations in small subunit rRNA identify functional sites and potential targets for antibiotics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 102:16620–16625 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Yassin A., Mankin A. S. 2007. Potential new antibiotic sites in the ribosome revealed by deleterious mutations in RNA of the large ribosomal subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 282:24329–24342 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Yonath A. 2005. Antibiotics targeting ribosomes: resistance, selectivity, synergism and cellular regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 74:649–679 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.